计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 548-555.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8634
王富顺1( ), 池宝涛1,2,*(
), 池宝涛1,2,*( ), 贾志超1, 郭前建1, 袁伟1
), 贾志超1, 郭前建1, 袁伟1
收稿日期:2022-09-06
出版日期:2023-09-25
发布日期:2023-11-02
通讯作者:
池宝涛
作者简介:王富顺, 男, 研究生, 研究方向为机械CAE、计算力学, E-mail: 13280673265@163.com
基金资助:
Fushun WANG1( ), Baotao CHI1,2,*(
), Baotao CHI1,2,*( ), Zhichao JIA1, Qianjian GUO1, Wei YUAN1
), Zhichao JIA1, Qianjian GUO1, Wei YUAN1
Received:2022-09-06
Online:2023-09-25
Published:2023-11-02
Contact:
Baotao CHI
摘要:
本文针对边界元法在计算薄型结构力学、裂纹扩展等物理问题时存在的积分难题, 提出一种基于自适应单元细分法的高效高精度近奇异域积分计算方法, 该方法基于二叉树数据结构的单元细分技术对体单元进行自适应细分, 消除单元几何形状所引起的近奇异性, 能直接用于计算连续核函数的近奇异域积分。针对间断核函数的近奇异域积分, 在细分单元的基础上采用腔面重建算法和投影算法, 重新构建源点附近的积分子单元。数值算例表明: 本方法可采用较少的积分点得到准确结果, 是处理近奇异域积分的一种有效方法。
王富顺, 池宝涛, 贾志超, 郭前建, 袁伟. 基于自适应单元细分法的高效高精度近奇异域积分计算[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(5): 548-555.
Fushun WANG, Baotao CHI, Zhichao JIA, Qianjian GUO, Wei YUAN. Efficient and High Precision Nearly Singular Domain Integrals Calculation Based on Adaptive Element Subdivision Method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 548-555.
图1 边界积分方程中核函数的基本类型(a) 间断核函数;(b) 连续核函数
Fig.1 Basic types of the fundamental solutions in the boundary integral equations(a) the discontinuous kernel; (b) the continuous kernel
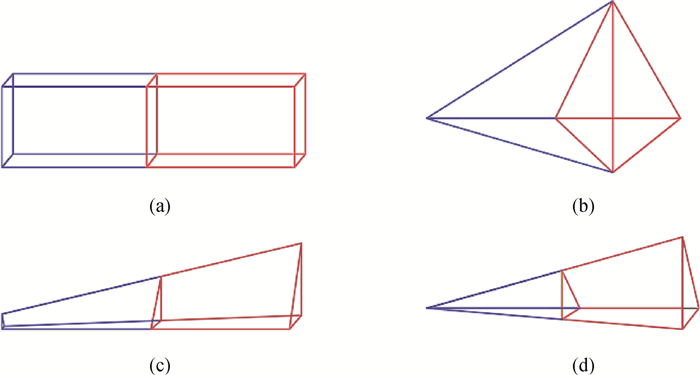
图3 不同类型体单元的细分方式(a) 六面体单元;(b) 四面体单元;(c) 三棱柱单元;(d) 细长型四面体单元
Fig.3 Subdivision of different types of volume element (a) hexahedral element; (b) tetrahedral element; (c) pentahedral element; (d) slender tetrahedral element
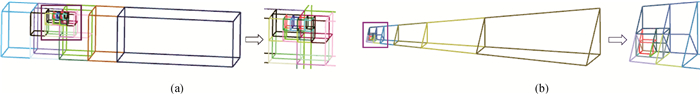
图4 连续核函数的近奇异域细分方案(a) 细长条状六面体单元;(b) 细长条状三棱柱单元
Fig.4 BTSM for nearly singular domain integrals with continuous kernels (a) subdivision of slender hexahedral element; (b) subdivision of slender pentahedral element
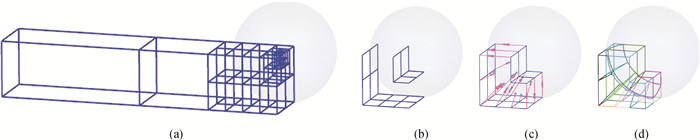
图5 “阶梯型”有效投影腔面的构建(a) 体二叉树平衡后的单元细分;(b) 有效内、外投影腔面的构建;(c) 内、外腔面投影点;(d) 球面附近单元子块
Fig.5 Construction of valid core cavities for projection (a) ultimate subdivision sub-elements; (b) the core projection cavities; (c) matching the core projection cavity to sphere; (d) convert relative sub-elements into well-shaped serendipity patches

图8 两种不同类型球面的参数表示(a) 单极点球面;(b) 单极球的局部坐标系
Fig.8 Parametric representation of two types of spheres (a) polar sphere; (b) local coordinate system of polar sphere
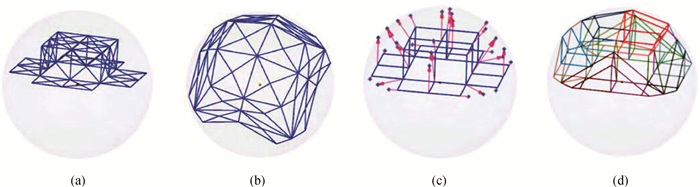
图9 基于Harmonic参数化的腔面投影算法示意图(a) 有效投影腔面划分;(b) 计算参数空间投影点;(c) 判断目标投影点位置;(d) 腔面投影划分
Fig.9 The Harmonic projection algorithm schematic diagram (a) triangulation of the projection cavity faces; (b) calculated projection points in parameter space; (c) map of relative projection points; (d) relative inner-ring projection points and sub-elements
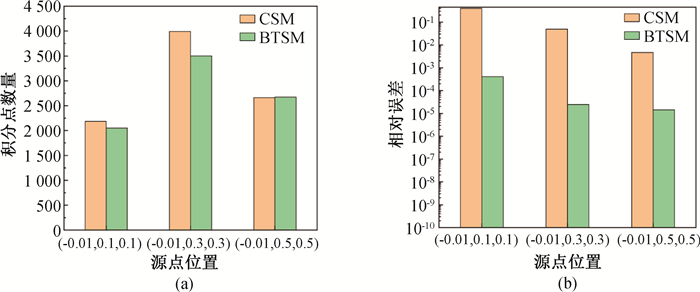
图13 连续核函数的近奇异域积分计算结果(a) BTSM与CSM的积分点数量;(b) BTSM与CSM的计算精度
Fig.13 Comparison of accuracy of BTSM and CSM (a) the integral points number of BTSM and CSM; (b) the accuracy of BTSM and CSM
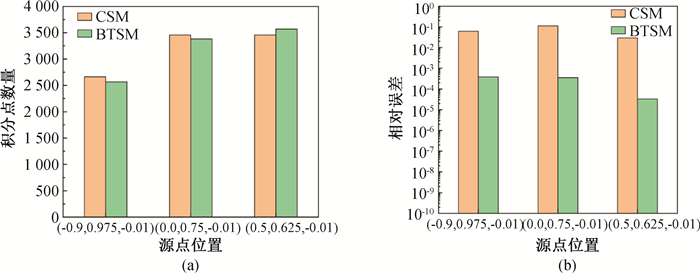
图15 间断核函数的近奇异域积分计算结果(a) BTSM与CSM的积分点数量;(b) BTSM与CSM的计算精度
Fig.15 Comparison of accuracy of BTSM and CSM (a) the integral points number of the BTSM and CSM; (b) the accuracy of the BTSM and CSM
| 1 |
梁钰, 郑保敬, 高效伟, 等. 基于POD模型降阶法的非线性瞬态热传导分析[J]. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2018, 48(12): 36- 45.
|
| 2 |
高效伟, 徐兵兵, 吕军, 等. 自由单元法及其在结构分析中的应用[J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(3): 703- 713.
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
谷岩, 张耀明. 双材料界面裂纹复应力强度因子的正则化边界元法[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(4): 1049- 1058.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
汪超, 谢能刚, 黄璐璐. 基于扩展等几何分析和混沌离子运动算法的带孔结构形状优化设计[J]. 工程力学, 2019, 36(4): 248- 256.
|
| 11 |
李聪, 牛忠荣, 胡宗军, 等. 三维切口/裂纹结构的扩展边界元法分析[J]. 力学学报, 2020, 52(5): 1394- 1408.
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
池宝涛, 张见明, 鞠传明, 等. 基于T-Spline的全自动几何拓扑修复方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1511- 1526.
|
| 17 |
|
| [1] | 曹衍闯, 校金友, 文立华, 王政. 大规模宽频弹性动力学分析的快速定向压缩边界元法[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(3): 305-316. |
| [2] | 周焕林, 严俊, 余波, 陈豪龙. 基于改进布谷鸟算法识别瞬态热传导问题的导热系数[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(2): 212-220. |
| [3] | 王现辉, 郑兴帅, 乔慧, 张小明. 二维Helmholtz边界超奇异积分方程解析研究[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(6): 666-672. |
| [4] | 孙锐, 胡宗军, 牛忠荣. 三维声场边界元法几乎奇异积分问题分析[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(5): 611-618. |
| [5] | 王现辉, 乔慧, 张小明, 谷金良. 基于等几何分析的边界元法求解Helmholtz问题[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(1): 61-66. |
| [6] | 张锐, 文立华, 校金友. 大规模声学边界元法的GPU并行计算[J]. 计算物理, 2015, 32(3): 299-309. |
| [7] | 葛仁余, 牛忠荣, 程长征, 胡宗军, 薛伟伟. 边界元法分析二维线弹性裂纹扩展[J]. 计算物理, 2015, 32(3): 310-320. |
| [8] | 黄铄, 校金友, 胡玉财, 王焘. 声学Burton-Miller方程边界元法GPU并行计算[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(4): 481-487. |
| [9] | 谷岩, 张耀明, 李功胜. 精确几何单元下弹性薄体结构问题的边界元法分析[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(3): 397-403. |
| [10] | 崔晓兵, 季振林. 消声器声学性能预测的子结构快速多极子边界元法[J]. 计算物理, 2010, 27(5): 711-716. |
| [11] | 程长征, 牛忠荣, 周焕林, 杨智勇. 热应力边界元法中几乎超奇异积分的计算[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(1): 113-118. |
| [12] | 王雪仁, 季振林. 有流消声器四极参数和传递损失的边界元法预测[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24(6): 717-724. |
| [13] | 何锃, 吕浚潮, 戴呈豪. 新型快速多极边界元法求解电荷任意分布的二维静电场[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24(4): 433-438. |
| [14] | 李亚莎, 王泽忠, 卢斌先. 三维静电场线性插值边界元中的解析积分方法[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24(1): 59-64. |
| [15] | 殷海荣, 宫玉彬, 魏彦玉, 黄民智, 路志刚, 王文祥. 虚边界元法与强流电子枪的电子轨迹模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2006, 23(6): 647-654. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
