Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 243-252.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8847
• Research Reports • Previous Articles
Zhiwei DAI, Duqu WEI*( )
)
Received:2023-10-23
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-04-08
Contact:
Duqu WEI
Zhiwei DAI, Duqu WEI. Dynamics of Tangent-type Memory Hindmarsh-Rose Neural Networks under Electromagnetic Radiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2025, 42(2): 243-252.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8847
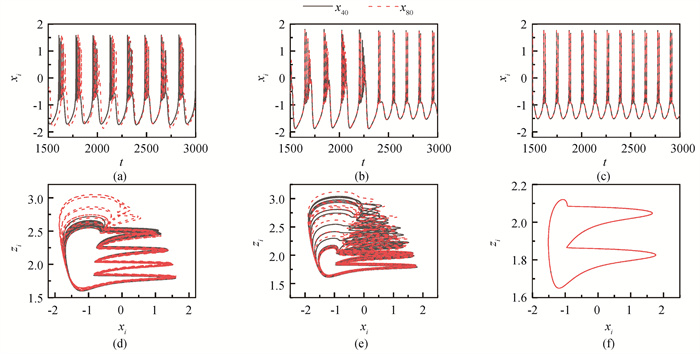
Fig.1 Time series and phase diagrams of two memristor at different k1 with HR neurons (i=40, 80) (k2=0) (a)、(d) k1=0.001;(b)、(e) k1=0.01;(c)、(f) k1=0.02

Fig.4 Time series and phase diagrams of two memristor HR neurons at different k2 (i=40, 80, k1=0)(a) and (d) k2=0.3;(b) and (e) k2=0.4;(c) and (f) k2=0.5
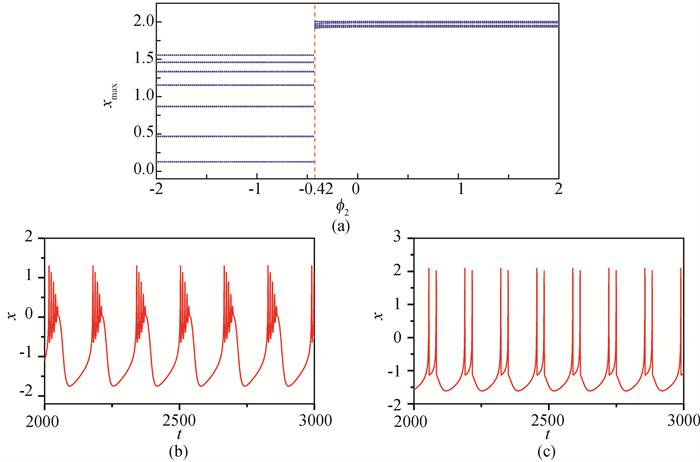
Fig.6 State switching with k1=0, k2=0.3, ϕ1=1 (a) non-negative maximum bifurcation diagram; (b) neuron membrane potential time series at ϕ2=-0.5; (c) neuron membrane potential time series at ϕ2=-0.4
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
唐利红, 贺宗梅, 姚延立. 具有隐藏超级多稳定性的磁感应HR神经元及其电路实现[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 589- 597.
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
刘丽君, 韦笃取. 忆阻Rulkov神经网络同步研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(3): 389- 400.
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
陆丽梅, 韦笃取. 电磁场耦合忆阻Izhikevich神经网络电活动研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 490- 499.
DOI |
| 35 |
周倩, 韦笃取. 场耦合忆阻神经网络的电活动[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(6): 750- 756.
DOI |
| 36 |
DOI |
| 37 |
DOI |
| [1] | Yibo ZHAO, Qing YANG, Chengcheng YU, Minghua LIU. Novel Magnetron Memristor Coupled Hindmarsh-Rose Neuron Model and Its DNA Image Application in Encryption [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2025, 42(2): 232-242. |
| [2] | Wei HUANG, Duqu WEI. Coherent Resonance in Hindmarsh-Rose Neural Network under Electromagnetic Field Coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2025, 42(1): 98-105. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
