计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 210-221.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8609
所属专题: 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊
• 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊 • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2022-08-12
出版日期:2023-03-25
发布日期:2023-07-05
通讯作者:
周维民
作者简介:张智猛,男,博士,副研究员,硕士生导师,主要从事激光等离子体物理相互作用研究,E-mail:zmzhang_zju@sina.com
基金资助:
Zhimeng ZHANG( ), Wei QI, Bo CUI, Bo ZHANG, Wei HONG, Weimin ZHOU*(
), Wei QI, Bo CUI, Bo ZHANG, Wei HONG, Weimin ZHOU*( )
)
Received:2022-08-12
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-07-05
Contact:
Weimin ZHOU
摘要:
针对强流离子束在固体等离子体靶中的输运问题, 详细介绍一种粒子/流体混合模拟方法, 发展了二维数值模拟程序Opic2D-hybrid, 研究强流质子束在聚乙烯和固态铝靶中的集体输运行为。结果表明: 强流质子束在固体靶中输运时产生的自生磁场有利于横向箍缩质子束流。并且靶加热离化产生的大量自由电子, 也有利于减弱固体靶的阻止本领, 从而拉长质子束流射程。但是靶温度升高也会降低电阻率, 抑制自生磁场产生。同时靶离化也会带来更强的离子-离子散射效应, 导致质子束的空间扩散。这些效应彼此间相互竞争, 决定了强流质子束的输运行为。还分析了影响磁场产生的物理因素, 提出多种手段提高自生磁场强度, 从而实现强流质子束在固体靶中的箍缩传输。
张智猛, 齐伟, 崔波, 张博, 洪伟, 周维民. 强流离子束在固体等离子体靶输运的混合粒子模拟方法[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(2): 210-221.
Zhimeng ZHANG, Wei QI, Bo CUI, Bo ZHANG, Wei HONG, Weimin ZHOU. Hybrid Particle-in-cell/Fluid Method for Intense Ion Beam Transport in Solid Plasmas[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(2): 210-221.
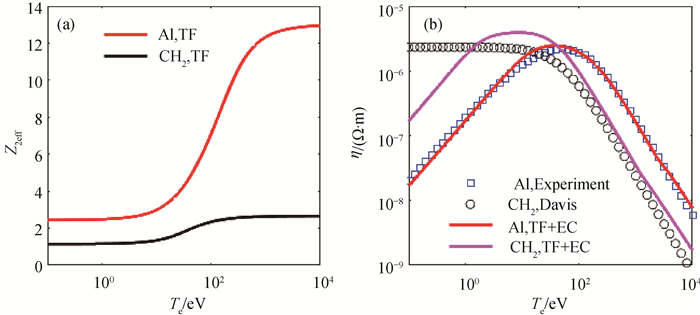
图1 固体铝Al和聚乙烯CH2的(a)平均离化度和(b)电阻率(固体铝Al的材料常数ks =Av =0.2;聚乙烯CH2,ks =2, Av =10。)
Fig.1 (a) Averaged ionization and (b) resistivity of solid aluminum Al and polyethylene CH2 (Here ks =Av =0.2 are adopted for Al while they are ks =2 and Av =10 for CH2.)
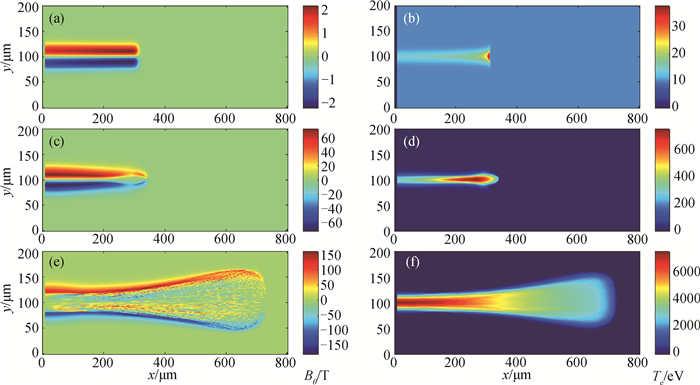
图2 在30 ps时刻,5 MeV准直质子束入射到CH2靶中的角向磁场Bθ和靶温度Te分布,质子束电流密度:(a)~(b) 109 A·cm-2,(c)~(d) 1011 A·cm-2,(e)~(f) 1013 A·cm-2
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of the magnetic field Bθ and the target temperature Te at t=30 ps, which are caused by the 5 MeV collimated proton beam propagates into the solid CH2 target. The proton current densities are (a)~(b) 109 A·cm-2, (c)~(d) 1011 A·cm-2 and (e)~(f) 1013 A·cm-2
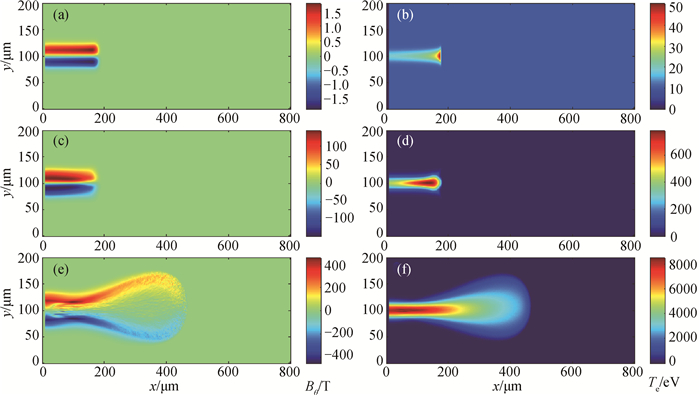
图3 在30 ps时刻,5 MeV准直质子束入射到Al靶中的角向磁场Bθ和靶温度Te分布,质子束电流密度:(a)~(b) 109 A·cm-2,(c)~(d) 1011 A·cm-2,(e)~(f) 1013 A·cm-2
Fig.3 The spatial distribution of the magnetic field Bθ and the target temperature Te at f = 30 ps, which are caused by the 5 MeV collimated proton beam propagates into the solid Al target. The proton current densities are (a)~(b) 109 A·cm-2, (c)~(d) 1011 A·cm-2 and (e)~(f) 1013 A·cm-2
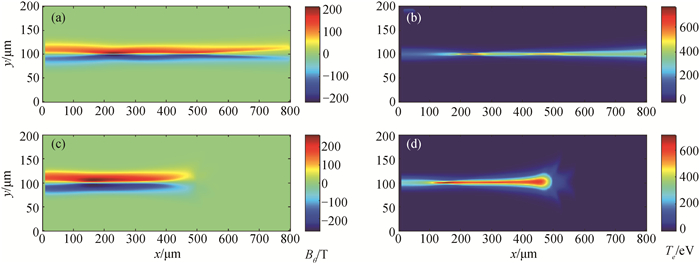
图4 在30 ps时刻,10 MeV准直质子束入射到靶中的角向磁场Bθ和靶温度Te分布。(束腰半径w = 10 μm)(a)~(b) CH2靶;(c)~(d) Al靶
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of the magnetic field Bθ and the target temperature Te at t = 30 ps, which are caused by the 10 MeV collimated proton beam propagates into the solid targets. The proton beam has a waist of 10 μm. The target materials are (a)~(b) CH2 and (c)~(d) Al.
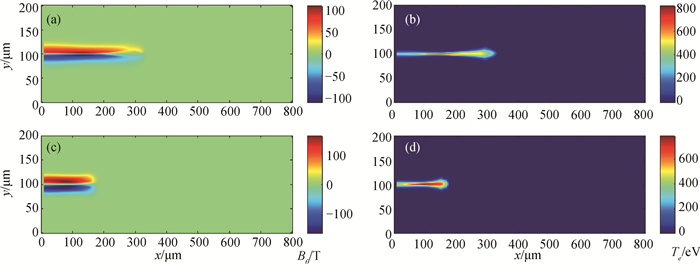
图5 在30 ps时刻,5 MeV准直质子束入射到靶中的角向磁场Bθ和靶温度Te分布(质子束电流密度为1011 A·cm-2,束腰半径w = 5 μm) (a)~(b) CH2靶;(c)~(d) Al靶
Fig.5 The spatial distribution of the magnetic field Bθ and the target temperature Te at t = 30 ps, which are caused by the 5 MeV collimated proton beam propagates into the solid targets. The proton beam has a current density of 1011 A·cm-2 and a waist of 5 μm. The target materials are (a)~(b) CH2 and (c)~(d) Al.
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
DOI |
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
DOI |
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
DOI |
| 41 |
DOI |
| 42 |
DOI |
| 43 |
DOI |
| [1] | 徐涵, 卓红斌, 杨晓虎, 侯永, 银燕, 刘杰. 超热电子在稠密等离子体中输运的混合粒子模拟方法[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(5): 505-525. |
| [2] | 孙民德, 刘波, 石贤峰, 沈皓, 宓詠. STIM的计算机模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2002, 19(2): 183-188. |
| [3] | 谭震宇, 何延才. 低能电子非弹性散射阻止本领[J]. 计算物理, 1995, 12(3): 315-319. |
| [4] | 王友年, 马腾才. 强耦合简并电子气中离子阻止本领和能量离散的数值计算[J]. 计算物理, 1990, 7(2): 235-240. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
