计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 147-158.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8622
所属专题: 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊
• 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊 • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2022-08-15
出版日期:2023-03-25
发布日期:2023-07-05
通讯作者:
周沧涛
作者简介:黄太武, 男, 博士, 教授, 硕士生导师, 研究方向为激光等离子体物理, E-mail: huangtaiwu@sztu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Taiwu HUANG( ), Ke JIANG, Ran LI, Cangtao ZHOU*(
), Ke JIANG, Ran LI, Cangtao ZHOU*( )
)
Received:2022-08-15
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-07-05
Contact:
Cangtao ZHOU
摘要:
本文介绍近期针对非均匀等离子体对强激光传播和电子束输运影响取得的研究进展, 首先研究弱无序分布等离子体对强激光传播的影响, 提出强激光在弱无序等离子体中存在非线性分支流传输机制, 并阐明光电离效应及相对论效应对分支流的重要影响。此外, 研究等离子体密度梯度对相对论电子束输运过程的影响, 发现相对论电子束输运所激发的静电波在空间固定点处的波数或相速度随时间变化, 并且不依赖于等离子体密度的上升或下降, 静电波的局域空间波数最终随时间逐渐增大, 这导致在非均匀等离子体中静电波通过朗道阻尼方式将能量耗散转移给背景电子, 表现为一种由背景等离子体密度梯度引起的束流能量耗散新机制。
黄太武, 蒋轲, 李然, 周沧涛. 非均匀等离子体对强激光传播及电子束输运的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(2): 147-158.
Taiwu HUANG, Ke JIANG, Ran LI, Cangtao ZHOU. Propagation of Intense Laser and Transport of Relativistic Electron Beam in Inhomogeneous Plasmas[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(2): 147-158.
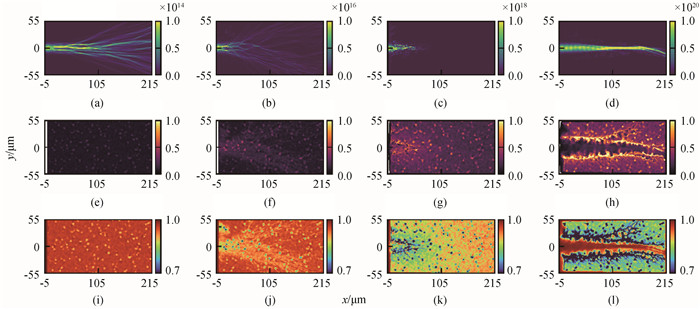
图2 (a)~(d) 激光强度空间分布I/(W·cm-2);(c)~(h) 电子密度空间分布ne/nc;(i)~(l) 等离子体折射率η空间分布(从左至右I = 1014, 1016, 1018, 1020W·cm-2。)
Fig.2 Distributions of (a)~(d) laser intensity I/W·cm-2; (c)~(h) electron density ne/nc and (i)~(l) plasma refractive index η (From left to right, I = 1014, 1016, 1018, 1020 W·cm-2.)
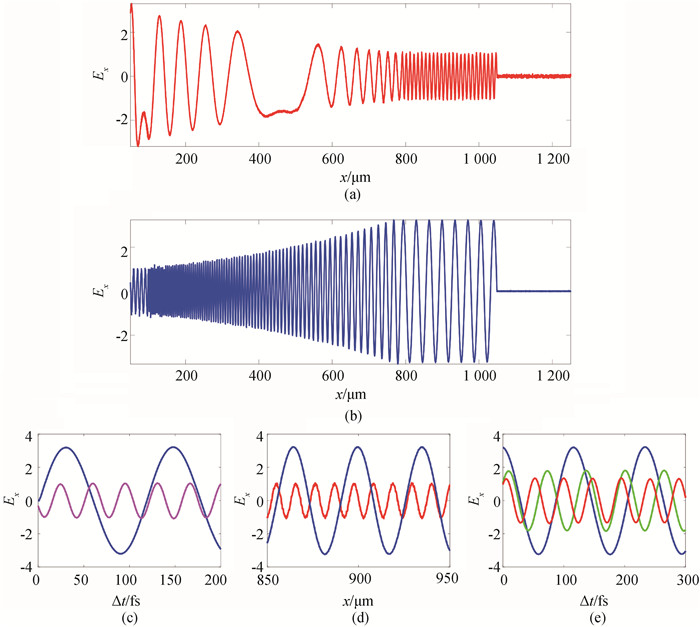
图4 相对论电子束在等离子体(情形A和情形B)中输运时激发的静电波场(非均匀等离子体区域(区域Ⅱ)为100 μm~790 μm。)(a)~(b) t = 3 500 fs时刻(红线为情形B,蓝线为情形A)的静电波场; (c) 情形A中,x = 50 μm (品红线,位于区域Ⅰ)以及x = 900 μm(蓝线,位于区域Ⅲ)处电场随时间的变化; (d) 850 μm~950 μm非均匀区域内,情形B(红线)以及情形A(蓝线)的电场分布,所示时刻为t = 3 500 fs; (e) 情形A中,x = 270 μm(红线)、x = 445 μm(绿线)、以及x = 820 μm(蓝线)处电场随时间的变化
Fig.4 Electrostatic wave field excited by relativistic electron beam transport in background plasma in Cases A and B, where inhomogeneous plasma is distributed in the region of 100 μm~790 μm (a)~(b) electrostatic wave field for Case B (the red line) and Case A (the blue line) at t = 3 500 fs; (c) temporal evolution of the electric field at positions of x = 50 μm (the magenta line) and x = 900 μm (the blue line) in Case A; (d) electric field in the region of 850 μm~950 μm at t = 3 500 fs, where the red line represents the Case B and the blue one represents Case A; (e) temporal evolution of the electric field at positions of x = 270 μm (red line), x = 445 μm (green line), and x = 820 μm (blue line) in Case A
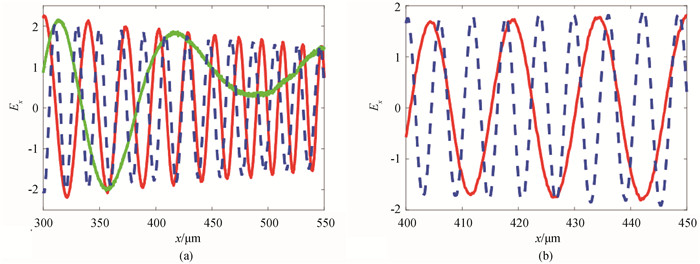
图5 (a) 情形B中300 ~ 550 μm区域内,t = 1 840 fs(红色实线)、t = 3 600 fs(绿色实线)以及t = 5 400 fs (蓝色虚线)时刻的静电波场分布; (b) 情形A中400 ~ 450 μm区域内,t = 1 840 fs(红色实线)以及t = 5 400 fs(蓝色虚线)时刻的静电波场分布
Fig.5 (a) Electrostatic wave field in the region of 300 ~ 550 μm for Case B at different time moments of t = 1 840 fs (red-solid line), t = 3 600 fs (green-solid line), and t = 5 400 fs (blue-dotted line); (b) electrostatic wave field in the region of 400 ~ 450 μm for Case A at different time moments of t = 1 840 fs (red-solid line) and t = 5 400 fs (blue-dotted line)

图6 (a) t ≈ 830 fs,情形C中50~250 μm区域内的静电波场分布; (b)~(d) 130~140 μm区域内,t ≈ 830 fs(红线)、t ≈ 2 800 fs(绿线)以及t ≈ 5 000 fs(蓝线)时刻的静电波场分布(在情形C中,非均匀等离子体分布在100~169 μm的区域。)
Fig.6 (a) Electrostatic wave field in 50~250 μm region for Case C at t ≈ 830 fs; (b)~(d) electrostatic wave field in 130~140 μm region at time moments of t ≈ 830 fs (red line), t ≈ 2 800 fs (green line), and t ≈ 5 000 fs (blue line) (In Case C, the inhomogeneous plasma is distributed in 100~169 μm.)
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
贺贤土. 等离子体中大幅波与低频振荡粒子非线性相互作用效应[J]. 物理学报, 1982, 31 (10): 1317- 1336.
|
| 16 |
贺贤土. 等离子体波-粒子非线性作用的有质动力和自生磁场效应[J]. 物理学报, 1983, 32 (3): 325- 337.
|
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
DOI |
| 35 |
DOI |
| 36 |
DOI |
| 37 |
DOI |
| 38 |
DOI |
| 39 |
DOI |
| 40 |
DOI |
| 41 |
DOI |
| 42 |
DOI |
| 43 |
蔡洪波, 周沧涛, 贾青, 等. 激光驱动强流电子束产生和控制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27 (3): 032001.
DOI |
| 44 |
DOI |
| 45 |
DOI |
| 46 |
DOI |
| 47 |
DOI |
| 48 |
DOI |
| 49 |
DOI |
| 50 |
DOI |
| 51 |
DOI |
| 52 |
|
| 53 |
DOI |
| 54 |
DOI |
| 55 |
PIDWERBETSKY A. Simulation and analysis of wave propagation through random media[D]. New York: Cornell University, 1988.
|
| 56 |
DOI |
| 57 |
DOI |
| 58 |
DOI |
| 59 |
DOI |
| 60 |
DOI |
| 61 |
DOI |
| [1] | 吕文娟, 吴斌兵, 刘士炜, 段皓, 刘杰. 超强激光场中氘氚核聚变截面研究进展[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 127-142. |
| [2] | 常恒心, 许铮, 姚伟鹏, 谢雨, 乔宾. 量子电动力学—粒子模拟极端等离子体动力学研究[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(5): 526-542. |
| [3] | 陈民, 盛政明, 郑君, 马燕云, 张杰. 粒子模拟程序的发展及其在激光等离子体相互作用研究中的应用[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(1): 43-50. |
| [4] | 胡友俊, 杨维纮, 陈银华, 张羽. 磁化非均匀等离子体中模转换机制对电磁波吸收的数值研究[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24(3): 330-336. |
| [5] | 张公让, 匡光力. HT-7托卡马克中低杂波和离子波恩斯坦波协同作用的数值研究[J]. 计算物理, 2006, 23(3): 325-334. |
| [6] | 刘世兴, 王怀民, 祁月盈, 刘学深, 丁培柱. 强激光场中CO分子经典轨迹的辛算法[J]. 计算物理, 2005, 22(4): 325-328. |
| [7] | 祁月盈, 刘晓艳, 丁培柱. 强激光场中一维原子的渐近边界条件[J]. 计算物理, 2003, 20(5): 377-380. |
| [8] | 刘学深, 刘晓艳, 杨玉军, 丁培柱, 朱颀人. 强场一维模型问题的保Wronskian守恒算法[J]. 计算物理, 2001, 18(6): 487-490. |
| [9] | 蔡宗良, 张建泉, 刘峰, 强希文. 脉冲强激光产生的激波在靶材中的传播过程[J]. 计算物理, 1997, 14(S1): 426-428. |
| [10] | 陈荣华, 张建泉, 李邦固, 刘峰, 强希文. 脉冲强激光冲击力学效应的数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 1997, 14(S1): 682-683. |
| [11] | 王敏, 李京. 虚阴极产生微波的一些基本特性[J]. 计算物理, 1996, 13(1): 38-42. |
| [12] | 陈发良. 强激光照射下受预内压作用的球壳的热力响应[J]. 计算物理, 1994, 11(3): 269-277. |
| [13] | 简广德, 潘传红. 在碰撞等离子体中阿尔芬(ALFVEN)波动力理论计算[J]. 计算物理, 1990, 7(4): 481-487. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
