计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 199-209.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8621
所属专题: 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊
• 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊 • 上一篇 下一篇
张文帅1( ), 蔡洪波1,*(
), 蔡洪波1,*( ), 张恩浩2, 杜报1, 邹士阳1, 朱少平1,2,*(
), 张恩浩2, 杜报1, 邹士阳1, 朱少平1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-22
出版日期:2023-03-25
发布日期:2023-07-05
通讯作者:
蔡洪波, 朱少平
作者简介:张文帅,男,博士研究生,助理研究员,研究方向为等离子体冲击波物理,E-mail:zhang_wenshuai@iapcm.ac.cn
基金资助:
Wenshuai ZHANG1( ), Hongbo CAI1,*(
), Hongbo CAI1,*( ), Enhao ZHANG2, Bao DU1, Shiyang ZOU1, Shaoping ZHU1,2,*(
), Enhao ZHANG2, Bao DU1, Shiyang ZOU1, Shaoping ZHU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-22
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-07-05
Contact:
Hongbo CAI, Shaoping ZHU
摘要:
利用全动理学粒子(PIC)模拟研究不同马赫(Mach)数条件下等离子体碰撞冲击波的结构。研究发现: 在低Mach数条件下, 冲击波波阵面位置物理量的分布较为平缓(努森数较小), 等离子体的粘性和热流可由经典输运理论描述, 这种情况下数值求解双流体方程组得到的冲击波结构与PIC模拟一致。随着冲击波Mach数的增加, 冲击波波阵面位置物理量的分布变陡, 努森数增加, 动理学效应对等离子体输运的影响变得显著。高Mach数条件下, 动理学效应主要体现在"先驱离子"对离子粘性和热流的增强以及电子非局域输运对电子热流的影响。通过影响等离子体输运行为, 动理学效应可以显著影响冲击波的结构特征。
张文帅, 蔡洪波, 张恩浩, 杜报, 邹士阳, 朱少平. 马赫数对等离子体碰撞冲击波结构的影响———全动理学模拟研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(2): 199-209.
Wenshuai ZHANG, Hongbo CAI, Enhao ZHANG, Bao DU, Shiyang ZOU, Shaoping ZHU. Influence of Mach Number on Structure of Collisional Plasma Shock Waves: Fully Kinetic Simulations[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(2): 199-209.
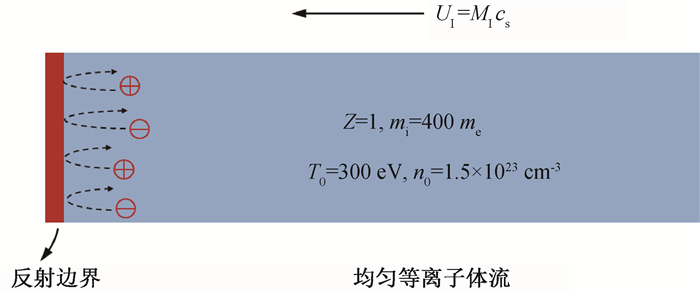
图1 PIC模拟设置示意图(向左运动的均匀等离子体流在左边界被反射,并通过粒子碰撞在边界附近堆积,产生向右运动的冲击波。)
Fig.1 Schematic presentation of the PIC simulation setup (A uniform plasma flow drifting towards the left boundary is reflected and accumulates near the boundary due to particle collisions, resulting in a right-propagating shock wave.)
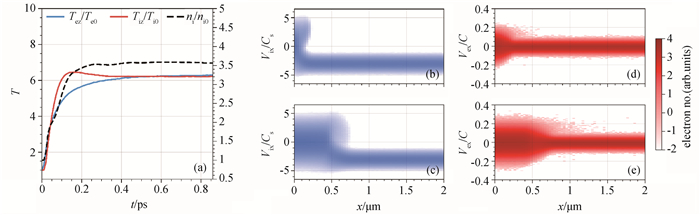
图2 (a) 左边界处等离子体温度和密度的时间演化;(b)和(d) 0.1 ps及(c)和(e)0.6 ps时刻离子和电子的相空间分布
Fig.2 (a) Time evolution of plasma temperature and density near the left boundary; Ion and electron phase space distribution in logarithm scale at (b) and (d) 0.1 ps and (c) and (e) 0.6 ps
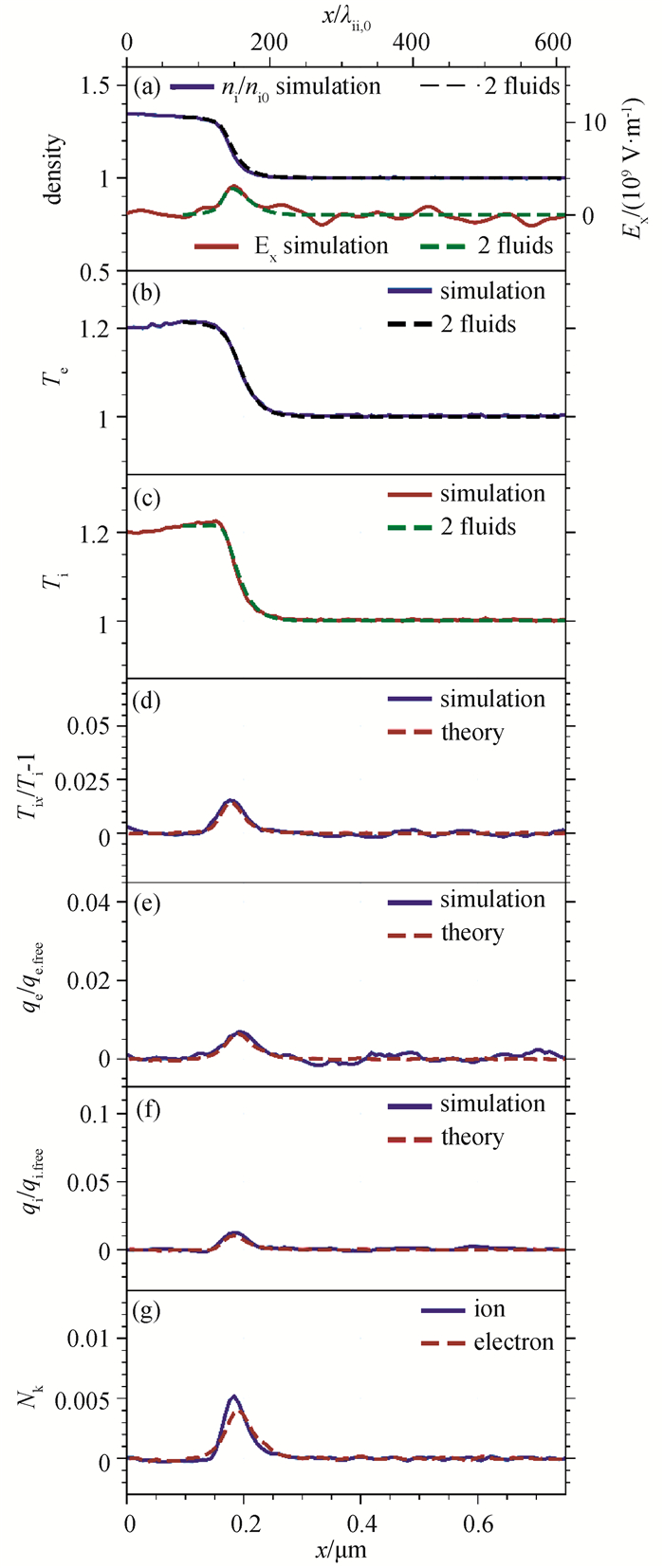
图3 (a)~(c) 模拟(实线)和双流体理论(虚线)得到的离子密度、电场和温度空间分布;(d)~(f)模拟(实线)和输运理论(虚线)给出的粘性与热流分布;(g) 努森数的空间分布(模拟结果为y方向平均结果,Msh = 1.22,t = 0.3 ps时刻。)
Fig.3 (a)~(c) Spatial profiles of ion density, electric field and temperature from PIC simulations (solid lines) and two-fluid theory (dashed lines); (d)~(f) Spatial profiles of viscosity and heat flux from simulations (solid lines) and transport theory (dashed lines); (g) Spatial profiles of the Knudsen number (Simulations results averaged over y for Msh = 1.22 at t = 0.3 ps.)
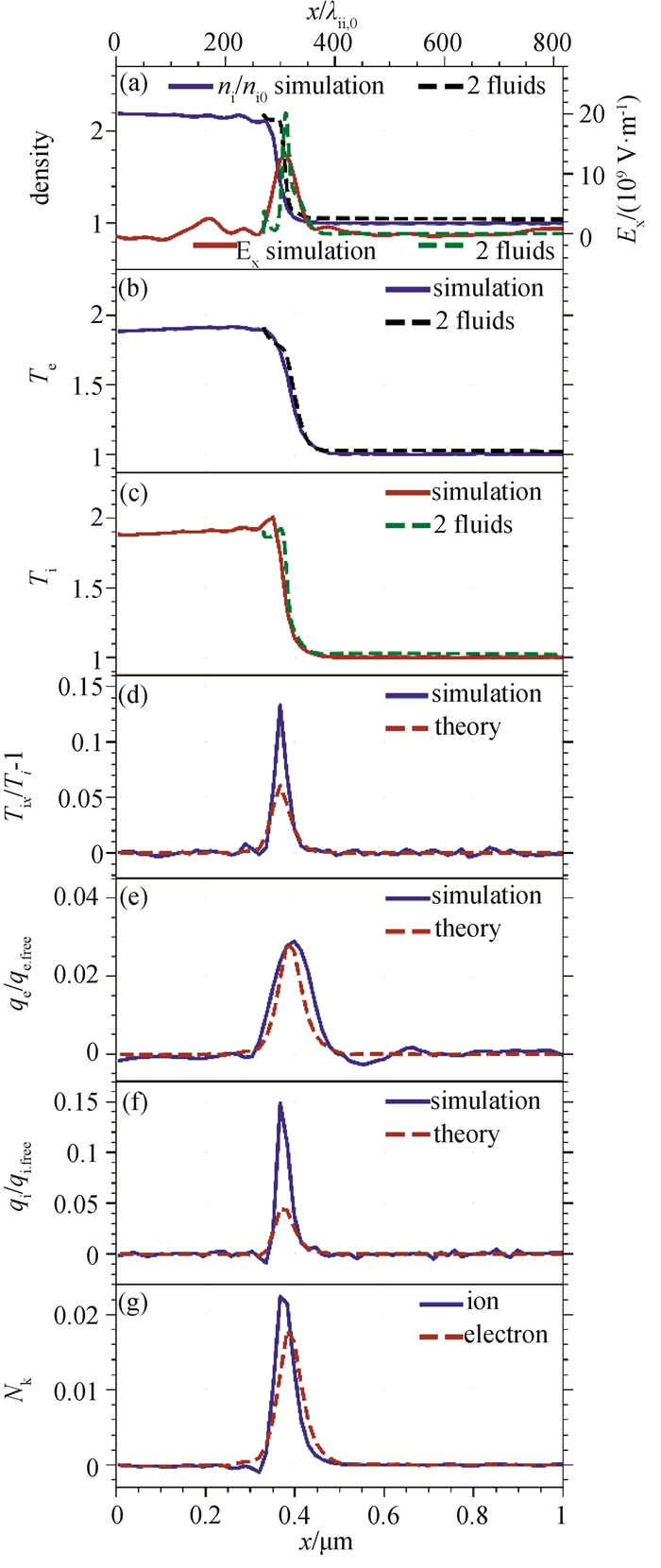
图4 (a)~(c)模拟(实线)和双流体理论(虚线)得到的离子密度、电场和温度空间分布;(d)~(f) 模拟(实线)和输运理论(虚线)给出的粘性与热流分布;(g) 努森数空间分布(模拟结果为y方向平均,Msh = 1.87,t = 0.64 ps时刻。)
Fig.4 (a)~(c) Spatial profiles of ion density, electric field and temperature from simulations (solid lines) and two-fluid theory (dashed lines); (d)~(f) Spatial profiles of viscosity and heat flux from simulations (solid lines) and transport theory (dashed lines). (g) Spatial profiles of the Knudsen number (Simulations results averaged over y for Msh = 1.87 at t = 0.64 ps.)
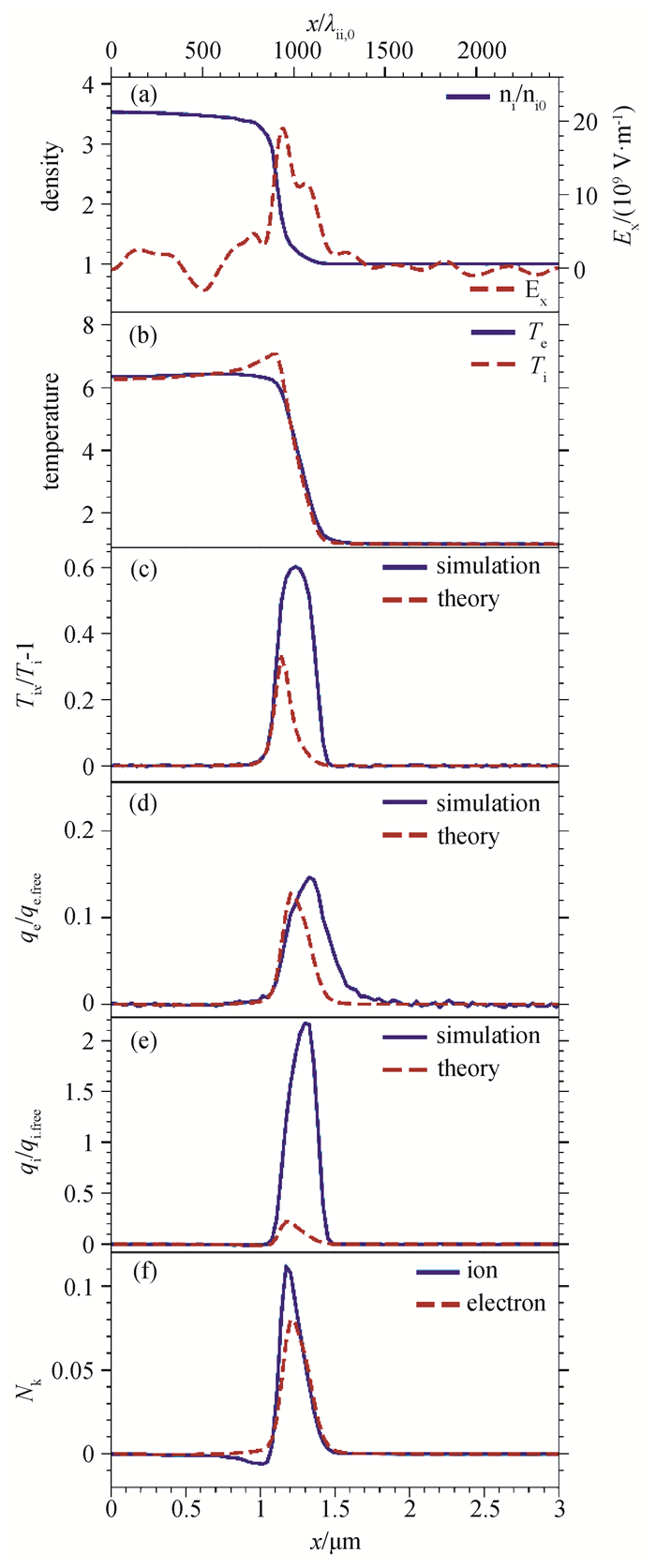
图5 (a)~(b) 模拟得到的离子密度、电场和温度分布;(c)~(e)模拟(实线)和输运理论(虚线)给出的粘性与热流分布;(f) 努森数空间分布(模拟结果为y方向平均,Msh = 4.2,t = 1.4 ps时刻。)
Fig.5 (a)~(b) Spatial profiles of ion density, electric field and temperature from simulations; (c)~(e) Spatial profiles of viscosity and heat flux from simulations (solid lines) and transport theory (dashed lines); (f) Spatial profiles of the Knudsen number (Simulations results averaged over y for Msh = 4.2 at t = 1.4 ps.)
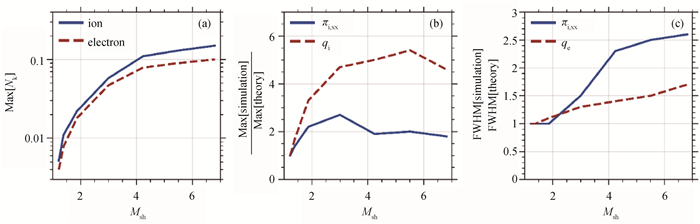
图6 (a) PIC模拟得到的峰值电子和离子努森数随冲击波Mach数的变化;(b) 峰值离子粘性应力和热流的PIC模拟与输运理论值之比;(c) PIC模拟与输运理论得到的离子粘性应力和电子热流分布的半高全宽之比
Fig.6 (a) Shock Mach number dependence of the maximum Knudsen number from PIC simulations; (b) Ratio of the maximum ion viscous stress and ion heat flux from the PIC simulations to that from the transport theory; (c) Ratio of the full-width-half-maximum of the spatial profiles of the simulated and theoretical ion viscous stress and electron heat flux
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
DOI |
| 35 |
DOI |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
