计算物理 ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 564-578.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8473
肖聪1,2( ), 张士诚1,2, 马新仿1,2, 周彤3, 侯腾飞4
), 张士诚1,2, 马新仿1,2, 周彤3, 侯腾飞4
收稿日期:2021-11-17
出版日期:2022-09-25
发布日期:2023-01-07
作者简介:肖聪(1989-),男,博士,主要从事基于深度学习和模型降维技术的数据同化以及反问题研究,E-mail:xclmjtud@yahoo.com
基金资助:
Cong XIAO1,2( ), Shicheng ZHANG1,2, Xinfang MA1,2, Tong ZHOU3, Tengfei HOU4
), Shicheng ZHANG1,2, Xinfang MA1,2, Tong ZHOU3, Tengfei HOU4
Received:2021-11-17
Online:2022-09-25
Published:2023-01-07
摘要:
提出一种基于映射递归神经网络(aNN)的代理模型, 借助于深度学习框架中易于使用的自动微分工具, 有效生成模型降阶伴随算子, 实现高效反演建模。与降阶切线线性模型相似, 基于投影的神经网络(POD-aNN)结构加速降阶子空间的伴随模型的建立。POD-aNN由一个降维单元和一个用于投影的中间非线性过渡单元组成, 二者分别用于将状态系统分解为低维子空间和近似系统状态的时变演化。因此, 伴随模型在缩减的空间中运行, 计算量和内存需求可以忽略不计。结合二维石油模型展开油藏参数反演研究。结果表明: 该方法在显著降低计算量的前提下取得了满意的参数反演结果, 从而证明了该方法的有效性, 并为应用神经网络模型到实际参数反演案例提供理论基础。
肖聪, 张士诚, 马新仿, 周彤, 侯腾飞. 基于模型降维和递归神经网络的油藏参数反演[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 564-578.
Cong XIAO, Shicheng ZHANG, Xinfang MA, Tong ZHOU, Tengfei HOU. Model-reduced Autoregressive Neural Network for Parameter Inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 564-578.
| 参数 | 取值 | 参数 | 取值 | |
| 网格数 | 20 × 20 | 生产时间/d | 1800 | |
| 水、油密度/(kg·m-3) | 1 014; 859 | 训练数据集,Ns | 400,600,800,1000 | |
| 水、油黏度/(mP·s) | 0.4; 2 | 测试数据集,Nt | 200 | |
| 地层水、油饱和度 | Sw = 0.2; So = 0.8 | 初始学习效率 | 0.001 | |
| 初始地层压力/MPa | 30 | 优化算子 | Adam | |
| 生产井压力/MPa | 25 | 每训练周期样本数 | 100 | |
| 注入井排量/(m3·d-1) | 150 | 训练周期数 | 500 |
表1 模型大小、流体特性和注入井/生产井设置以及训练POD-aNN的超参数
Table 1 Model size, fluid properties, injection/production well settings and hyperparameters for training POD-aNN
| 参数 | 取值 | 参数 | 取值 | |
| 网格数 | 20 × 20 | 生产时间/d | 1800 | |
| 水、油密度/(kg·m-3) | 1 014; 859 | 训练数据集,Ns | 400,600,800,1000 | |
| 水、油黏度/(mP·s) | 0.4; 2 | 测试数据集,Nt | 200 | |
| 地层水、油饱和度 | Sw = 0.2; So = 0.8 | 初始学习效率 | 0.001 | |
| 初始地层压力/MPa | 30 | 优化算子 | Adam | |
| 生产井压力/MPa | 25 | 每训练周期样本数 | 100 | |
| 注入井排量/(m3·d-1) | 150 | 训练周期数 | 500 |
| 神经网络层 | 输入维数 | 输出维数 |
| 输入层 | (Nψ+ Nξ, 1) | (140, 2) |
| 残差块1 | (140, 2) | (140, 2) |
| 残差块2 | (140, 2) | (130, 2) |
| 残差块1 | (130, 2) | (130, 2) |
| 残差块2 | (130, 2) | (120, 2) |
| 残差块1 | (120, 2) | (120, 2) |
| 残差块2 | (120, 2) | (120, 1) |
| 全连接层 | (120, 1) | (Nξ, 1) |
表2 二维石油模型的POD-aNN神经网络结构设置
Table 2 POD-aNN neural network structure setting for two-dimensional oil model
| 神经网络层 | 输入维数 | 输出维数 |
| 输入层 | (Nψ+ Nξ, 1) | (140, 2) |
| 残差块1 | (140, 2) | (140, 2) |
| 残差块2 | (140, 2) | (130, 2) |
| 残差块1 | (130, 2) | (130, 2) |
| 残差块2 | (130, 2) | (120, 2) |
| 残差块1 | (120, 2) | (120, 2) |
| 残差块2 | (120, 2) | (120, 1) |
| 全连接层 | (120, 1) | (Nξ, 1) |
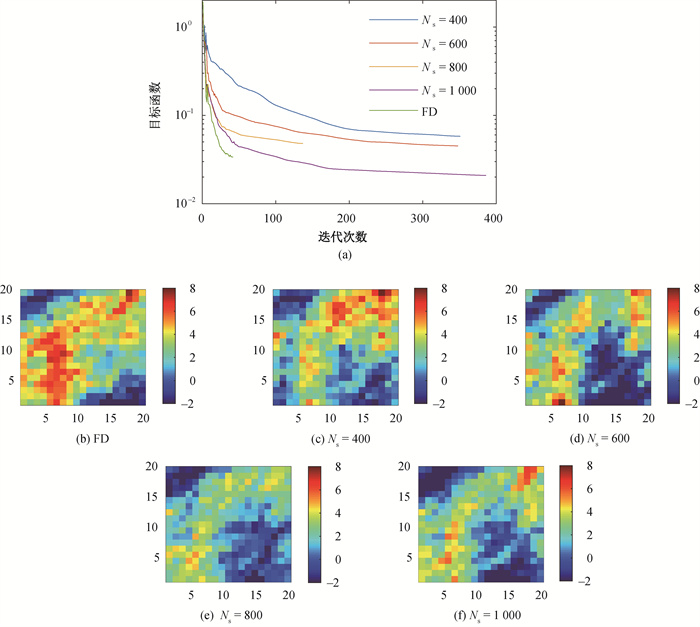
图10 不同训练集的目标函数的演化和地质渗透率场反演结果
Fig.10 Evolution of logarithmic objective function and updated geological permeability fields with respect to different number of training samples
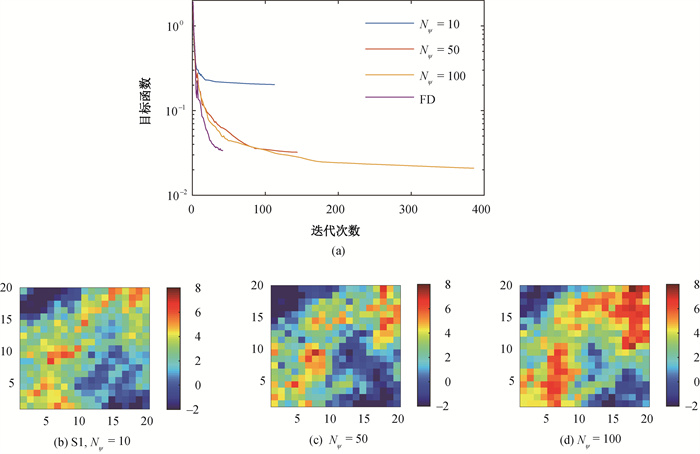
图11 不同POD模式的目标函数的演化和地质渗透率场反演结果
Fig.11 Evolution of logarithmic objective function and updated geological permeability fields with respect to different number of POD modes
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| [1] | 张珑慧, 由长福. 基于有限体积虚拟区域方法的两相流动直接模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(3): 291-297. |
| [2] | 张艳玉, 李威威, 陈会娟. 基于聚类分析的降阶模型在低渗透油藏数值模拟中的应用[J]. 计算物理, 2015, 32(5): 603-609. |
| [3] | 刘福平, 王安玲, 杨长春. 地层渗透参数反演计算[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(6): 879-885. |
| [4] | 陈荣钱, 伍贻兆, 夏健. 应用随机模型方法预测汽车风噪声[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(1): 98-104. |
| [5] | 邓枫, 覃宁, 伍贻兆. EGO方法的训练算法及应用[J]. 计算物理, 2012, 29(3): 326-332. |
| [6] | 陈荣钱, 伍贻兆, 夏健. 基于SNGR方法的后缘噪声数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(5): 698-704. |
| [7] | 索奇峰, 吴晴, 钟易成, 李明水. 振动桥梁CFD数值模拟的网格运动算法[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(4): 547-553. |
| [8] | 吴晴, 钟易成, 余少志, 胡骏. 基于LU-SGS的非结构弹簧网格迭代算法[J]. 计算物理, 2009, 26(6): 806-812. |
| [9] | 成娟, 舒其望. 计算流体力学中的高精度数值方法回顾[J]. 计算物理, 2009, 26(5): 633-655. |
| [10] | 王逸斌, 伍贻兆, 刘学强. 耦合辐射的三维热化学非平衡流数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(4): 421-426. |
| [11] | 招启军, 徐国华, 王适存. 基于CFD/Kirchhoff方法的直升机旋翼高速脉冲噪声模拟分析[J]. 计算物理, 2006, 23(2): 137-143. |
| [12] | 汪建兵, 康宁. 粘性不可压流体流动问题用直角坐标网格的贴体解法[J]. 计算物理, 2004, 21(4): 290-298. |
| [13] | 高智, 向华, 申义庆. 摄动有限体积法重构近似高精度的意义[J]. 计算物理, 2004, 21(2): 131-136. |
| [14] | 孙维志, 韩华. 用进化策略方法反演二维弹性波动方程的参数[J]. 计算物理, 2002, 19(6): 544-548. |
| [15] | 白文, 刘国俊, 周天孝. 飞机构型Euler绕流结构网格方法计算的可信度[J]. 计算物理, 2000, 17(S1): 149-155. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
