Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 101-108.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8328
• Research Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hui GAO1( ), Zaifa YANG1, Jingfen ZHAO1, Huimin YUAN1, Zhie LIU1, Xian ZHAO2
), Zaifa YANG1, Jingfen ZHAO1, Huimin YUAN1, Zhie LIU1, Xian ZHAO2
Received:2021-01-04
Online:2022-01-25
Published:2022-09-03
Hui GAO, Zaifa YANG, Jingfen ZHAO, Huimin YUAN, Zhie LIU, Xian ZHAO. Effect of Nb, Sn, Cu, Fe and Cr on Zr (0001) Surface Nodular Corrosion Resistance: First Principles Study[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(1): 101-108.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8328
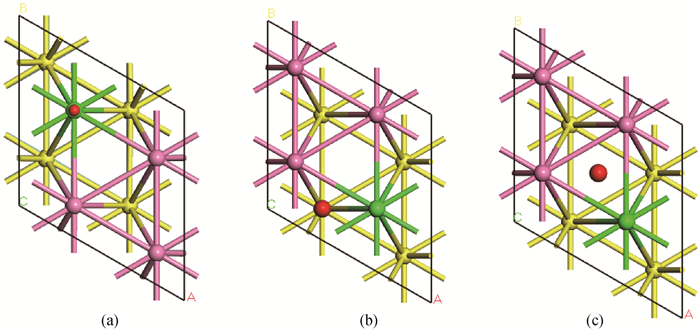
Fig.1 Top view of atmoic structure of Zr (0001) crystal face (a) Oxygen atom is at the top position; (b) Oxygen atom is at the hcp position; (c) Oxygen atom is at the fcc position (The purple and yellow spheres represent Zr atoms in the first layer and the second layer, respectively. The red spheres represent oxygen atoms and the green ones represent alloying elements. The black line represents boundary of supercell and the sticks indicate bonds between atoms.)
| position | pure-Zr | Nb | Sn | Cu | Fe | Cr |
| top | -7.46 | -8.02 | -3.22 | -4.54 | -5.50 | -6.54 |
| hcp | -10.75 | -12.80 | -12.21 | -12.32 | -8.31 | -11.69 |
| fcc | -11.13 | -13.18 | -11.94 | -12.27 | -12.07 | -9.14 |
Table 1 Adsorption energies of oxygen on Zr(0001) crystal face and Zr(0001) crystal face with Nb、Sn、Cu、Fe、Cr(Eb/eV)
| position | pure-Zr | Nb | Sn | Cu | Fe | Cr |
| top | -7.46 | -8.02 | -3.22 | -4.54 | -5.50 | -6.54 |
| hcp | -10.75 | -12.80 | -12.21 | -12.32 | -8.31 | -11.69 |
| fcc | -11.13 | -13.18 | -11.94 | -12.27 | -12.07 | -9.14 |
| Cu | Sn | Nb | Fe | Cr | |
| The first layer | Cu-Zr; Zr-Zr | Sn-Zr; Zr-Zr | Nb-Zr; Zr-Zr | Fe-Zr; Zr-Zr | Cr-Zr; Zr-Zr |
| 0.311;0.327 | 0.334;0.326 | 0.320;0.322 | 0.392;0.306 | 0.321;0.313 | |
| The second layer | Zr-Zr | ||||
| 0.323;0.324 | 0.325;0.326 | 0.324;0.321 | 0.325;0.322 | 0.331;0.322 | |
| The third layer | Zr-Zr | ||||
| 0.323;0.325 | 0.326;0.325 | 0.324;0.324 | 0.318;0.320 | 0.325;0.328 | |
Table 2 Bond lengths of oxidation Zr(0001) crystal face containing alloying elements (in the top three layers) (in nm)
| Cu | Sn | Nb | Fe | Cr | |
| The first layer | Cu-Zr; Zr-Zr | Sn-Zr; Zr-Zr | Nb-Zr; Zr-Zr | Fe-Zr; Zr-Zr | Cr-Zr; Zr-Zr |
| 0.311;0.327 | 0.334;0.326 | 0.320;0.322 | 0.392;0.306 | 0.321;0.313 | |
| The second layer | Zr-Zr | ||||
| 0.323;0.324 | 0.325;0.326 | 0.324;0.321 | 0.325;0.322 | 0.331;0.322 | |
| The third layer | Zr-Zr | ||||
| 0.323;0.325 | 0.326;0.325 | 0.324;0.324 | 0.318;0.320 | 0.325;0.328 | |
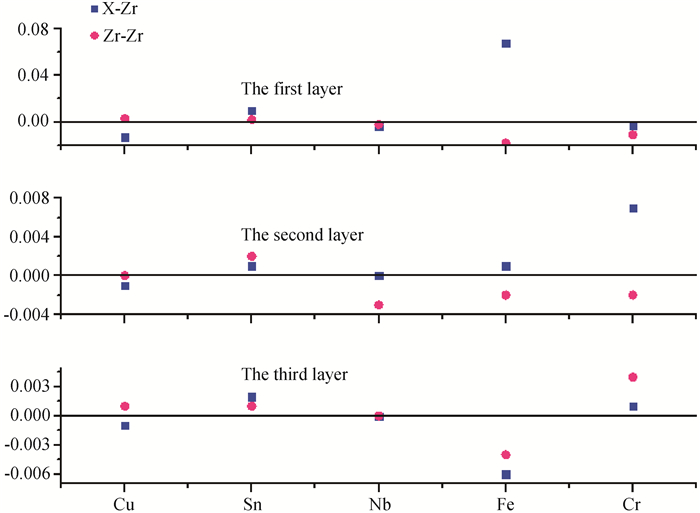
Fig.2 Difference of bond length between the two nearest chemical bonds (X-Zr (X=Nb, Sn, Cu, Fe, Cr), Zr-Zr) and the two zirconium in a perfect crystal after the oxidation of Zr(0001)crystal surface (unit in nm)
| Cu | Sn | Nb | Fe | Cr |
| 1.69 | -0.87 | 0.16 | -0.78 | -0.32 |
Table 3 Partial poly energy of Nb, Sn, Cu, Fe and Cr on the surface of Zr(0001)(Es/eV)
| Cu | Sn | Nb | Fe | Cr |
| 1.69 | -0.87 | 0.16 | -0.78 | -0.32 |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
NIKULINA A V, MARKELOV V A. Zirconium alloy E635 as a material for fuel rod cladding and other components of VVER and RBMK cores[C]. Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Zirconium in the Nuclear Industry, Germany: ASTM International, 1995.
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
GEORGE P, SABOL G P, GERALD R, et al. Development of a cladding alloy for high burnup[C]. Zirconium in the Nuclear Industry: 8th International Symposium, San Diego: ASTM International, 1989.
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| [1] | Hongfei ZHAN, Zhenning CAI, Guanghui HU. Wigner Ground State Calculation Based on Imaginary Time Propagation Method and Spectral Method [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(6): 651-665. |
| [2] | Wumaierjiang NAIPISAI, Haokui YAN, Abulimiti BUMALIYA, Danqi WANG, Mei XIANG, Huan AN. Spectrum and Dissociation Characteristics of CHBr3 Molecule Under External Electric Fields [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 624-630. |
| [3] | Hang JI, Zhongmou SUN, Zhuoyan ZHOU, Yuzhu LIU. Modulation and Degradation of CO Molecular and Ionic Properties with External Electric Field [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(3): 327-334. |
| [4] | CHAI Rukuan, LIU Yuetian, YANG Li, ZHANG Yixin, XIN Jing, MA Jing. Adsorption Mechanism of Two Organic Molecules with Different Polarities on Calcite (104) Surface: Density Functional Theory Study [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(2): 221-230. |
| [5] | CHEN Yu, XING Yongming. Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure on Magneto-optical Properties of Al14Mn2P16: A Density Functional Theory Study [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(2): 231-239. |
| [6] | YIN Haifeng, ZENG Chunhua, CHEN Wenjing. Plasmon Excitations in Two-dimensional Binary Silicon Carbide Nanostructures [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(5): 603-609. |
| [7] | HE Zhiwei, ZHANG Xiurong. Structure and Properties of (BN)25 Clusters [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(2): 219-224. |
| [8] | ZHOU Kang, FENG Qing, TIAN Yun, LI Ke, ZHOU Qingbin. Oxidizing Gas NO2 Optical Gas Sensing Characteristics of Transition Metal Cu and Cr Doped TiO2 Surfaces [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(6): 702-710. |
| [9] | XIE Jianming, CHEN Hongxia, ZHUANG Guoce. A study on Physical Properties of Mn-Doped (ZnSe)12 Clusters [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(4): 481-486. |
| [10] | LI Dawei, GAO Yunliang, ZHU Yuanjiang, LI Jinping. Density Functional Theory Calculations of Ga Doped δ-Pu [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(4): 487-493. |
| [11] | LIN Yan, LIU Yun, PENG Qingwei, WEI Xiaonan, TANG Yanlin. Calculation of Structural Parameters and Frontier Orbital of Cucurbituril (5-10) with Density Functional Theory [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(2): 221-229. |
| [12] | CHEN Hongxia, DU Sijie, ZHUANG Guoce. Structure and magnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO clusters [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(1): 112-118. |
| [13] | LI Anjun, ZHU Yuanqiang, SU Hong, YANG Zehong. Mechanism of Acetylenic-Keton Intramolecular Cyclization Reaction Catalyzed by AuCl3 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(6): 679-684. |
| [14] | MA Hongji, ZHANG Guoying, FANG Geliang. First-Principles Study on Dehydrogenation Ability of MgH2 Hydrogen Storage Materials with Component Element Substitution [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(6): 705-712. |
| [15] | LIU Tao, YANG Ziyi, ZHOU Hongwu, NING Jianghua, GAO Tao. Structural and Electronic Properties of Nonconventional Superconductor PuCoGa5:Density Functional Study [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(5): 626-630. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
