Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 67-80.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8533
• Research Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Peng DONG( ), Xinwei LIAO*(
), Xinwei LIAO*( )
)
Received:2022-03-17
Online:2023-01-25
Published:2023-07-04
Contact:
Xinwei LIAO
Peng DONG, Xinwei LIAO. An Efficient Approach for Automatic Well-testing Interpretation Based on Surrogate Model and Deep Reinforcement Learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(1): 67-80.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8533
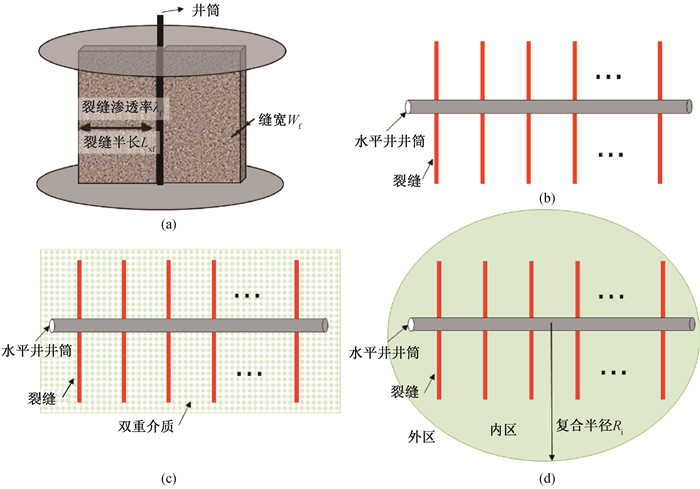
Fig.1 Physical model schematics of a fractured well (a) vertical fractured well model; (b) multiple-fractured horizontal well model; (c) dual-porosity horizontal well model; (d) radial composite horizontal well model
| 参数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 分布 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 |
| CD | 20 | 2 000 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| S | 0.01 | 1 | 均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Lxf/m | 30 | 300 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| CfD | 400 | 25 000 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| nf | 5 | 25 | 均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | |
| Lw/m | 200 | 2 000 | 均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | |
| ω | 0.01 | 0.2 | 均匀分布 | √ | |||
| λ | 10-8 | 10-4 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | |||
| Ri/m | 200 | 4 000 | 均匀分布 | √ | |||
| M | 2 | 10 | 均匀分布 | √ |
Table 1 Parameter range and distribution of well-testing models
| 参数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 分布 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 |
| CD | 20 | 2 000 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| S | 0.01 | 1 | 均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Lxf/m | 30 | 300 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| CfD | 400 | 25 000 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| nf | 5 | 25 | 均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | |
| Lw/m | 200 | 2 000 | 均匀分布 | √ | √ | √ | |
| ω | 0.01 | 0.2 | 均匀分布 | √ | |||
| λ | 10-8 | 10-4 | 对数均匀分布 | √ | |||
| Ri/m | 200 | 4 000 | 均匀分布 | √ | |||
| M | 2 | 10 | 均匀分布 | √ |
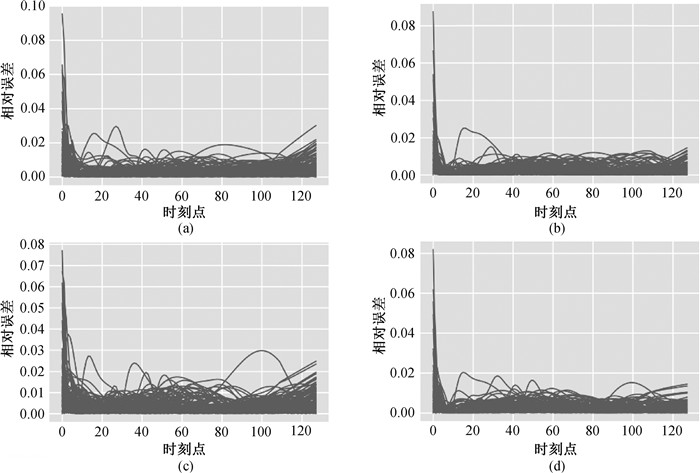
Fig.3 Relative errors of predicted pressure and derivative in different models in the test set at each time point (a) vertical fractured well model; (b) multiple-fractured horizontal well model; (c) dual-porosity horizontal well model; (d) radial composite horizontal well model
| 试井模型 | 物理模型计算时间/s | 代理模型 | |
| 训练时间/min | 预测时间/s | ||
| 垂直裂缝 | 4.23 | 7.1 | 0.018 |
| 水平井 | 7.71 | 7.5 | 0.023 |
| 双重介质水平井 | 13.63 | 8.2 | 0.021 |
| 径向复合水平井 | 12.87 | 7.7 | 0.027 |
Table 2 Computational efficiency of physical model and proxy model
| 试井模型 | 物理模型计算时间/s | 代理模型 | |
| 训练时间/min | 预测时间/s | ||
| 垂直裂缝 | 4.23 | 7.1 | 0.018 |
| 水平井 | 7.71 | 7.5 | 0.023 |
| 双重介质水平井 | 13.63 | 8.2 | 0.021 |
| 径向复合水平井 | 12.87 | 7.7 | 0.027 |
| 试井模型 | 变量 | 训练时间/min | |
| 代理模型训练 | 智能体训练 | ||
| 垂直裂缝 | CD, S, Lxf, CfD | 6.3 | 67 |
| 水平井 | CD, S, Lxf, CfD | 7.5 | 70 |
| 双重介质水平井 | Lxf, Cfd, ω, λ | 7.1 | 68 |
| 径向复合水平井 | Lxf, Cfd, Ri, M | 7.6 | 72 |
Table 3 Inverted variables and agent training time
| 试井模型 | 变量 | 训练时间/min | |
| 代理模型训练 | 智能体训练 | ||
| 垂直裂缝 | CD, S, Lxf, CfD | 6.3 | 67 |
| 水平井 | CD, S, Lxf, CfD | 7.5 | 70 |
| 双重介质水平井 | Lxf, Cfd, ω, λ | 7.1 | 68 |
| 径向复合水平井 | Lxf, Cfd, Ri, M | 7.6 | 72 |
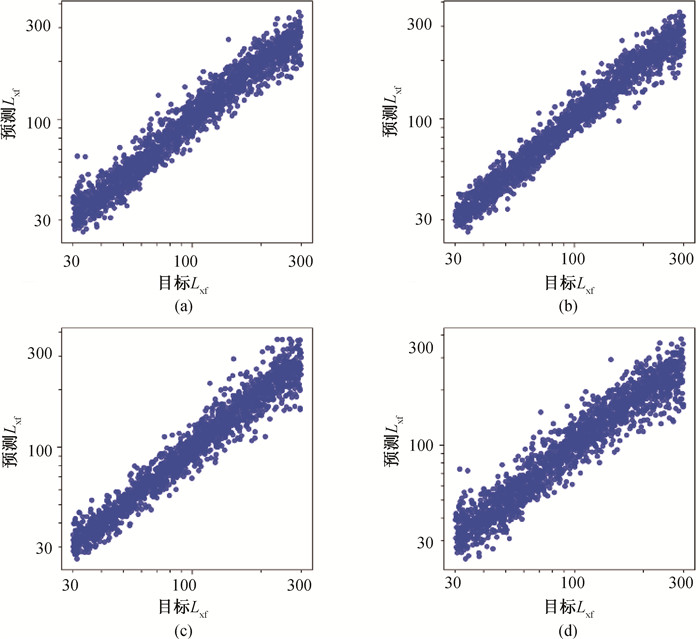
Fig.12 Scatter plots of 1000 times curve matching of agent for fracture half length (a) vertical fractured well model; (b) multiple-fractured horizontal well model; (c) dual-porosity horizontal well model; (d) radial composite horizontal well model
| 模型 | 参数 | 平均相对误差/% | R2 |
| 垂直裂缝 | log (CD) | 4.658 4 | 0.830 2 |
| S | 11.718 4 | 0.893 9 | |
| log (Lxf) | 2.551 5 | 0.898 4 | |
| log (CfD) | 2.701 8 | 0.825 7 | |
| 水平井 | log (CD) | 5.112 0 | 0.849 3 |
| S | 15.223 9 | 0.834 3 | |
| log (Lxf) | 3.709 9 | 0.892 8 | |
| log (CfD) | 4.600 5 | 0.885 2 | |
| 双重介质水平井 | log (Lxf) | 2.069 5 | 0.894 8 |
| log (CfD) | 3.608 4 | 0.852 1 | |
| ω | 6.925 1 | 0.869 5 | |
| λ | 5.680 4 | 0.898 4 | |
| 径向复合水平井 | log (Lxf) | 3.713 4 | 0.891 9 |
| log (CfD) | 5.376 5 | 0.843 7 | |
| Ri | 2.976 5 | 0.896 8 | |
| M | 7.454 3 | 0.829 6 |
Table 4 Error statistics of parameter inversion results
| 模型 | 参数 | 平均相对误差/% | R2 |
| 垂直裂缝 | log (CD) | 4.658 4 | 0.830 2 |
| S | 11.718 4 | 0.893 9 | |
| log (Lxf) | 2.551 5 | 0.898 4 | |
| log (CfD) | 2.701 8 | 0.825 7 | |
| 水平井 | log (CD) | 5.112 0 | 0.849 3 |
| S | 15.223 9 | 0.834 3 | |
| log (Lxf) | 3.709 9 | 0.892 8 | |
| log (CfD) | 4.600 5 | 0.885 2 | |
| 双重介质水平井 | log (Lxf) | 2.069 5 | 0.894 8 |
| log (CfD) | 3.608 4 | 0.852 1 | |
| ω | 6.925 1 | 0.869 5 | |
| λ | 5.680 4 | 0.898 4 | |
| 径向复合水平井 | log (Lxf) | 3.713 4 | 0.891 9 |
| log (CfD) | 5.376 5 | 0.843 7 | |
| Ri | 2.976 5 | 0.896 8 | |
| M | 7.454 3 | 0.829 6 |
| log CD | S | log Lxf | log CfD | |
| 初始参数 | 1.501 | 0.066 | 1.506 | 2.782 |
| 步骤1 | 2.003 | 0.240 | 1.712 | 2.812 |
| 步骤2 | 2.219 | 0.191 | 1.868 | 3.502 |
| 步骤3 | 2.563 | 0.161 | 1.958 | 3.722 |
| 步骤4 (预测结果) | 2.815 | 0.076 8 | 2.006 | 3.908 |
| 目标参数 | 2.735 | 0.0691 | 2.053 | 3.857 |
| 相对误差/% | 2.83 | 11.12 | 2.33 | 1.31 |
Table 5 Parameters inversion process and result in Case 1
| log CD | S | log Lxf | log CfD | |
| 初始参数 | 1.501 | 0.066 | 1.506 | 2.782 |
| 步骤1 | 2.003 | 0.240 | 1.712 | 2.812 |
| 步骤2 | 2.219 | 0.191 | 1.868 | 3.502 |
| 步骤3 | 2.563 | 0.161 | 1.958 | 3.722 |
| 步骤4 (预测结果) | 2.815 | 0.076 8 | 2.006 | 3.908 |
| 目标参数 | 2.735 | 0.0691 | 2.053 | 3.857 |
| 相对误差/% | 2.83 | 11.12 | 2.33 | 1.31 |
| log Lxf | log CfD | ω | log λ | |
| 初始参数 | 1.477 | 2.602 | 0.011 | -8.854 |
| 步骤1 | 1.602 | 2.616 | 0.037 | -7.374 |
| 步骤2 | 1.903 | 2.811 | 0.074 | -7.092 |
| 步骤3 | 1.987 | 3.389 | 0.065 | -6.431 |
| 步骤4 (预测结果) | 2.013 | 3.610 | 0.054 | -6.773 |
| 目标参数 | 1.954 | 3.699 | 0.050 | -7.000 |
| 相对误差/% | 3.00 | 2.40 | 8.32 | 3.24 |
Table 6 Parameters inversion process and result in Case 2
| log Lxf | log CfD | ω | log λ | |
| 初始参数 | 1.477 | 2.602 | 0.011 | -8.854 |
| 步骤1 | 1.602 | 2.616 | 0.037 | -7.374 |
| 步骤2 | 1.903 | 2.811 | 0.074 | -7.092 |
| 步骤3 | 1.987 | 3.389 | 0.065 | -6.431 |
| 步骤4 (预测结果) | 2.013 | 3.610 | 0.054 | -6.773 |
| 目标参数 | 1.954 | 3.699 | 0.050 | -7.000 |
| 相对误差/% | 3.00 | 2.40 | 8.32 | 3.24 |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
严涛. 试井多解性问题研究[J]. 海洋石油, 2008, (3): 46- 50.
|
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
文必龙, 李艳春. 基于大数据的试井解释参数分析[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2019, 36 (9): 64- 69.
|
| 6 |
张晓东. 试井曲线计算机自动拟合算法及应用[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, (4): 135- 137.
|
| 7 |
王一, 陈殿远, 韩鑫, 等. 基于信赖域算法的试井曲线自动拟合研究[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版), 2019, 21 (4): 47- 50.
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
吴明录, 姚军, 王子胜, 等. 利用双种群遗传算法进行数值试井自动拟合[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2007, (2): 81- 83.
DOI |
| 10 |
王培玺, 张静. 基于分群式粒子群算法的压裂水平井试井曲线自动拟合[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36 (2): 136- 140.
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
GOMEZ S, CAMACHO R, VASQUEZ M, et al. Well test characterization of naturally fractured vuggy reservoirs, with a global optimization method[C]. Offshore Technology Conference, 2014.
|
| 13 |
胡修凤. 基于BP神经网络的沁中南煤层气井解吸压力预测及应用[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2017.
|
| 14 |
ALMARAGHI A M, EL-BANBI A H. Automatic reservoir model identification using artificial neural networks in pressure transient analysis[C]. Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2015.
|
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
糜利栋, 顾少华, 薛亮, 等. 基于数据驱动技术的智能试井解释方法——以有水气藏产水气井为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41 (2): 119- 124.
|
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
李道伦, 刘旭亮, 查文舒, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的径向复合油藏自动试井解释方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47 (3): 583- 591.
|
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
周子琪. 基于深度学习的试井和测井资料解释方法研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2021.
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| [1] | ZHANG De-zhi, YAO Jun. Sensitivity of Testing Parameters of a Two Phase Well with Polymer Flooding [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2006, 23(4): 425-430. |
| [2] | Wu Shengchang, Yuan Yirang, Bai Donghua. SOME METHEMATICAL PROBLEMS IN COMPUTATIONAL PETROLEUM GEOLOGY [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1997, 14(S1): 407-409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
