Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 461-472.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8636
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wanpo ZHU( ), Shuanghui HU, Xuefeng OUYANG, Sijie OUYANG, Yuandan LAN
), Shuanghui HU, Xuefeng OUYANG, Sijie OUYANG, Yuandan LAN
Received:2022-09-07
Online:2023-07-25
Published:2023-10-13
Wanpo ZHU, Shuanghui HU, Xuefeng OUYANG, Sijie OUYANG, Yuandan LAN. Discrete Alfvén Eigenmodes in High Performance Scenarios with ITBs on EAST[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 461-472.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8636
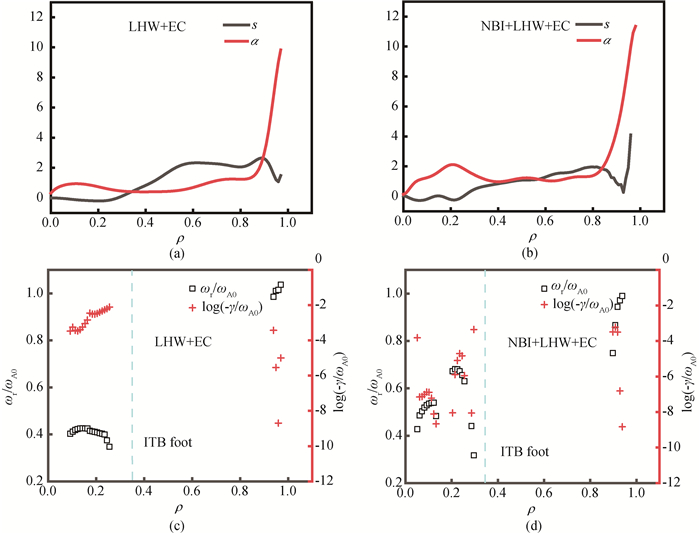
Fig.5 Operating parameters (s, α) for (a) EAST#80307 discharge and (b) EAST#80399 discharge, respectively; distributions of the real and imaginary frequency of αTAE (1, 0) mode versus ρ in (c) EAST#80307 and (d) EAST#80399 discharge, respectively
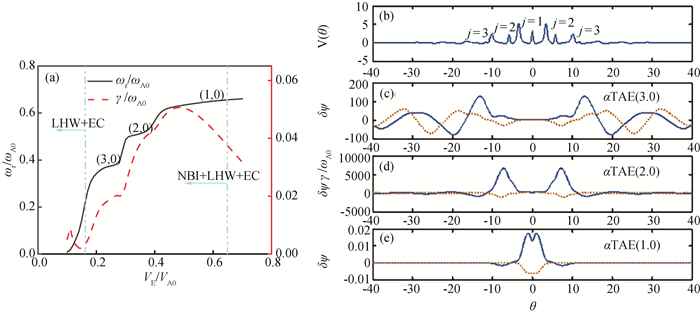
Fig.6 (a) Real frequency and growth rate of αTAEs with vE/vA0; (b) potentials V(θ), (c) αTAE(3, 0), (d) αTAE(2, 0), (e) αTAE(1, 0) mode structure excited by energetic particles (s=-0.19, α=2.11, q=2.06)
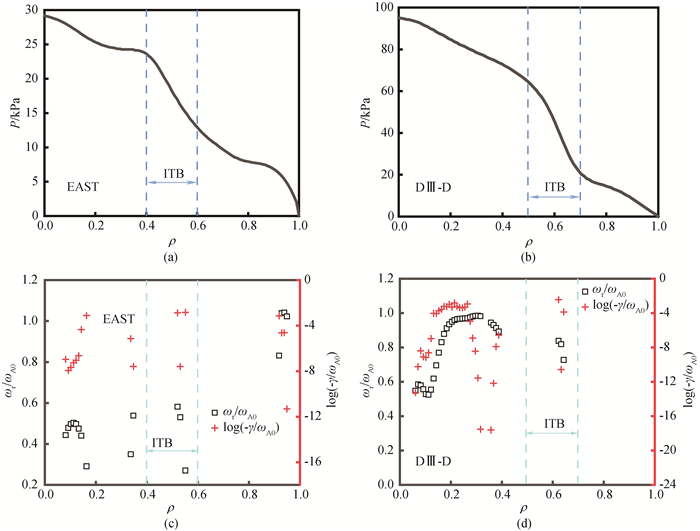
Fig.7 Pressure profiles of (a) EAST preview scenario discharge and DIII-D#159220 discharge; distributions of αTAE (1, 0) mode versus ρ of (c) EAST and (d) DIII-D, respectively.
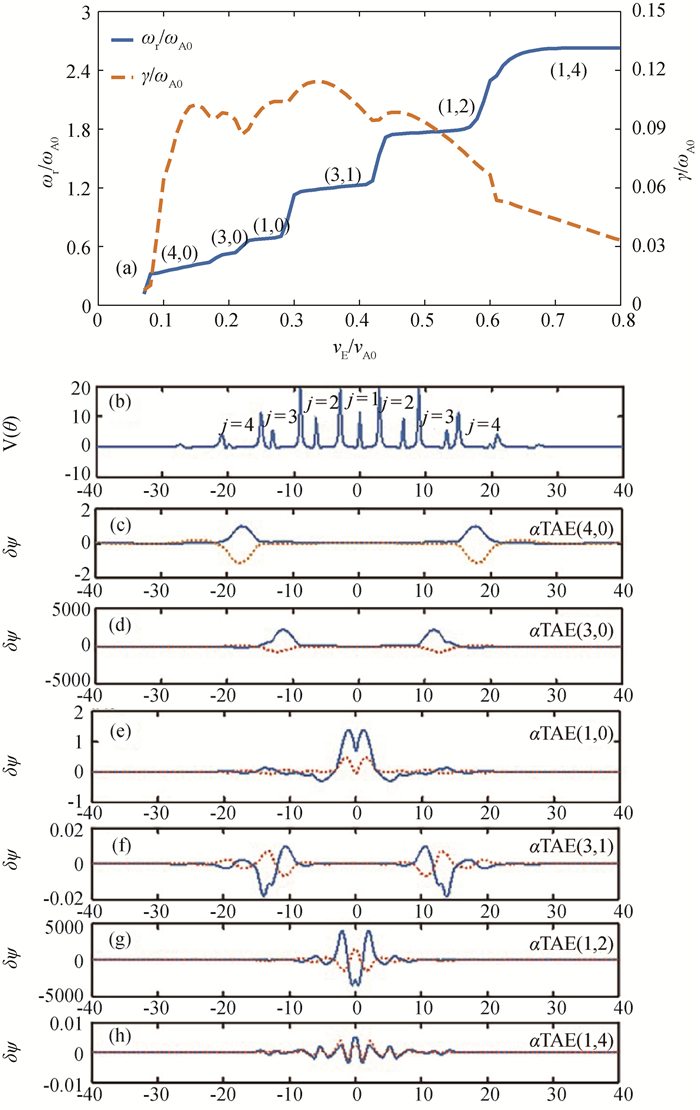
Fig.11 In CFETR, (a) real frequency (─) and growth rate (┄) of αTAEs vary with vE/vA0 at ρ=0.3; (b) potentials V(θ); (c) αTAE(4, 0); (d) αTAE(3, 0), (e) αTAE(1, 0), (f) αTAE(3, 1), (g) αTAE(1, 2), (h) αTAE(1, 4)mode structure excited by energetic particles
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
王一如, 胡双辉, 姚龙宝, 等. DIII-D高性能运行参数下的离散阿尔芬本征模[J]. 核聚变与等离体物理, 2012, 32 (2): 140- 147.
|
| 13 |
王军, 胡纯栋, 胡双辉, 等. 中性束注入在EAST中激发的离散阿尔文芬稳定性[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62 (3): 035201.
|
| 14 |
闫星辰, 胡双辉, 吴昊. EAST自举电流条件下离散阿尔芬本征模[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2017, 47 (6): 93- 99.
|
| 15 |
何秋明, 胡双辉, 吴昊, 等. HL-2A托卡马克等离子体中的离散阿尔芬本征模[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2019, 49 (4): 88- 97.
|
| 16 |
赵庆飞, 胡双辉, 何秋明, 等. CFETR条件下高能粒子激发的离散阿尔芬本征模[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2020, 50 (8): 136- 145.
|
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
DOI |
| 36 |
DOI |
| 37 |
DOI |
| 38 |
邹云鹏. 托卡马克装置中阿尔芬本征模稳定性及高能粒子输运模拟研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2019.
|
| 39 |
刘利. 中国聚变工程实验堆标准运行模式的演化设计研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018.
|
| [1] | Jingkun XU, Weihua WANG. Hybrid Simulation of Non-resonant Fishbone Instabilities Excited by Passing Energetic Particles in EAST Tokamak [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(3): 291-300. |
| [2] | Renzhu ZHU, Jiafeng HE, Taihao HUANG, Xinglei RUAN, Yuchen XU, Jin GUO, Tianyuan LIU, Shifeng MAO, Minyou YE. Performance of Numerical Calculation of Transport Equations of Scrape-off Layer Plasma: Pressure Correction Algorithms [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(1): 29-39. |
| [3] | Shuyu ZHENG, Jiazhen PENG, Xianmei ZHANG, Erbing XUE, Limin YU. Prediction of Energy Confinement Time in Tokamak Based on Neural Networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(4): 423-430. |
| [4] | LIU Zuguang, LI Xinxia, YANG Ming. Effect of Lower Hybrid Wave Current Drive with High Component N‖ on EAST [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(4): 467-472. |
| [5] | ZHA Xuejun, ZHONG Dejun, WANG Fuqiong, CHEN Yiping, LU Hongwei, HU Liqun. Monte-Carlo Modelling of Impurity Transport in EAST Tokamak [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2015, 32(6): 715-721. |
| [6] | HAO Jianli, CHEN Wenzhen, YANG Lei, WANG Shaoming. Criteria of Flow Instabilities in Steam Generator U-Tubes with Natural Circulation [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2013, 30(4): 515-519. |
| [7] | LIU Yan, GONG Xueyu, YANG Lei, PENG Xiaowei, YIN Lan. Numerical Solution of Full Wave Equation for Fast Wave Current Drive in Tokamak [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2012, 29(3): 375-382. |
| [8] | ZUO Suihan, YANG Yong, LI Dong. Investigation on Cross-flow Instabilities in Swept-wing Boundary Layers with Linear Parabolized Stability Equations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2010, 27(5): 665-670. |
| [9] | HUANG Qin-chao, WANG Hua-zhong, LUO Jia-rong, YUAN Qi-ping. A Simulation of the EAST MHD Equilibrium Configuration [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2006, 23(2): 231-236. |
| [10] | LU Quan-ming, WANG Shui. 2D HYBRID METHOD AND ITS APPLICATIONS [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2002, 19(3): 208-212. |
| [11] | LIU Jin-yuan, GONG Ye. SIMPLIFIED ANALYSES AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE ARC HELICAL INSTABILITY THEORY [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2000, 17(S1): 107-112. |
| [12] | Zhang Xianmei, Li Youyi, Wan Baonian. Calculation of neutral atom density distributions in tokamaks with monte carlo method [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1999, 16(6): 606-609. |
| [13] | Ye Wenhua, Zhang Weiyan, Chen Guangnan, Jin Changqiu, Zhang Jun. NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE FCT METHOD ON RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR AND RICHTMYER-MESHKOV INSTABILITIES [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1998, 15(3): 277-282. |
| [14] | Wang Shaojie, Qiu Lijian. ANALYSIS OF THE α PARTICLE TRANSPORT IN TOKAMAKS BY THE TWO-DIMENSIONAL TIME-DEPENDENT FOKKER-PLANCK EQUATION [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1996, 13(2): 129-135. |
| [15] | Liu Cheng an, Liu Chaofen, Huang Zhengfeng, Liu Zhongxing. STUDY OF MULTI-DIMENSIONAL NEUTRONICS CALCULATION OF THE FUSION-FISSION HYBRID EXPERIMENTAL REACTOR [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1992, 9(3): 274-278. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
