Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 352-360.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8243
• Research Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jing BAI( ), Zhijing HUANG, Guoning TANG(
), Zhijing HUANG, Guoning TANG( )
)
Received:2020-06-18
Online:2021-05-25
Published:2021-09-30
Contact:
Guoning TANG
CLC Number:
Jing BAI, Zhijing HUANG, Guoning TANG. Terminating Arrhythmia by Using Motion Controller[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(3): 352-360.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8243
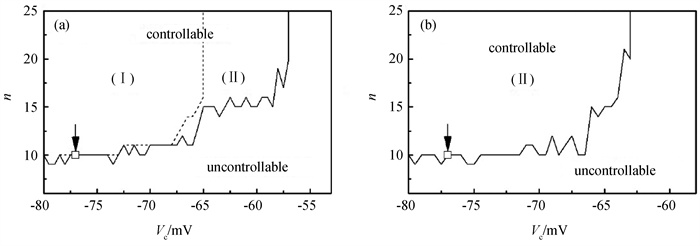
Fig.1 Controllable regions of (a) spiral wave and (b) spatiotemporal chaos in the n-Vc parameter plane (□ and the points above □ are controllable points that have not been confirmed by numerical simulation. The area above the solid curve is controllable area and the rest is uncontrollable area. The area above the dotted line in (a) is controllable area (Ⅰ) in which spiral wave can be controlled quickly. The other is controllable area (Ⅱ) in which spiral wave cannot be controlled quickly.)
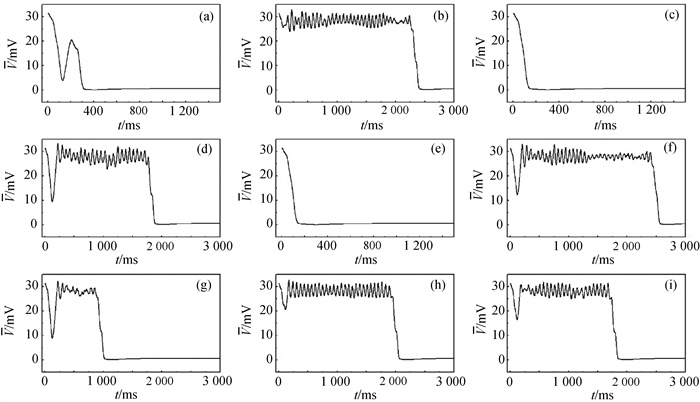
Fig.3 Evolution of the mean membrane potential difference at ${\bar G}$si= 0.02 mS ·cm-2 (a) Vc=-78 mV, n= 9; (b) Vc=-73.5 mV, n= 9; (c) Vc=-73.5 mV, n= 10; (d) Vc= -65 mV, n= 15; (e) Vc= -65 mV, n= 16; (f) Vc= -62.5 mV, n= 16; (g) Vc= -62.5 mV, n= 25; (h)Vc= -59 mV, n= 16; (i) Vc= -59 mV, n= 25
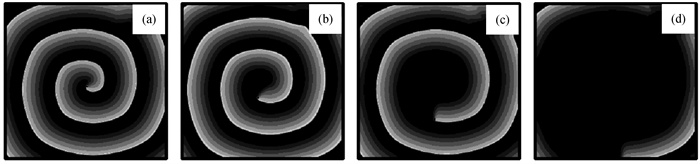
Fig.4 Patterns of membrane potential at different moments for ${\bar G}$si= 0.02 mS ·cm-2, Vc = -73 mV and n = 10 (a) t = 4 ms; (b) t = 20 ms; (c) t = 48 ms; (d) t = 104 ms

Fig.6 Patterns of membrane potential at different moments for ${\bar G}$si= 0.02 mS ·cm-2, Vc= -60 mV and n= 16 (a) t= 4 ms; (b) t= 40 ms; (c) t= 248 ms; (d) t= 456 ms; (e) t= 712 ms; (f) t= 1 180 ms; (g) t= 1 560 ms; (h) t= 1 660 ms; (i)t= 1 760 ms
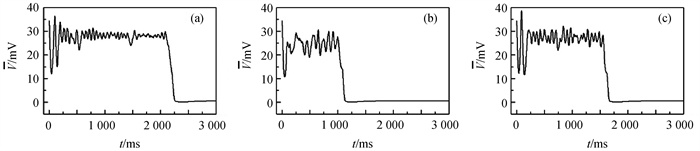
Fig.8 Evolution of the mean membrane potential difference at ${\bar G}$si= 0.05 mS ·cm-2 (a) Vc= -72.5 mV, n = 10; (b) Vc= -72.5 mV, n = 20; (c) Vc= -63 mV, n = 20

Fig.9 Patterns of membrane potential at different moments for ${\bar G}$si= 0.05 mS ·cm-2, Vc= -66.5 mV and n = 12 (a) t = 0 ms; (b) t = 20 ms; (c) t = 40 ms; (d) t = 140 ms; (e) t = 440 ms; (f) t = 800 ms; (g) t = 1 340 ms; (h) t = 1 580 ms; (i) t = 1 700 ms
| 1 |
DAVIDENKO J M, PERTSOV A V, SALOMONSZ R, et al. Stationary and drifting spiral waves of excitation in isolated cardiac muscle[J]. Nature, 1992, 355 (6358): 349- 351.
DOI |
| 2 |
DAVIDENKO J M, KENT P F, et al. Sustained vortex-like waves in normal isolated ventricular muscle[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1990, 87 (22): 8785- 8789.
DOI |
| 3 |
WITKOWSKI F X, LEON L J, PENKOSKE P A, et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of ventricular fibrillation[J]. Nature, 1998, 392 (6671): 78- 82.
DOI |
| 4 |
STEWART J A. Automated external defibrillators in the hospital: A case of medical reversal[J]. American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2018, 36 (5): 871- 874.
DOI |
| 5 |
WALCOTT G P, KILLINGSWORTH C R, IDEKER R E. Do clinically relevant transthoracic defibrillation energies cause myocardial damage and dysfunction?[J]. Resuscitation, 2003, 59 (1): 59- 70.
DOI |
| 6 |
SANTANGELI P, MUSER D, MAEDA S, et al. Comparative effectiveness of antiarrhythmic drugs and catheter ablation for the prevention of recurrent ventricular tachycardia in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2016, 13 (7): 1552- 1559.
DOI |
| 7 |
QIN D, LEEF G, ALAM M B, et al. Comparative effectiveness of antiarrhythmic drugs for rhythm control of atrial fibrillation[J]. Journal of Cardiology, 2016, 67 (5): 471- 476.
DOI |
| 8 |
BOKHARI F, NEWMAN D, GREENE M, et al. Long-term comparison of the implantable cardioverter defibrillator versus amiodarone eleven-year follow-up of a subset of patients in the Canadian implantable defibrillator study (CIDS)[J]. Circulation, 2004, 110 (2): 112- 116.
DOI |
| 9 |
HOLMQVIST F, KESEK M, ENGLUND A, et al. A decade of catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias in Sweden: Ablation practices and outcomes[J]. European Heart Journal, 2019, 40 (10): 820- 830.
DOI |
| 10 |
RAZMINIA M, WILLOUGHBY M C, DEMO H, et al. Fluoroless catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias: A 5-year experience[J]. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 2017, 40 (4): 425- 433.
DOI |
| 11 |
MARROUCHE N F, BRACHMANN J, ANDRESEN D, et al. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with heart failure[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2018, 378 (5): 417- 427.
DOI |
| 12 |
NARAYAN S M, KRUMMEN D E, SHIVKUMAR K, et al. Treatment of atrial fibrillation by the ablation of localized sources[J]. Journal American College of Cardiology, 2012, 60 (7): 628- 636.
DOI |
| 13 |
NARAYAN S M, KRUMMEN D E, RAPPEL W J, et al. Clinical mapping approach to diagnose electrical rotors and focal impulse sources for human atrial fibrillation[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 2012, 23 (5): 447- 454.
DOI |
| 14 |
CHENG E P, LIU C F, YEO I, et al. Risk of mortality following catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2019, 74 (18): 2254- 2264.
DOI |
| 15 |
BOHNEN M, STEVENSON W G, TEDROW U B, et al. Incidence and predictors of major complications from contemporary catheter ablation to treat cardiac arrhythmias[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2011, 8 (11): 1661- 1666.
DOI |
| 16 |
BINGEN B O, ENGELS M C, SCHALIJ M J, et al. Light-induced termination of spiral wave arrhythmias by optogenetic engineering of atrial cardiomyocytes[J]. Cardiovascular Research, 2014, 104 (1): 194- 205.
DOI |
| 17 |
MAJUMDER R, FEOLA I, TEPLENIN A S, et al. Optogenetics enables real-time spatiotemporal control over spiral wave dynamics in an excitable cardiac system[J]. eLife, 2018, 7, e41076.
DOI |
| 18 |
ZHANG H, CAO Z J, HU G, et al. Suppress winfree turbulence by local forcing excitable systems[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 94 (18): 188301.
DOI |
| 19 |
ZHANG H, HU B, HU G. Suppression of spiral waves and spatiotemporal chaos by generating target waves in excitable media[J]. Physical Review E, 2003, 68 (2): 026134.
DOI |
| 20 |
YUAN G Y, YANG S P, et al. Elimination of spiral waves and spatiotemporal chaos by the pulse with a specific spatiotemporal configuration[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2008, 17 (5): 1925- 1934.
DOI |
| 21 | 王春妮, 马军. 分布式电流刺激抑制心肌组织中螺旋波[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62 (8): 084501. |
| 22 | YANG C Y, LIU H Y, TANG G N. Simulation on control of spiral wave by two-stage pulse force[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2014, 31 (5): 625- 630. |
| 23 | 潘军廷, 何银杰, 张宏, 等. 极化电场对可激发介质中螺旋波的控制[J]. 物理学报, 2020, 69 (8): 080503. |
| 24 |
BOCCIA E, LUTHER S, PARLITZ U. Modelling far field pacing for terminating spiral waves pinned to ischaemic heterogeneities in cardiac tissue[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 2017, 375 (2096): 20160289.
DOI |
| 25 | ZHONG M, TANG G N. Suppression of spiral waves and spatiotemporal chaos in cardiac tissues with controll of calcium and potassium ionic currents[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2011, 28 (1): 119- 124. |
| 26 |
李倩昀, 黄志精, 唐国宁. 通过抑制波头旋转消除心脏中的螺旋波和时空混沌[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67 (24): 248201.
DOI |
| 27 |
潘飞, 王小艳, 唐国宁, 等. 通过放慢钠通道开闭控制心脏中的螺旋波和时空混沌[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65 (19): 198201.
DOI |
| 28 | MA J, WU N J, et al. A local phase control of spiral and spatiotemporal chaos[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2006, 23 (2): 243- 248. |
| 29 |
PANDIT S V, JALIFE J. Rotors and the dynamics of cardiac fibrillation[J]. Circulation Research, 2013, 112 (5): 849- 862.
DOI |
| 30 | CHEN J X, WEI G N, LI B W, et al. Motion of spiral waves induced by local pacing[J]. Central European Journal of Physics, 2008, 6 (3): 427- 433. |
| 31 |
LIU G Q, YING H P. Motion of spiral tip driven by local forcing in excitable media[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2014, 23 (5): 050502.
DOI |
| 32 |
LEE Y S, SONG J S, HWANG M, et al. A new efficient method for detecting phase singularity in cardiac fibrillation[J]. Plos One, 2016, 11 (12): e0167567.
DOI |
| 33 |
LUO C H, RUDY Y. A model of the ventricular cardiac action potential: Depolarization, repolarization, and their interaction[J]. Circulation Research, 1991, 68 (6): 1501- 1526.
DOI |
| 34 |
FAST V G, ROHR S, IDEKER R E. Nonlinear changes of transmembrane potential caused by defibrillation shocks in strands of cultured myocytes[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 2000, 278 (3): H688- H697.
DOI |
| [1] | Shaoying CHEN, Xueli WANG, Zhimei GAO, Guoyong YUAN. Dynamics of Spiral Waves in Complex Ginzburg-Landau Systems Subjected to Feedback Derived from an Annular Domain [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(1): 118-126. |
| [2] | Furong GUAN, Chengqian LI, Minyi DENG. Spiral Wave Dynamics of Excited Medium: Effect of Relative Refractory [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(6): 749-756. |
| [3] | HUANG Zhijing, BAI Jing, TANG Guoning. Mechanism of Spontaneous Formation of Spiral Wave in Neuronal Network with Unidirectional Coupling [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(5): 612-622. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xueliang, TAN Huili, TANG Guoning, DENG Minyi. Mechanical Deformation of Myocardial Tissue with Cellular Automaton [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(3): 294-302. |
| [5] | YANG Cuiyun, LIU Haiying, TANG Guoning. Simulation on Control of Spiral Wave by Two-stage Pulse Force [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2014, 31(5): 625-630. |
| [6] | CHEN Xiqiong, DENG Minyi, TANG Guoning, KONG Lingjiang. Effect of Conduction Delay on Dynamics of Spiral Waves [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2013, 30(4): 620-626. |
| [7] | CHEN Shaoying, YUAN Guoyong, WU Gang, CUI Qianqian, FAN Hongling. Effect of Lévy Noise and Periodic Force on Dynamics of Spiral Waves [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2012, 29(4): 620-626. |
| [8] | LI Guangzhao, TANG Guoning. Numerical Study on Depolarization in Dynamics of Spiral Waves in Excitable Media [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2011, 28(4): 626-632. |
| [9] | ZHONG Min, TANG Guoning. Suppression of Spiral Waves and Spatiotemporal Chaos in Cardiac Tissues with Controll of Calcium and Potassium Ionic Currents [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2011, 28(1): 119-124. |
| [10] | MA Jun, WU Ning-jie, YING He-ping, PU Zhong-sheng. A Local Phase Control of Spiral and Spatiotemporal Chaos [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2006, 23(2): 243-248. |
| [11] | YUE Li-juan, SHEN Ke. Spatiotemporal Chaos Control in Coupled Bistable Map Lattice Systems [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2005, 22(2): 130-136. |
| [12] | YAN Guang-wu. Lattice Boltzmann Model for Nonlinear Chemical Waves in the Excitable Media [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2003, 20(4): 356-358. |
| [13] | Wang Jinlan, Chen Guangzhi. Spatiotemporal chaos synchronization by active-occasional coupling [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1999, 16(5): 511-516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
