Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 199-209.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8621
Special Issue: 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊
• The 60th Anniversary of Academician He Xiantu's Scientific Research Work: A Special Issue of Research Progress in Laser Fusion • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenshuai ZHANG1( ), Hongbo CAI1,*(
), Hongbo CAI1,*( ), Enhao ZHANG2, Bao DU1, Shiyang ZOU1, Shaoping ZHU1,2,*(
), Enhao ZHANG2, Bao DU1, Shiyang ZOU1, Shaoping ZHU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-22
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-07-05
Contact:
Hongbo CAI, Shaoping ZHU
Wenshuai ZHANG, Hongbo CAI, Enhao ZHANG, Bao DU, Shiyang ZOU, Shaoping ZHU. Influence of Mach Number on Structure of Collisional Plasma Shock Waves: Fully Kinetic Simulations[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(2): 199-209.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8621
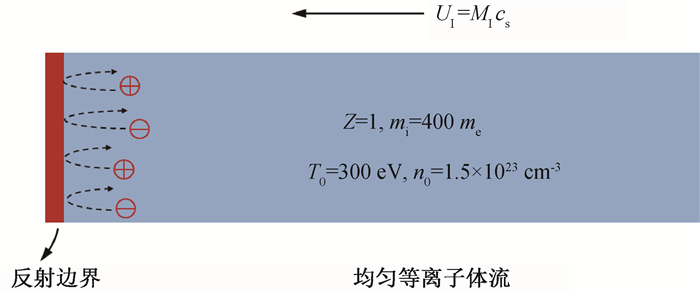
Fig.1 Schematic presentation of the PIC simulation setup (A uniform plasma flow drifting towards the left boundary is reflected and accumulates near the boundary due to particle collisions, resulting in a right-propagating shock wave.)
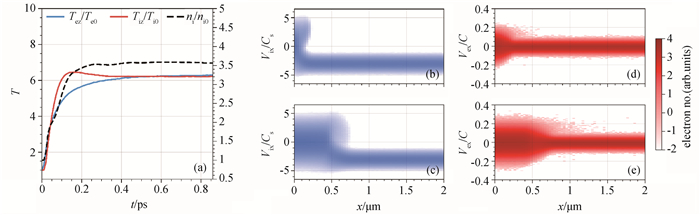
Fig.2 (a) Time evolution of plasma temperature and density near the left boundary; Ion and electron phase space distribution in logarithm scale at (b) and (d) 0.1 ps and (c) and (e) 0.6 ps
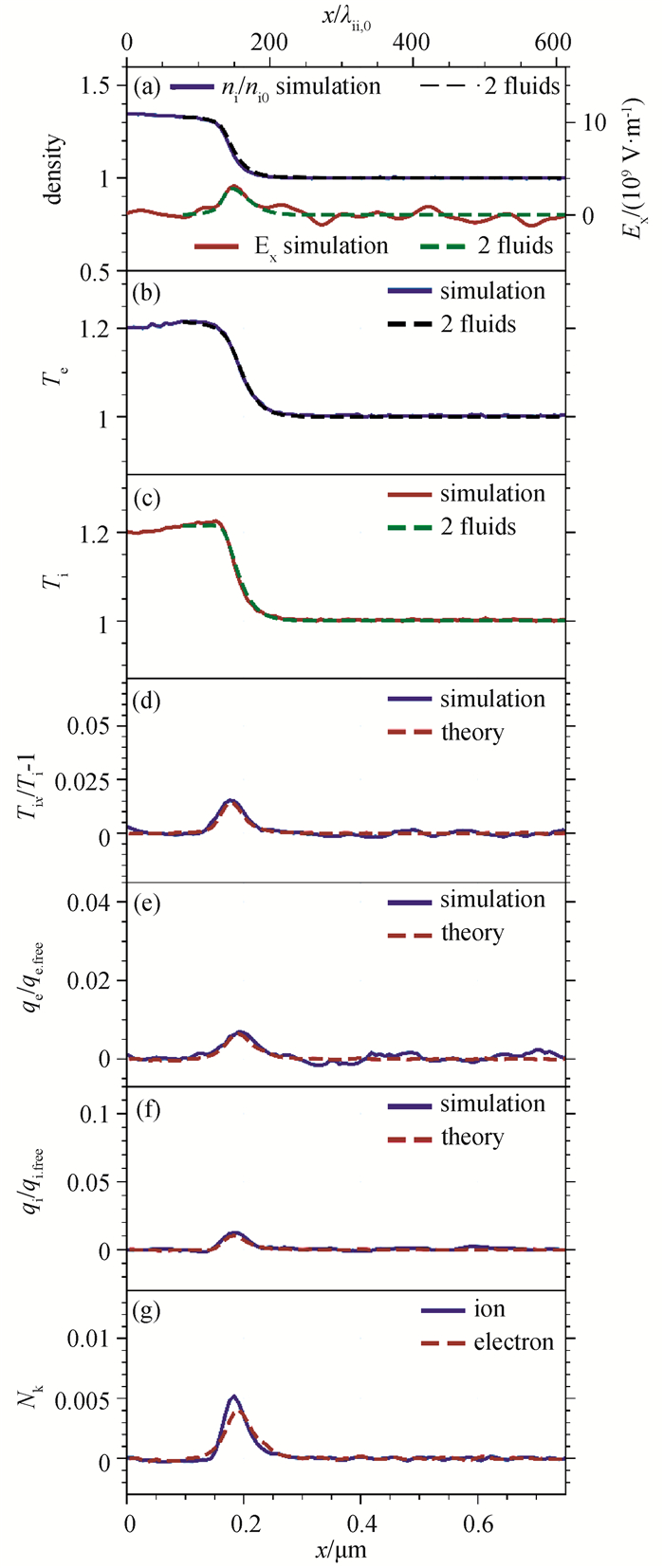
Fig.3 (a)~(c) Spatial profiles of ion density, electric field and temperature from PIC simulations (solid lines) and two-fluid theory (dashed lines); (d)~(f) Spatial profiles of viscosity and heat flux from simulations (solid lines) and transport theory (dashed lines); (g) Spatial profiles of the Knudsen number (Simulations results averaged over y for Msh = 1.22 at t = 0.3 ps.)
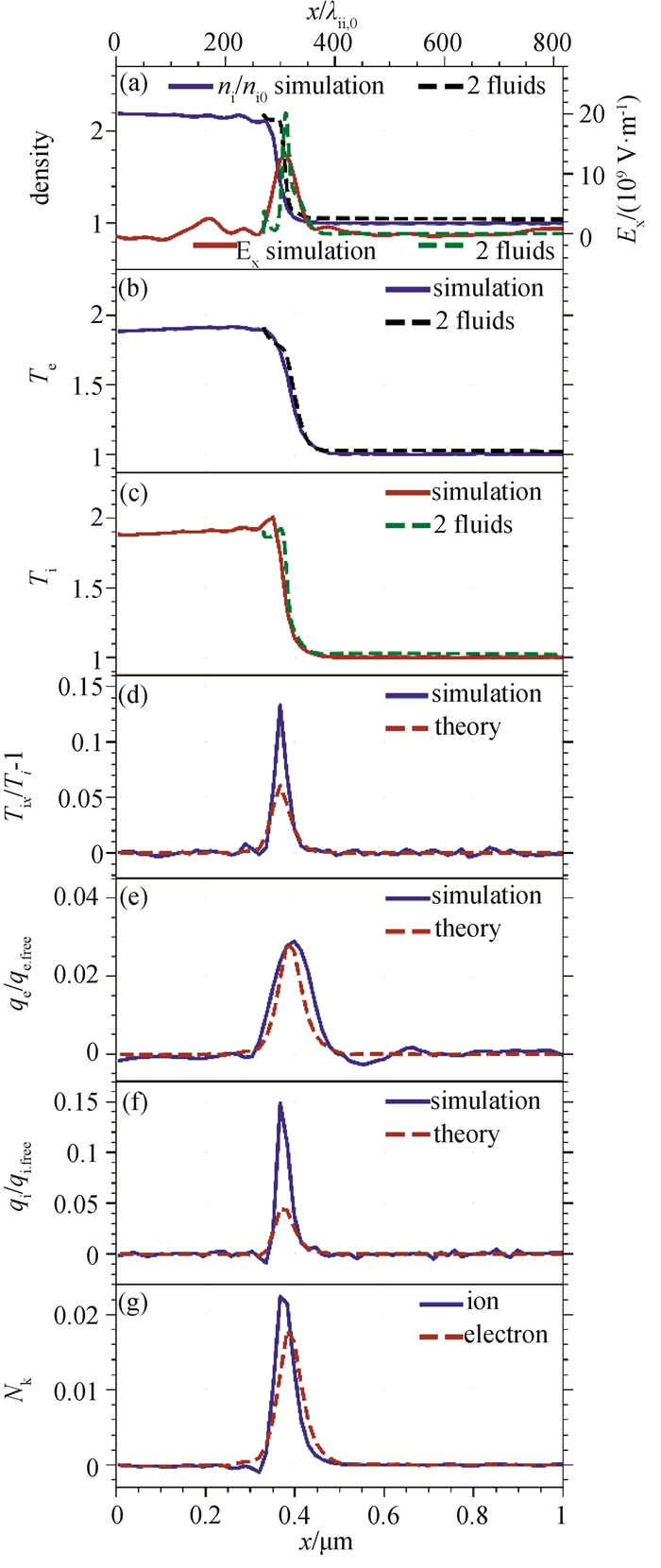
Fig.4 (a)~(c) Spatial profiles of ion density, electric field and temperature from simulations (solid lines) and two-fluid theory (dashed lines); (d)~(f) Spatial profiles of viscosity and heat flux from simulations (solid lines) and transport theory (dashed lines). (g) Spatial profiles of the Knudsen number (Simulations results averaged over y for Msh = 1.87 at t = 0.64 ps.)
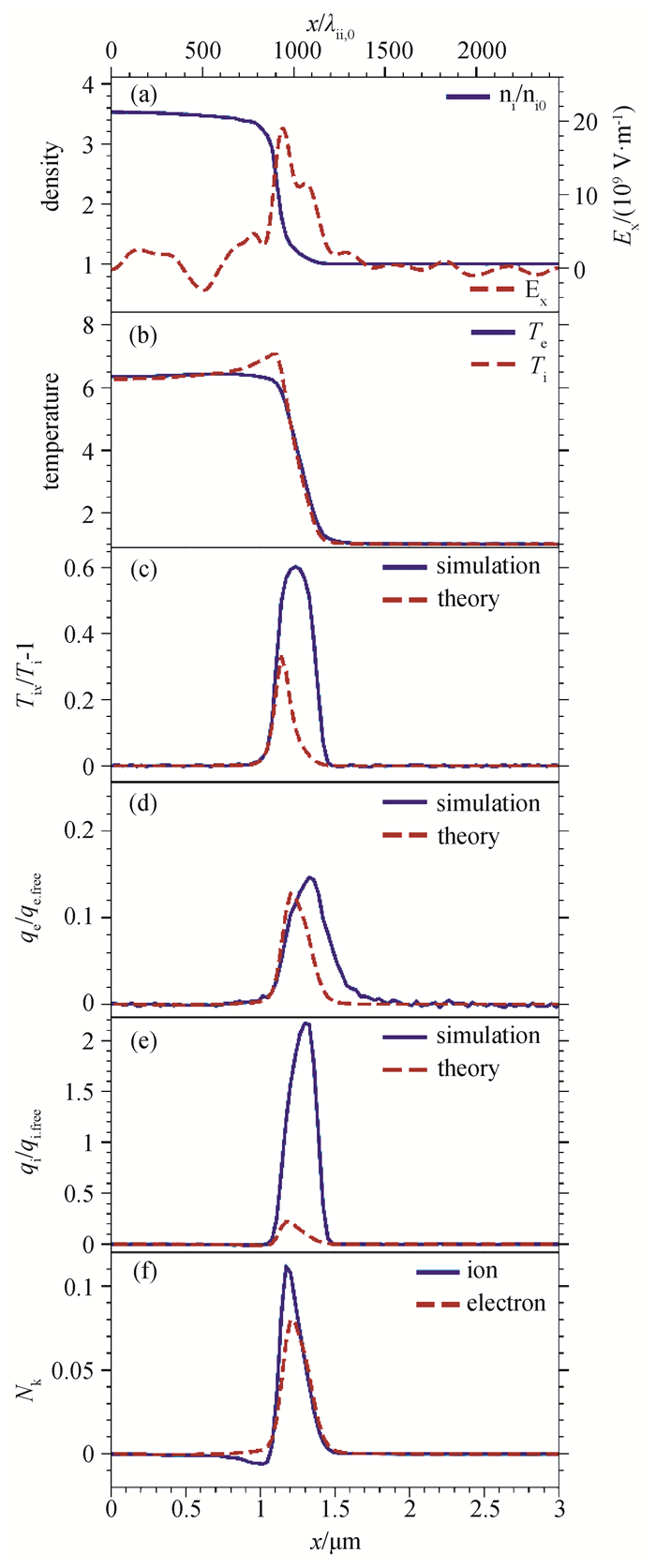
Fig.5 (a)~(b) Spatial profiles of ion density, electric field and temperature from simulations; (c)~(e) Spatial profiles of viscosity and heat flux from simulations (solid lines) and transport theory (dashed lines); (f) Spatial profiles of the Knudsen number (Simulations results averaged over y for Msh = 4.2 at t = 1.4 ps.)
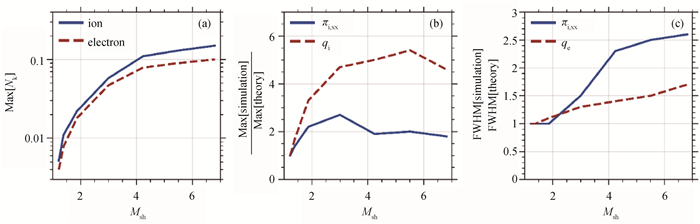
Fig.6 (a) Shock Mach number dependence of the maximum Knudsen number from PIC simulations; (b) Ratio of the maximum ion viscous stress and ion heat flux from the PIC simulations to that from the transport theory; (c) Ratio of the full-width-half-maximum of the spatial profiles of the simulated and theoretical ion viscous stress and electron heat flux
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
DOI |
| 35 |
DOI |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
