Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 548-555.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8634
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fushun WANG1( ), Baotao CHI1,2,*(
), Baotao CHI1,2,*( ), Zhichao JIA1, Qianjian GUO1, Wei YUAN1
), Zhichao JIA1, Qianjian GUO1, Wei YUAN1
Received:2022-09-06
Online:2023-09-25
Published:2023-11-02
Contact:
Baotao CHI
Fushun WANG, Baotao CHI, Zhichao JIA, Qianjian GUO, Wei YUAN. Efficient and High Precision Nearly Singular Domain Integrals Calculation Based on Adaptive Element Subdivision Method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 548-555.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8634
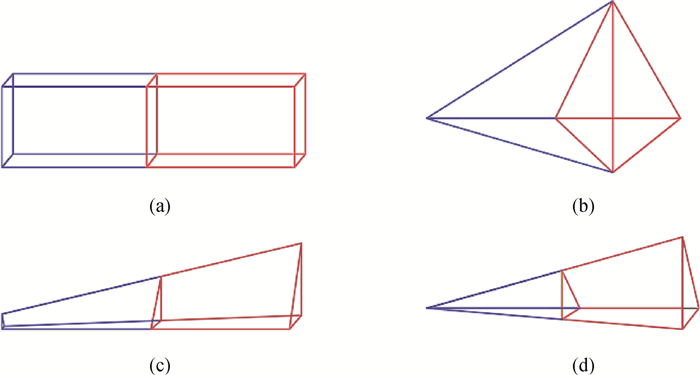
Fig.3 Subdivision of different types of volume element (a) hexahedral element; (b) tetrahedral element; (c) pentahedral element; (d) slender tetrahedral element
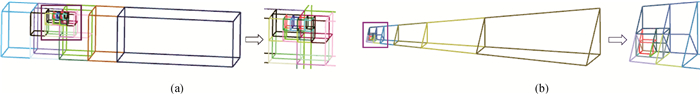
Fig.4 BTSM for nearly singular domain integrals with continuous kernels (a) subdivision of slender hexahedral element; (b) subdivision of slender pentahedral element
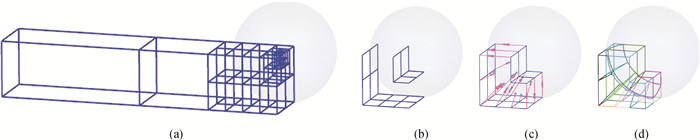
Fig.5 Construction of valid core cavities for projection (a) ultimate subdivision sub-elements; (b) the core projection cavities; (c) matching the core projection cavity to sphere; (d) convert relative sub-elements into well-shaped serendipity patches
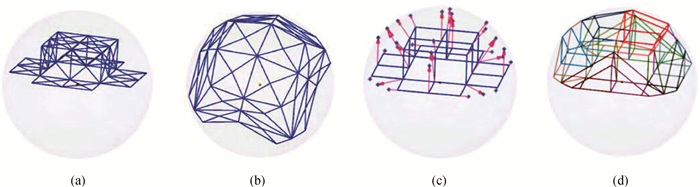
Fig.9 The Harmonic projection algorithm schematic diagram (a) triangulation of the projection cavity faces; (b) calculated projection points in parameter space; (c) map of relative projection points; (d) relative inner-ring projection points and sub-elements
| 1 |
梁钰, 郑保敬, 高效伟, 等. 基于POD模型降阶法的非线性瞬态热传导分析[J]. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2018, 48(12): 36- 45.
|
| 2 |
高效伟, 徐兵兵, 吕军, 等. 自由单元法及其在结构分析中的应用[J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(3): 703- 713.
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
谷岩, 张耀明. 双材料界面裂纹复应力强度因子的正则化边界元法[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(4): 1049- 1058.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
汪超, 谢能刚, 黄璐璐. 基于扩展等几何分析和混沌离子运动算法的带孔结构形状优化设计[J]. 工程力学, 2019, 36(4): 248- 256.
|
| 11 |
李聪, 牛忠荣, 胡宗军, 等. 三维切口/裂纹结构的扩展边界元法分析[J]. 力学学报, 2020, 52(5): 1394- 1408.
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
池宝涛, 张见明, 鞠传明, 等. 基于T-Spline的全自动几何拓扑修复方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1511- 1526.
|
| 17 |
|
| [1] | CAO Yanchuang, XIAO Jinyou, WEN Lihua, WANG Zheng. Fast Directional Boundary Element Method for Large Scale Wideband Elastodynamic Analysis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(3): 305-316. |
| [2] | ZHOU Huanlin, YAN Jun, YU Bo, CHEN Haolong. Identification of Thermal Conductivity for Transient Heat Conduction Problems by Improved Cuckoo Search Algorithm [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(2): 212-220. |
| [3] | WANG Xianhui, ZHENG Xingshuai, QIAO Hui, ZHANG Xiaoming. Analytical Study of Hypersinglar Integral Equations with Constant Element for 2D Helmholtz Problems [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(6): 666-672. |
| [4] | SUN Rui, HU Zongjun, NIU Zhongrong. Analysis of Nearly Singular Integral Problem in 3D Acoustic Field Boundary Element Method [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(5): 611-618. |
| [5] | WANG Xianhui, QIAO Hui, ZHANG Xiaoming, GU Jinliang. An Isogeometric Boundary Element Method for 3D Helmholtz Problems [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(1): 61-66. |
| [6] | GE Renyu, NIU Zhongrong, CHENG Changzheng, HU Zongjun, XUE Weiwei. Propagation Analysis of Two-dimensional Linear Elastic Crack with Boundary Element Method [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2015, 32(3): 310-320. |
| [7] | SUN Shili, SUN Yilong, HU Jingzhong, HU Jian. Free Surface Effect and Spike of a Cylinder Piercing Water Surface [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2013, 30(2): 187-193. |
| [8] | HUANG Shuo, XIAO Jinyou, HU Yucai, WANG Tao. GPU-accelerated Boundary Element Method for Burton-Miller Equation in Acoustics [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2011, 28(4): 481-487. |
| [9] | GU Yan, ZHANG Yaoming, LI Gongsheng. Boundary Element Analysis of Thin-walled Structures in Elasticity Problems with Exact Geometrical Representation [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2011, 28(3): 397-403. |
| [10] | YAN Hui, XIAO Changhan, ZHANG Zhaoyang, ZHU Xingle. Iterative Method for Continuation of Three-component Magnetic Field [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2010, 27(5): 705-710. |
| [11] | CHENG Changzheng, NIU Zhongrong, ZHOU Huanlin, YANG Zhiyong. Evaluation of Nearly Hyper-singular Integrals in Thermal Stress Boundary Element Method [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2008, 25(1): 113-118. |
| [12] | WANG Xueren, JI Zhenlin. Boundary Element Analysis of Four-pole Parameters and Transmission Loss of Silencers with Flow [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2007, 24(6): 717-724. |
| [13] | HE Zeng, LÜ Junchao, DAI Chenghao. A Fast Multiple Boundary Element Method for Two-dimensional Electrostatic Field with Arbitrary Plane Charge Distribution [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2007, 24(4): 433-438. |
| [14] | LI Yasha, WANG Zezhong, LU Binxian. Analytical Integrals in the Linear Interpolation BEM for 3-D Electrostatic Fields [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2007, 24(1): 59-64. |
| [15] | YIN Hai-rong, GONG Yu-bin, WEI Yan-yu, HUANG Min-zhi, LU Zhi-gang, WANG Wen-xiang. Virtual Boundary Method and Electron Trace in a Power Electron Gun [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2006, 23(6): 647-654. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
