Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 361-370.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8398
• Research Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yanli ZOU( ), Shuyi TAN, Xinyan LIU, Shaoze ZHANG, Haoqian LI
), Shuyi TAN, Xinyan LIU, Shaoze ZHANG, Haoqian LI
Received:2021-05-14
Online:2022-05-25
Published:2022-09-02
Yanli ZOU, Shuyi TAN, Xinyan LIU, Shaoze ZHANG, Haoqian LI. Power System Critical Node Identification Based on Subnetwork Partition[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(3): 361-370.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8398
| 节点有功功率 | 平均功率 | ||||
| 节点1 | 节点2 | 节点3 | 节点6 | 节点8 | |
| 1.8 | 1.89 | 1.8 | 3.22 | 1.8 | 2.1 |
Table 1 Active power and average power of generators in IEEE14 grid
| 节点有功功率 | 平均功率 | ||||
| 节点1 | 节点2 | 节点3 | 节点6 | 节点8 | |
| 1.8 | 1.89 | 1.8 | 3.22 | 1.8 | 2.1 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 1 | 0.141 | 0 | 0.094 | 0.627 | 0.276 | 0.016 | 0 | 0.061 | 0.084 | 0.276 | 0.276 | 0.276 | 0.087 |
| 0 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.339 | 0.325 | 0.143 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.219 | 0.211 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.21 |
| 0 | 0.108 | 1 | 0.565 | 0.047 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.356 | 0.318 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.314 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.559 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.061 | 0.559 | 0.559 | 0.559 | 0.067 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.821 | 1 | 0.363 | 0.324 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.32 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 2 Coefficient distribution matrix K of IEEE14 grid
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 1 | 0.141 | 0 | 0.094 | 0.627 | 0.276 | 0.016 | 0 | 0.061 | 0.084 | 0.276 | 0.276 | 0.276 | 0.087 |
| 0 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.339 | 0.325 | 0.143 | 0.06 | 0 | 0.219 | 0.211 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.21 |
| 0 | 0.108 | 1 | 0.565 | 0.047 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.356 | 0.318 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.314 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.559 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.061 | 0.559 | 0.559 | 0.559 | 0.067 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.821 | 1 | 0.363 | 0.324 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.32 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
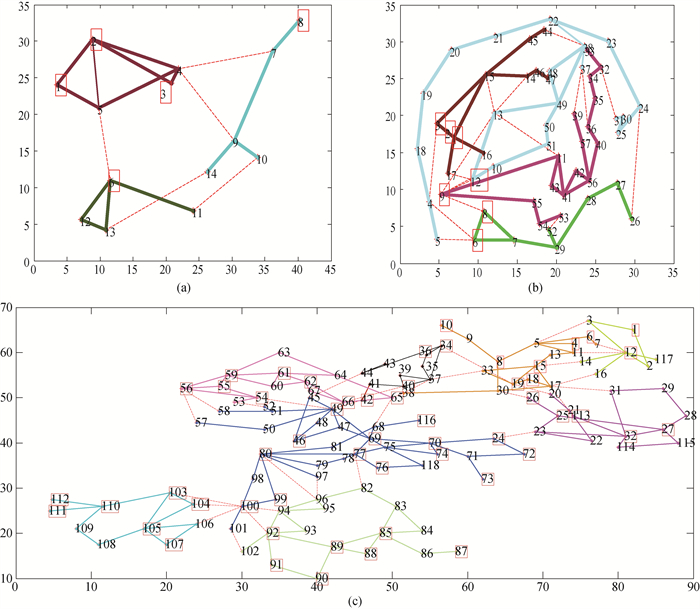
Fig.2 Subnet division result (Red boxes indicate generator nodes. Red dotted lines indicate inter network connections. Solid lines indicate internal connections.) (a)IEEE14 network; (b)IEEE57 network; (c)IEEE118 network
| 网络 | 模块度Q |
| IEEE14 | 0.403 8 |
| IEEE57 | 0.449 1 |
| IEEE118 | 0.646 3 |
Table 3 Subnet partition modularity of IEEE grids
| 网络 | 模块度Q |
| IEEE14 | 0.403 8 |
| IEEE57 | 0.449 1 |
| IEEE118 | 0.646 3 |
| 网络 | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 |
| IEEE14 | 0.739 3 | 0.817 8 | 0.756 2 | |
| IEEE57 | 2.150 8 | 1.729 3 | 2.411 8 | 2.118 6 |
Table 4 Structure coefficients of subnets in IEEE grids
| 网络 | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 |
| IEEE14 | 0.739 3 | 0.817 8 | 0.756 2 | |
| IEEE57 | 2.150 8 | 1.729 3 | 2.411 8 | 2.118 6 |
| 网络 | ||||
| IEEE14 | 0.319 6 | 0.353 5 | 0.326 9 | |
| IEEE57 | 0.255 7 | 0.205 6 | 0.286 8 | 0.251 9 |
Table 5 Normalized structure coefficients of subnets
| 网络 | ||||
| IEEE14 | 0.319 6 | 0.353 5 | 0.326 9 | |
| IEEE57 | 0.255 7 | 0.205 6 | 0.286 8 | 0.251 9 |
| 网络 | 子网1内节点 | 子网2内节点 | 子网3内节点 | 子网4内节点 |
| IEEE14 | 1,2,3,4,5 | 7,8,9,10,14 | 6,11,12,13 | |
| IEEE57 | 1,2,3,14,15,16,17,37,38,44,45,46,47 | 4,5,10,12,13, 18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,30,31,48,49,50,51 | 9,11,32,33,34,35,36,39,40,41,42,43,53,54,55,56,57 | 6,7,8,26,27,28,29,52 |
Table 6 Nodes in subnets of IEEE grids
| 网络 | 子网1内节点 | 子网2内节点 | 子网3内节点 | 子网4内节点 |
| IEEE14 | 1,2,3,4,5 | 7,8,9,10,14 | 6,11,12,13 | |
| IEEE57 | 1,2,3,14,15,16,17,37,38,44,45,46,47 | 4,5,10,12,13, 18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,30,31,48,49,50,51 | 9,11,32,33,34,35,36,39,40,41,42,43,53,54,55,56,57 | 6,7,8,26,27,28,29,52 |
| 序号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 原节点编号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 |
Table 7 Renumbering subnet nodes of C1 subnet in IEEE57
| 序号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 原节点编号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 |
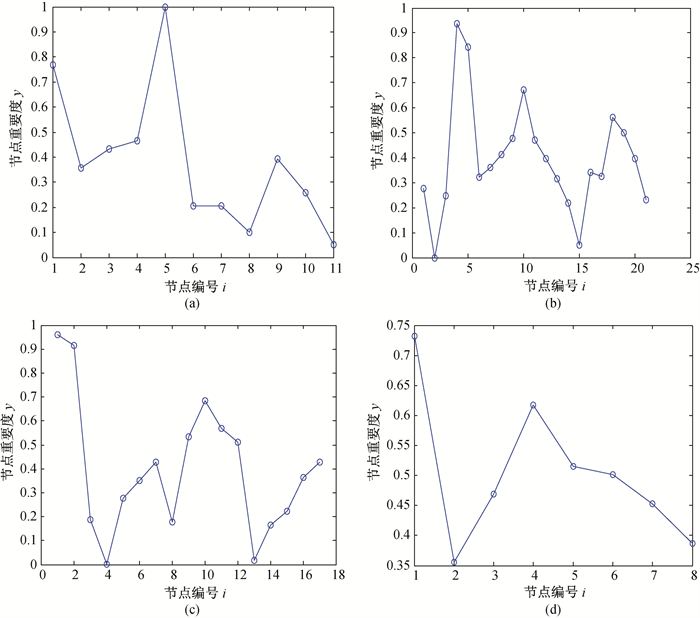
Fig.3 Ranking of key nodes in subnets of IEEE57 grid (Node importance y is calculated with multi-attribute decision-making method[20].) (a)subnet C1; (b)subnet C2; (c)subnet C3; (d)subnet C4
| 排序 | 本文方法(SD-MA) | PageRank | 多属性决策法(MA)[ |
| 1 | 12 | 13 | 13 |
| 2 | 15 | 9 | 9 |
| 3 | 13 | 38 | 38 |
| 4 | 9 | 15 | 12 |
| 5 | 11 | 12 | 15 |
| 6 | 41 | 32 | 49 |
| 7 | 3 | 56 | 11 |
| 8 | 1 | 4 | 41 |
| 9 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 10 | 27 | 41 | 4 |
Table 8 IEEE 57 node importance ranking
| 排序 | 本文方法(SD-MA) | PageRank | 多属性决策法(MA)[ |
| 1 | 12 | 13 | 13 |
| 2 | 15 | 9 | 9 |
| 3 | 13 | 38 | 38 |
| 4 | 9 | 15 | 12 |
| 5 | 11 | 12 | 15 |
| 6 | 41 | 32 | 49 |
| 7 | 3 | 56 | 11 |
| 8 | 1 | 4 | 41 |
| 9 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 10 | 27 | 41 | 4 |
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
李浩乾, 邹艳丽, 张少泽, 等. 基于复杂网络的电网结构健壮性及Braess悖论现象研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38 (4): 470- 478.
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
何铭, 邹艳丽, 梁明月, 等. 基于多属性决策的电力网络关键节点识别[J]. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2020, 17 (3): 27- 37.
|
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
邹艳丽, 汪洋, 刘树生, 等. 带有邻居度信息的容量负载模型下电网级联故障研究[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 37 (4): 27- 36.
|
| 23 |
|
| [1] | Zheng GAO, Yanli ZOU, Junwan HU, Gaohua YAO, Tanghuimei LIU. Coupling Strength Allocation Strategy in Power Grids Based on Complex Network Theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 579-588. |
| [2] | Shaoze ZHANG, Yanli ZOU, Shuyi TAN, Haoqian LI, Xinyan LIU. Analysis of Braess Paradox in an Interconnected Power Grid Based on Complex Network Theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(2): 233-243. |
| [3] | Haoqian LI, Yanli ZOU, Shaoze ZHANG, Xinyan LIU, Shuyi TAN. Robustness of Power Grids Structure and Braess Paradox Phenomenon: A Complex Network Theory Study [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(4): 470-478. |
| [4] | ZOU Yanli, GAO Zheng, LIANG Mingyue, LI Zhihui, HE Ming. Optimization of Synchronization Performance and Robustness Analysis in Power Grids Based on Power Tracing [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(5): 623-630. |
| [5] | ZOU Yanli, WANG Ruirui, WU Lingjie, YAO Fei, WANG Yang. Optimization of Synchronization Performance in Power Grids with Local Order Parameters [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(4): 498-504. |
| [6] | WANG Yi, ZOU Yanli, HUANG Li, LI Ke. Key Nodes Identification of Power Grid Considering Local and Global Characteristics [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(1): 119-126. |
| [7] | LAN Qingyu, ZOU Yanli, FENG Cong. Cascading Failures of Power Grids Under Three Attack Strategies [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2012, 29(6): 943-948. |
| [8] | ZHOU Haiping, CAI Shaohong. A Cascading Failure Model for Power Systemes [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2011, 28(2): 313-316. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
