Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 233-243.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8387
• Research Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shaoze ZHANG, Yanli ZOU*( ), Shuyi TAN, Haoqian LI, Xinyan LIU
), Shuyi TAN, Haoqian LI, Xinyan LIU
Received:2021-04-28
Online:2022-03-25
Published:2022-06-24
Contact:
Yanli ZOU
Shaoze ZHANG, Yanli ZOU, Shuyi TAN, Haoqian LI, Xinyan LIU. Analysis of Braess Paradox in an Interconnected Power Grid Based on Complex Network Theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(2): 233-243.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8387
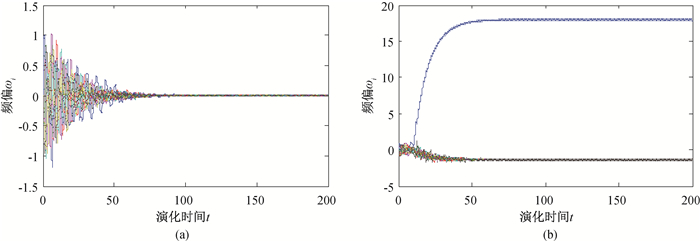
Fig.1 Frequency offset evolution of the original network of IEEE14 system and the network adding a new transmission line (a) original network; (b) network adding (1, 11) transmission line
| 网络 | 稳态频偏 |
| 原网络 | 0.00 |
| 新增(1, 11)传输线路 | 2.57 |
Table 1 Steady state frequency offset of the original network and the network adding (1, 11) transmission line in IEEE14 system
| 网络 | 稳态频偏 |
| 原网络 | 0.00 |
| 新增(1, 11)传输线路 | 2.57 |

Fig.3 Probability of Braess paradox phenomenon as adding a transmission line in a subnet in an interconneted power grid as functions of transmission power (a)IEEE14-14 subnet A; (b)IEEE14-14 subnet B; (c)IEEE14-30 subnet A; (d)IEEE14-30 subnet B
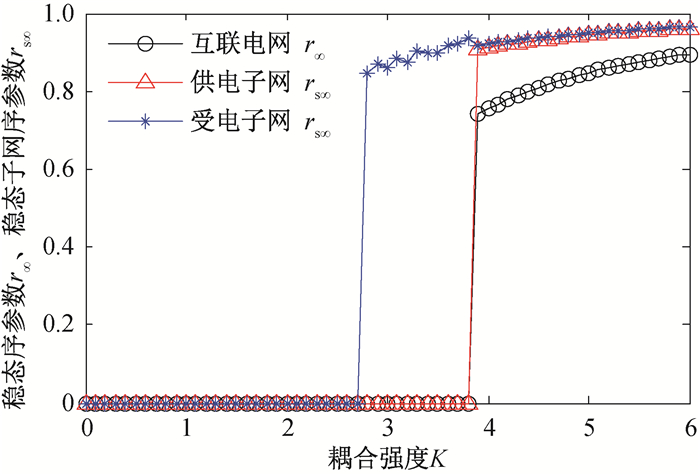
Fig.4 Steady state order parameters of IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid, the power supply subnet and the power receiving subnet as functions of the coupling strength
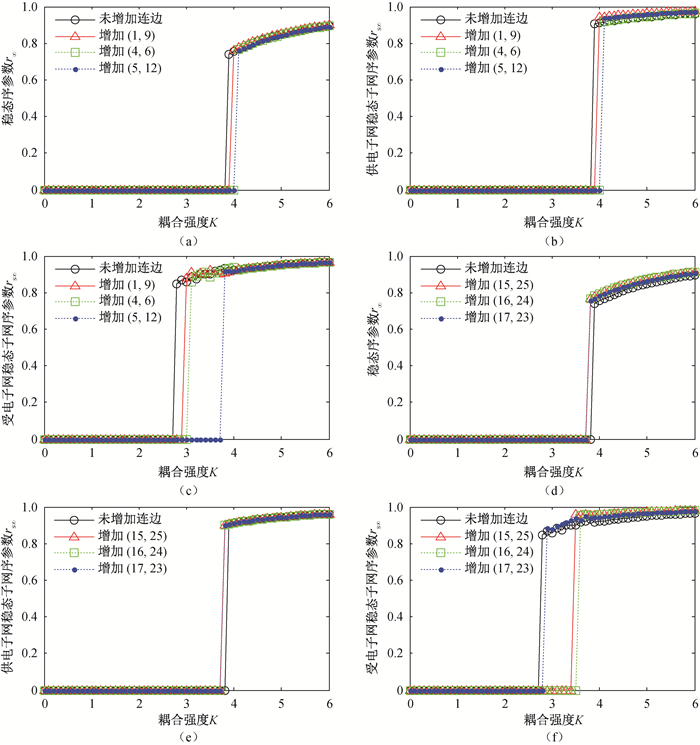
Fig.5 Synchronizability of IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid with a new transmission line in the power supply subnet and in the power receiving subnet, respectivlely (In (a), (b) and (c) the new transmission line is added in the power supply subnet, and in (d), (e) and (f) the new transmission line is added in the power receiving subnet.) (a) IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid; (b) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-14; (c) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-14; (d) IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid; (e) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-14; (f) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-14
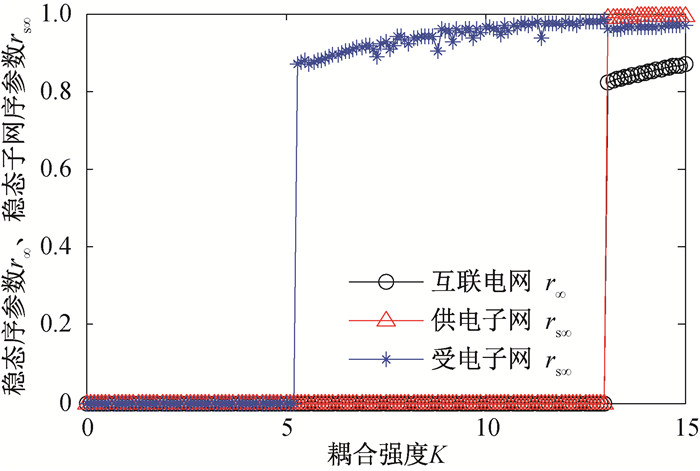
Fig.6 Steady state order parameter of IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid, the power supply subnet and the power receiving subnet as functions of the coupling strength
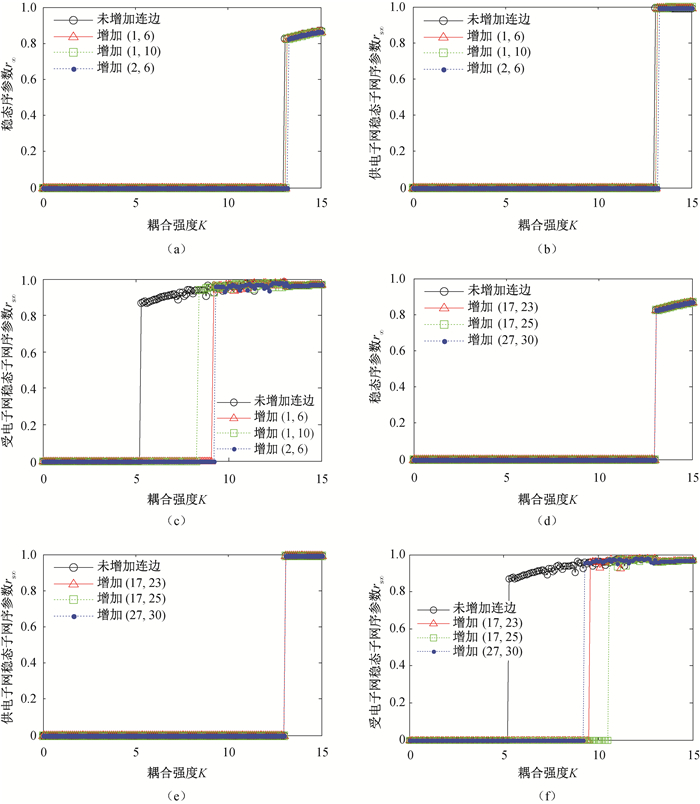
Fig.7 Synchronizability of IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid with a new transmission line in the power supply subnet and in the power receiving subnet, respectivlely (In (a), (b) and (c) the new transmission line is addded in the power supply subnet, and in (d), (e) and (f) the new transmission line is added in the power receiving subnet.) (a) IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid; (b) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-30; (c) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-30, (d) IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid; (e) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-30; (f) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-30
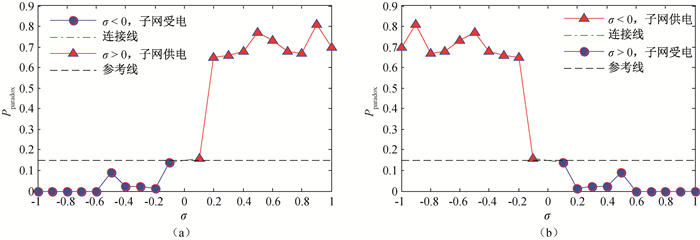
Fig.8 Probability of the Braess paradox phenomenon with a transmission line in a subnent in an interconneted power grid as functions of the transmission power (a) IEEE57-57 subnet A; (b) IEEE57-57 subnet B
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
鲁丛林, 蔡宁. Braess's paradox的博弈论分析[J]. 交通科学与工程, 2003, 19 (3): 69- 72.
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
XUE J, GEHLOT H, UKKUSURI S V. Braess's paradox in scale-free networks[C]. The 8th International Symposium on Dynamic Traffic Assignment, 2020.
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
张国宝. "西电东送"工程: 中国电力史上的重要篇章[J]. 中国经济周刊, 2019, 1 (12): 48- 52.
|
| 8 |
李飏, 周永章. 珠江流域"西电东送"能源空间配置的综合效益分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2008, (3): 147- 151.
DOI |
| 9 |
朱法华, 王圣, 刘思湄. 中国电力规划环评的发展与建议[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2007, 23 (5): 9- 13.
DOI |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
BAILLIEUL J, ZHANG B, WANG S. The Kirchhoff-Braess paradox and its implications for smart microgrids[C]. 2015 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2015: 6556-6563.
|
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
WANG X, KOC Y, KOOIJ R E, et al. A network approach for power grid robustness against cascading failures[J]. Physics and Society, 2015, arXiv: 1505.06312.
|
| 16 |
FAZLYAB M, DORFLER F, PRECIADO V M, et al. Optimal network design for synchronization of Kuramoto oscillators[J]. Optimization and Control, 2015, arXiv: 1503.07154.
|
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣. 复杂网络理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006.
|
| 20 |
方锦清. 非线性网络的动力学复杂性研究的若干进展[J]. 自然科学进展, 2007, 17 (7): 841- 857.
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| [1] | Zheng GAO, Yanli ZOU, Junwan HU, Gaohua YAO, Tanghuimei LIU. Coupling Strength Allocation Strategy in Power Grids Based on Complex Network Theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 579-588. |
| [2] | Tao FU, Long WU, Chenguang LI. Site-bond Percolation Modeling of Real Networks: Generating Function Method [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(2): 212-222. |
| [3] | Haoqian LI, Yanli ZOU, Shaoze ZHANG, Xinyan LIU, Shuyi TAN. Robustness of Power Grids Structure and Braess Paradox Phenomenon: A Complex Network Theory Study [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(4): 470-478. |
| [4] | ZOU Yanli, GAO Zheng, LIANG Mingyue, LI Zhihui, HE Ming. Optimization of Synchronization Performance and Robustness Analysis in Power Grids Based on Power Tracing [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(5): 623-630. |
| [5] | SHI Jianping, LI Peisheng, LIU Guoping. Synchronization Control and Parameter Identification for Unified Chaotic System Based on Improved Clonal Selection Algorithm [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(2): 240-252. |
| [6] | ZHONG Guoxiang, WEI Duqu, ZHANG Bo. Remote Chaotic Synchronous Control of Inductive Load in Distributed Power Generation System [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(6): 719-725. |
| [7] | ZOU Yanli, WANG Ruirui, WU Lingjie, YAO Fei, WANG Yang. Optimization of Synchronization Performance in Power Grids with Local Order Parameters [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(4): 498-504. |
| [8] | SHI Jianping, YANG Lantian, LIU Dan. Synchronization and Parameter Identification of Chaotic Systems Based on Quantum-Behaved Particle Swarm Optimization [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(2): 236-244. |
| [9] | ZHA Jindao, LI Chunbiao. Chaos Synchronization Based on Gravitational Field Theory [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(6): 737-749. |
| [10] | LIU Lihua, WEI Duqu, ZHANG Bo. Synchronization Control of Chaos in Complex Motor Networks with Small-world Topology Based on Dynamic Relaying [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(6): 750-756. |
| [11] | WANG Yi, ZOU Yanli, HUANG Li, LI Ke. Key Nodes Identification of Power Grid Considering Local and Global Characteristics [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(1): 119-126. |
| [12] | QIAN Hui, YU Hongjie. Application of SC Projective Synchronization Method in Secure Communication [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2016, 33(1): 117-126. |
| [13] | AN haigang. Linkage Fluctuation in Double Variables of Time Series Based on Complex Networks [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2014, 31(6): 742-750. |
| [14] | FAN Wenli, LIU Zhigang. An Evaluation Method for Node Importance Based on Efficiency Matrix [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2013, 30(5): 714-719. |
| [15] | TANG Shengxue, CHEN Li, HUANG Jiaoying. Modeling and Identification of Associated Complex Networks [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2012, 29(2): 308-316. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
