Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 535-546.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8733
Siheng XIONG1( ), Huanhuan DUAN2, Guomin CUI1,*(
), Huanhuan DUAN2, Guomin CUI1,*( ), Yuan XIAO1, Zhikang YI1
), Yuan XIAO1, Zhikang YI1
Received:2023-03-21
Online:2024-07-25
Published:2024-08-24
Contact:
Guomin CUI
CLC Number:
Siheng XIONG, Huanhuan DUAN, Guomin CUI, Yuan XIAO, Zhikang YI. Mass Exchange Network Mass Transfer Load Infeasibility Treatment and Dynamic Regulation Strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(4): 535-546.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8733
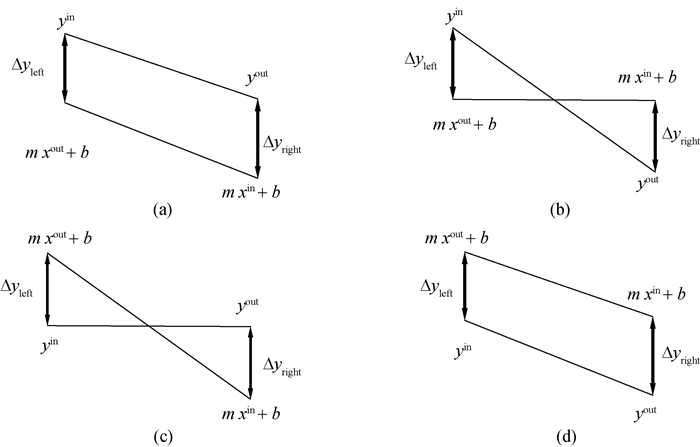
Fig.3 Four cases of mass transfer driving forces of the mass exchange unit (a) Δyleft > 0, Δyright > 0; (b) Δyleft > 0, Δyright < 0;(c) Δyleft < 0, Δyright > 0;(d) Δyleft < 0, Δyright < 0
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 0.9 | 0.07 | 0.000 3 | |||
| R2 | 0.1 | 0.051 | 0.000 1 | |||
| S1 | 2.3 | 0.000 6 | 0.031 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.004 |
| S2 | ∞ | 0.000 2 | 0.003 5 | 0.26 | 0 | 0.006 |
Table 1 Stream data of Case 1
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 0.9 | 0.07 | 0.000 3 | |||
| R2 | 0.1 | 0.051 | 0.000 1 | |||
| S1 | 2.3 | 0.000 6 | 0.031 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.004 |
| S2 | ∞ | 0.000 2 | 0.003 5 | 0.26 | 0 | 0.006 |
| IT/106 | C1 | C2 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
| 1 | 3 115 | 11 | 10 122 | 630 | 2 037 |
| 2 | 6 589 | 31 | 20 179 | 1 205 | 2 873 |
| 3 | 10 087 | 71 | 30 109 | 1 935 | 4 070 |
| 4 | 13 679 | 105 | 40 142 | 2 456 | 5 068 |
| 5 | 16 045 | 158 | 49 967 | 3 014 | 5 794 |
Table 2 Frequency of occurrence of two difference imperfect solutions
| IT/106 | C1 | C2 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
| 1 | 3 115 | 11 | 10 122 | 630 | 2 037 |
| 2 | 6 589 | 31 | 20 179 | 1 205 | 2 873 |
| 3 | 10 087 | 71 | 30 109 | 1 935 | 4 070 |
| 4 | 13 679 | 105 | 40 142 | 2 456 | 5 068 |
| 5 | 16 045 | 158 | 49 967 | 3 014 | 5 794 |
| 文献 | 单元数 | 总塔板数/块 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 5 | 25 | 313 292 | 431 613 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 326 700 | 422 293 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 24 | 311 297 | 420 545 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 20 | 317 986 | 412 500 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 314 114 | 409 704 |
| 5 | 21 | 314 777 | 410 369 | |
| 6 | 20 | 315 757 | 406 761 |
Table 3 Result comparison of Case 1
| 文献 | 单元数 | 总塔板数/块 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 5 | 25 | 313 292 | 431 613 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 326 700 | 422 293 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 24 | 311 297 | 420 545 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 20 | 317 986 | 412 500 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 314 114 | 409 704 |
| 5 | 21 | 314 777 | 410 369 | |
| 6 | 20 | 315 757 | 406 761 |
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 2 | 0.050 | 0.010 | |||
| R2 | 1 | 0.030 | 0.006 | |||
| S1 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| S2 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.030 | 1.53 | 0 | 0 |
| S3 | ∞ | 0.001 3 | 0.015 | 0.71 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
Table 4 Steam data of Case 2
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 2 | 0.050 | 0.010 | |||
| R2 | 1 | 0.030 | 0.006 | |||
| S1 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| S2 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.030 | 1.53 | 0 | 0 |
| S3 | ∞ | 0.001 3 | 0.015 | 0.71 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 文献 | 单元数 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | 投资费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 218 225 | 127 456 | 345 681 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 217 960 | 159 320 | 345 416 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 210 446 | 132 008 | 342 174 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 223 840 | 115 739 | 339 579 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 219 816 | 118 352 | 338 168 |
| 6 | 223 531 | 114 039 | 337 570 | |
| 8 | 198 453 | 138 018 | 336 471 |
Table 5 Result comparison of Case 2
| 文献 | 单元数 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | 投资费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 218 225 | 127 456 | 345 681 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 217 960 | 159 320 | 345 416 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 210 446 | 132 008 | 342 174 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 223 840 | 115 739 | 339 579 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 219 816 | 118 352 | 338 168 |
| 6 | 223 531 | 114 039 | 337 570 | |
| 8 | 198 453 | 138 018 | 336 471 |
| 1 |
SHORT M , ISAFIADE A J . Thirty years of mass exchanger network synthesis-A systematic review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 304, 127112.
DOI |
| 2 |
杨友麒. 质量交换网络[J]. 化工进展, 2007, 26 (2): 284- 289.
DOI |
| 3 |
薛东峰, 陈理, 袁一, 等. 质量交换网络综合[J]. 现代化工, 2001, 21 (6): 16-19, 21.
DOI |
| 4 |
WANG Bohong , ZHANG Sheng , GUO Lianghui , et al. Graphical approaches for cleaner production and sustainability in process systems[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 366, 132790.
DOI |
| 5 |
FARRAG N M , KAMEL D A , GHALLAB A O , et al. Graphical design and analysis of mass exchange networks using composition driving forces[J]. South African Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 36, 94- 104.
DOI |
| 6 | CHEN Chengliang , HUNG P S . Simultaneous synthesis of mass exchange networks for waste minimization[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2005, 29 (7): 1561- 1576. |
| 7 |
ISAFIADE A J , FRASER D M . Interval based MINLP superstructure synthesis of mass exchange networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2008, 86 (8): 909- 924.
DOI |
| 8 | 易智康, 崔国民, 周志强, 等. 棋盘模型同步优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40 (4): 500- 510. |
| 9 |
ZHOU Zhiqiang , CUI Guoming , XIAO Yuan . A novel node-based non-structural model for mass exchanger network synthesis using a stochastic algorithm[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 376, 134227.
DOI |
| 10 | GARRARD A , FRAGA E S . Mass exchange network synthesis using genetic algorithms[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 1998, 22 (12): 1837- 1850. |
| 11 |
李绍军, 阳永荣. 利用改进的遗传算法进行质量交换网络的最优综合[J]. 化工学报, 2002, (1): 60- 65.
DOI |
| 12 |
都健, 高志辉, 陈理, 等. 采用浓度差同步优化的质量交换网络设计[J]. 化工学报, 2007, (7): 1768- 1775.
DOI |
| 13 |
谢会, 史彬, 鄢烈祥, 等. 列队竞争算法综合质量交换网络[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2010, 27 (12): 1617- 1620.
DOI |
| 14 | TAO Shaohui , JIANG Mengmeng , LIU Mingyue , et al. a mixed discrete PSO algorithm for synthesis of mass exchange network with incompatible multicomponent[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2017, 61, 709- 714. |
| 15 | 马秀宝, 盖照亮, 崔国民, 等. 基于强制进化随机游走算法的质量交换网络综合[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39 (4): 479- 490. |
| 16 | 马秀宝, 崔国民, 周志强, 等. 带有个体淘汰的强制进化随机游走算法优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40 (3): 376- 388. |
| 17 |
XIAO Yuan , CUI Guomin . A novel random walk algorithm with compulsive evolution for heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 115, 1118- 1127.
DOI |
| 18 | PAPALEXANDRI K P , PISTIKOPOULOS E N , FLOUDAS A . Mass exchange networks for waste minimization: A simultaneous approach: Process design[J]. Chemical Engineering Research & Design, 1994, 72 (3): 279- 294. |
| 19 | YEE T F , GROSSMANN I E . Simultaneous optimization models for heat integration-Ⅱ. Heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 1990, 14 (10): 1165- 1184. |
| 20 |
XU Yue , KAYANGE H A , CUI Guomin . A nodes-based non-structural model considering a series structure for heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Processes, 2020, 8 (6): 695.
DOI |
| 21 |
SHENOY U V , FRASER D M . A new formulation of the Kremser equation for sizing mass exchangers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58 (22): 5121- 5124.
DOI |
| 22 |
EL-HALWAGI M M , MANOUSIOUTHAKIS V . Synthesis of mass exchange networks[J]. AIChE Journal, 1989, 35 (8): 1233- 1244.
DOI |
| 23 | AZEEZ O S , ISAFIADE A J , FRASER D M . Supply-based superstructure synthesis of heat and mass exchange networks[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2013, 56, 184- 201. |
| 24 | HALLALE N , FRASER D M . Capital and total cost targets for mass exchange networks: Part 1: Simple capital cost models[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2000, 23 (11/12): 1661- 1679. |
| 25 |
王江峰, 沈静珠, 李有润, 等. 多目标模糊评价遗传算法综合质量交换网络[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2002, 16 (5): 549- 554.
DOI |
| 26 | 高志辉. 费用最小的质量交换网络综合研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2007. |
| 27 | SINGH D , KHANAM S . Synthesis of mass exchanger network considering piping and pumping costs using process integration principles[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering & Process Technology, 2017, 8 (1): 1000322. |
| 28 | 侯创. 基于污染物排放最小化的化工工艺质量交换网络的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2020. |
| [1] | Zhikang YI, Guomin CUI, Zhiqiang ZHOU, Yuan XIAO, Siheng XIONG, Xiubao MA. A Chessboard Model for Simultaneous Optimization of Mass Exchange Networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 500-510. |
| [2] | Xiubao MA, Guomin CUI, Zhiqiang ZHOU, Yuan XIAO, Yue XU, Qiguo YANG. Optimizing Mass Exchange Network Using RWCE Algorithm with Individual Elimination [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(3): 376-388. |
| [3] | Xiu-bao MA, Zhao-liang GAI, Guo-min CUI, Zhi-qiang ZHOU, Xin-yu HAN, Qi-guo YANG. Mass Exchanger Network Synthesis Based on Random Walk Algorithm with Compulsive Evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(4): 479-490. |
| [4] | Zhengheng HAN, Guomin CUI, Weijie ZHANG, Qianqian ZHAO, Yuan XIAO, Guanhua ZHANG. Structural Diversity Analysis and Improved Optimization Strategy of Heat Exchanger Networks Based on NW-NSM Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(4): 479-488. |
| [5] | ZHANG Dingtai, CUI Guomin, LI Wanzong, XU Yue. Improved RWCE Algorithm with Integer/Continuous Variable Separation Optimization Strategy to Protect Efficient Structure [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2021, 38(1): 89-98. |
| [6] | JIN Yan, CUI Guomin, CAO Mei, SHEN Hao, CHEN Zihe. Improvement of Evolutionary Ability of Heat Exchange Network Structure with Periodic Advantage Structure Extraction and Search Path Enhancement [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(6): 725-733. |
| [7] | JIANG Yiwen, CUI Guomin, BAO Zhongkai, LIU Huolin, ZHOU Jinjia. A Heat Exchanger Network Optimization Strategy for Internal Utility Evolution [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(3): 341-351. |
| [8] | SU Geman, CUI Guomin, BAO Zhongkai, XIAO Yuan, CEN Zhenyu. Analysis and Treatment on Structures with Temperature Cross in Heat Exchanger Network [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(1): 107-118. |
| [9] | BAO Zhongkai, CUI Guomin, CAO Chong, REN Jie, LI Menghong. Heat Exchanger Network Optimization Based on Inner Utility Placement Strategy [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(6): 707-718. |
| [10] | LI Jian, CUI Guomin, CHEN Jiaxing, XIAO Yuan. Simultaneous Synthesis of Heat Exchanger Network by Random Walk Algorithm with Compulsive Evolution Based on Trilevel Protection Strategy [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(1): 69-79. |
| [11] | DENG Weidong, CUI Guomin, XIAO Yuan. A Coupled Evolutionary Strategy for Complex Heat Exchanger Network Optimization [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(6): 675-684. |
| [12] | ZHU Yushuang, CUI Guomin, XIAO Yuan, CHEN Jiaxing. A Random Walk Algorithm with Compulsive Evolution Combined with Restrictive-evolution Strategy for Heat Unit in Heat Exchanger Network Synthesis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(5): 593-602. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
