计算物理 ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 6-16.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8342
收稿日期:2021-02-10
出版日期:2022-01-25
发布日期:2022-09-03
通讯作者:
李茂生
作者简介:李宏明(1993-),男,河南信阳,硕士研究生,主要从事晶体塑性有限元模拟研究,E-mail: lihongming18@gscaep.ac.cn
基金资助:
Hongming LI1( ), Maosheng LI2,*(
), Maosheng LI2,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-10
Online:2022-01-25
Published:2022-09-03
Contact:
Maosheng LI
摘要:
将辐照硬化理论与晶体塑性理论结合, 运用ABAQUS有限元分析软件模拟辐照后多晶铜的拉伸过程。分析辐照效应对材料屈服强度、硬化过程、晶体变形等力学性能的影响, 研究位错密度的演化及空间分布规律。数值模拟表明: 辐照效应提高多晶铜的屈服应力, 影响不同阶段的硬化和软化现象; 辐照剂量增大导致位错密度增殖总体变缓, 空间不均匀度增大; 晶体的塑性变形及晶体转动也受到辐照的影响, 在相同的应变条件下, 辐照剂量越大, 晶体塑性变形程度越小, 塑性变形分布不均匀度变大, 同时晶体转动程度及转动角离散度增大。
李宏明, 李茂生. 晶体塑性有限元方法研究辐照对多晶铜力学性能的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(1): 6-16.
Hongming LI, Maosheng LI. Effect of Irradiation on Mechanical Properties of Polycrystalline Copper: Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(1): 6-16.
| 参量 | 符号 | 含义 | 值 | 单位 |
| k1 | 位错增殖系数 | 2×109 | m-1 | |
| χ | 相互作用参数 | 0.9 | ||
| Kocks-Mecking参数 | g | 归一化激活能 | 0.15 | |
| kB | 玻尔兹曼常数 | 1.38×10-23 | J·K-1 | |
| D | 拖曳力 | 2.5×108 | Pa | |
| 参考应变率 | 1×107 | s-1 | ||
| η | 辐照缺陷湮灭效率 | 20 | ||
| hn | 位错相互作用自硬化系数 | 0.5 | ||
| hd | 位错与缺陷相互作用系数 | 0.25 | ||
| 可调系数 | τ0 | 晶格固有阻力 | 0 | Pa |
| m | 敏感因子 | 0.1 | ||
| 参考剪切应变率 | 0.001 | s-1 | ||
| pann | 缺陷湮灭概率 | 4.2811×10-4 |
表1 物性参数
Table 1 Physical parameters
| 参量 | 符号 | 含义 | 值 | 单位 |
| k1 | 位错增殖系数 | 2×109 | m-1 | |
| χ | 相互作用参数 | 0.9 | ||
| Kocks-Mecking参数 | g | 归一化激活能 | 0.15 | |
| kB | 玻尔兹曼常数 | 1.38×10-23 | J·K-1 | |
| D | 拖曳力 | 2.5×108 | Pa | |
| 参考应变率 | 1×107 | s-1 | ||
| η | 辐照缺陷湮灭效率 | 20 | ||
| hn | 位错相互作用自硬化系数 | 0.5 | ||
| hd | 位错与缺陷相互作用系数 | 0.25 | ||
| 可调系数 | τ0 | 晶格固有阻力 | 0 | Pa |
| m | 敏感因子 | 0.1 | ||
| 参考剪切应变率 | 0.001 | s-1 | ||
| pann | 缺陷湮灭概率 | 4.2811×10-4 |
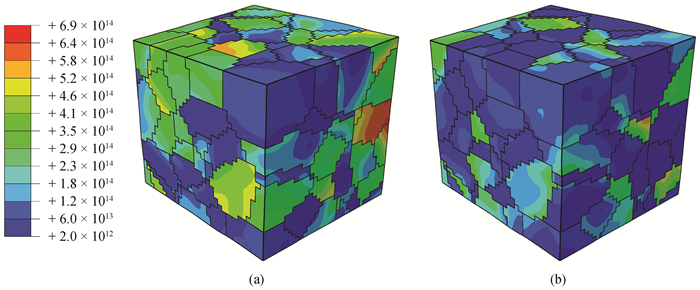
图3 无辐照时位错密度云图(a) (1 1 1)[0-1 1]滑移系位错;(b) (-1 1 1)[1 1 0]滑移系位错
Fig.3 Contour plots of dislocation density without irradiation (a) (1 1 1)[0-1 1]slip system dislocation; (b) (-1 1 1)[1 1 0]slip system dislocation
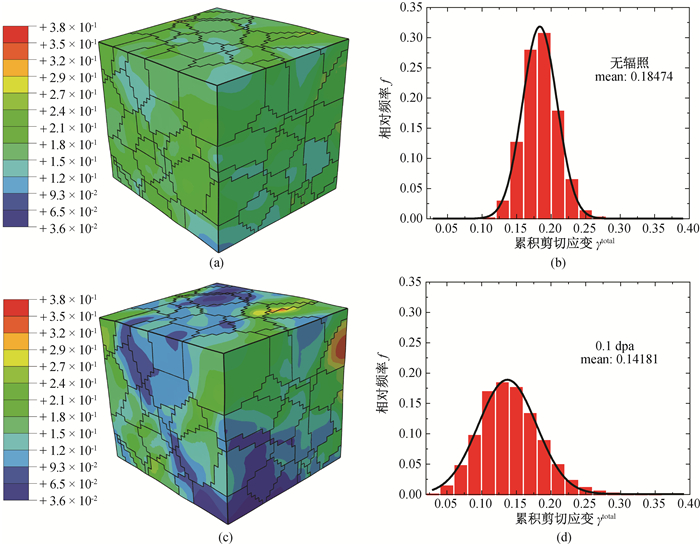
图6 累积剪切应变分布云图及频率统计直方图(a) 无辐照;(b) 无辐照;(c) 0.1 dpa;(d) 0.1 dpa
Fig.6 Contour plots and frequency statistics of cumulative shear strain distribution (a) no irradiation; (b) no irradiation; (c) 0.1 dpa; (d) 0.1 dpa

图8 不同辐照剂量下,晶体取向差云图(a) 无辐照;(b) 0.005 dpa;(c) 0.01 dpa;(d) 0.1 dpa
Fig.8 Contour plots of misorientation under different irradiation doses (a) no irradiation; (b) 0.005 dpa; (c) 0.01 dpa; (d) 0.1 dpa
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
DOI |
| 35 |
DOI |
| 36 |
DOI |
| 37 |
|
| [1] | 侯兆阳, 牛媛, 肖启鑫, 王真, 邓庆田. Al纳米线不同晶向力学行为和变形机制的模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(3): 341-351. |
| [2] | 郭怀民, 赵国忠, 姜丽娟. 磁电弹性体中螺型位错与唇口裂纹的相互作用[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(1): 33-40. |
| [3] | 郭怀民, 赵国忠. 磁电弹性体中多条位错与Griffith裂纹[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 198-204. |
| [4] | 高英俊, 杨瑞琳, 黄礼琳, 刘瑶. 纳观尺度裂纹扩展微观机理的晶体相场法研究[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 453-460. |
| [5] | 祁美玲, 杨琼, 王苍龙, 田园, 杨磊. 结构材料辐照损伤的分子动力学程序GPU并行化及优化[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 461-467. |
| [6] | 杨忠华, 刘贵立, 曲迎东, 李荣德. N掺杂碳纳米管环吸附Fe原子的第一性原理研究[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(3): 374-378. |
| [7] | 吴军来, 刘月田, 罗婕. 裂缝性应力敏感油藏流固耦合的数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2014, 31(4): 455-464. |
| [8] | 王瑞利, 林忠, 魏兰. 针对流体大变形问题网格邻域可变技术[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(4): 501-506. |
| [9] | 庞卫卫, 张广财, 许爱国, 卢果. 面心立方铜晶体中空洞生长与贯通的尺寸效应[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(4): 540-546. |
| [10] | 卢果, 方步青, 张广财. 基于连续介质位错理论的位错原子分布构造方法[J]. 计算物理, 2010, 27(2): 195-202. |
| [11] | 张秋葵, 罗立民. 一种抗单元逆转的软组织有限元模型[J]. 计算物理, 2009, 26(2): 169-174. |
| [12] | 王兵, 许厚谦. 含有大位移动边界的复杂流场的数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(4): 396-400. |
| [13] | 王超营, 孟庆元, 李成祥, 钟康游, 杨志伏. Si中30度部分位错弯结运动特性的分子模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(4): 488-492. |
| [14] | 马晓丹, 同登科, 马华伟. 变形双重介质分形油藏非达西流动分析[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24(2): 197-202. |
| [15] | 勇珩, 袁国兴, 裴文兵, 古培俊. 空腔靶大变形问题的网格构造[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24(1): 1-6. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
