计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 189-198.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8619
所属专题: 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊
• 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊 • 上一篇 下一篇
李志远( ), 李纪伟*(
), 李纪伟*( ), 王立锋, 戴振生, 谷建法, 何民卿, 吴俊峰, 叶文华, 贺贤土
), 王立锋, 戴振生, 谷建法, 何民卿, 吴俊峰, 叶文华, 贺贤土
收稿日期:2022-08-16
出版日期:2023-03-25
发布日期:2023-07-05
通讯作者:
李纪伟
作者简介:李志远,男,博士,助理研究员,研究方向为流体力学不稳定性和计算流体力学,E-mail:li_zhiyuan@iapcm.ac.cn
基金资助:
Zhiyuan LI( ), Jiwei LI*(
), Jiwei LI*( ), Lifeng WANG, Zhensheng DAI, Jianfa GU, Minqing HE, junfeng WU, Wenhua YE, Xiantu HE
), Lifeng WANG, Zhensheng DAI, Jianfa GU, Minqing HE, junfeng WU, Wenhua YE, Xiantu HE
Received:2022-08-16
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-07-05
Contact:
Jiwei LI
摘要:
研究针对混驱点火模型, 保持直驱激光能量不变, 针对1 200, 1 400和1 500 μm直驱光焦斑尺寸, 采用数值模拟, 研究其对点火性能的影响。研究表明: 直驱光焦斑尺寸是影响混驱点火性能的敏感因素。1 500 μm焦斑尺寸可实现近一维点火。1 400 μm焦斑尺寸放能接近一维放能的40%。1 200 μm焦斑尺寸点火失败, 仅仅处于燃烧等离子体状态。分析表明, 1 200 μm焦斑尺寸条件下点火失败的原因是: 其产生的局部强光强和高驱动不对称性, 会导致燃料熵增加及燃料面密度扰动增加。燃料熵的增加将会降低燃料压缩性, 不利于创造高温高压点火条件, 形成的燃烧波较弱。燃料面密度扰动增加会导致燃烧后壳层不稳定性剧烈增长。推断在小焦斑尺寸条件下, 弱燃烧波及高燃料面密度扰动增长, 会导致高密度尖钉难以被有效点燃, 无法形成升温与燃烧的正反馈。同时, 燃料区域内界面不稳定性发展产生的尖钉结构将降低热斑温度, 产生的气泡结构将引起热斑体积迅速变大, 导致热斑快速降温乃至点火失败。
李志远, 李纪伟, 王立锋, 戴振生, 谷建法, 何民卿, 吴俊峰, 叶文华, 贺贤土. 混合驱动中直驱激光焦斑尺寸对点火性能的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(2): 189-198.
Zhiyuan LI, Jiwei LI, Lifeng WANG, Zhensheng DAI, Jianfa GU, Minqing HE, junfeng WU, Wenhua YE, Xiantu HE. Impacts of Direct Drive Laser Focal Spot Size on Ignition Performance of Hybrid Drive Inertial Confinement Fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(2): 189-198.
| timp/ns | Vimp/(km · s-1) | Adiabat | Bangtime/ns | Stagnation time/ns | at the stagnation time | Neutron yield | Yield/MJ | ||
| Phs/Gbar | Tihs/keV | ρRfuel/(g · cm-2) | |||||||
| 7.72 | 445 | 3.7 | 7.98 | 7.95 | 1 069 | 8.7 | 1.04 | 7.08 × 1018 | 20 |
表1 一维内爆参数
Table 1 One dimensional implosion parameters
| timp/ns | Vimp/(km · s-1) | Adiabat | Bangtime/ns | Stagnation time/ns | at the stagnation time | Neutron yield | Yield/MJ | ||
| Phs/Gbar | Tihs/keV | ρRfuel/(g · cm-2) | |||||||
| 7.72 | 445 | 3.7 | 7.98 | 7.95 | 1 069 | 8.7 | 1.04 | 7.08 × 1018 | 20 |
| 焦斑尺寸/μm | timp/ns | Vimp/(km·s-1) | Adiabat | Bangtime/ns | Stagnation time/ns | at the stagnation time | Neutron yield | Yield/MJ | ||
| Phs/Gbar | Tihs/keV | ρRfuel/(g·cm-2) | ||||||||
| 1 200 | 7.68 | 423 | 5.37 | 7.98 | 7.97 | 312 | 4.57 | 0.9 | 6.80 × 1016 | 0.192 |
| 1 400 | 7.7 | 430 | 4.05 | 8.03 | 7.97 | 516 | 5.94 | 0.96 | 2.89 × 1018 | 8.14 |
| 1 500 | 7.75 | 439 | 3.74 | 8.02 | 7.99 | 934 | 7.34 | 1.14 | 7.00 × 1018 | 19.90 |
| 1D | 7.72 | 445 | 3.7 | 7.98 | 7.95 | 1 069 | 8.7 | 1.04 | 7.08 × 1018 | 20.00 |
表2 二维平均内爆参数
Table 2 Two-dimensional implosion parameters
| 焦斑尺寸/μm | timp/ns | Vimp/(km·s-1) | Adiabat | Bangtime/ns | Stagnation time/ns | at the stagnation time | Neutron yield | Yield/MJ | ||
| Phs/Gbar | Tihs/keV | ρRfuel/(g·cm-2) | ||||||||
| 1 200 | 7.68 | 423 | 5.37 | 7.98 | 7.97 | 312 | 4.57 | 0.9 | 6.80 × 1016 | 0.192 |
| 1 400 | 7.7 | 430 | 4.05 | 8.03 | 7.97 | 516 | 5.94 | 0.96 | 2.89 × 1018 | 8.14 |
| 1 500 | 7.75 | 439 | 3.74 | 8.02 | 7.99 | 934 | 7.34 | 1.14 | 7.00 × 1018 | 19.90 |
| 1D | 7.72 | 445 | 3.7 | 7.98 | 7.95 | 1 069 | 8.7 | 1.04 | 7.08 × 1018 | 20.00 |
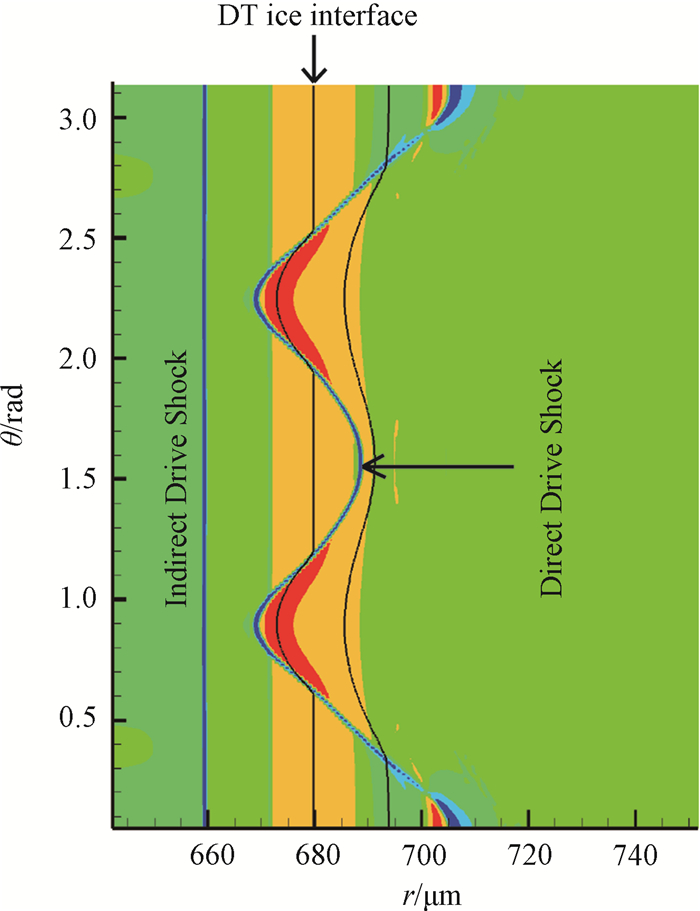
图7 1 200 μm焦斑尺寸条件下间驱冲击波进入DT气体区时冲击波位置图
Fig.7 The shock waves' contour when the indirect drive shock comes into the DT gas region under the condition of 1 200 μm focal spot radius

图8 三个焦斑尺寸条件下离子温度和热斑质量随热斑面密度变化曲线
Fig.8 The relationship between the ion temperature and the hotspot areal density and the relationship between the hotspot mass and the hotspot areal density under the different focal spot radius
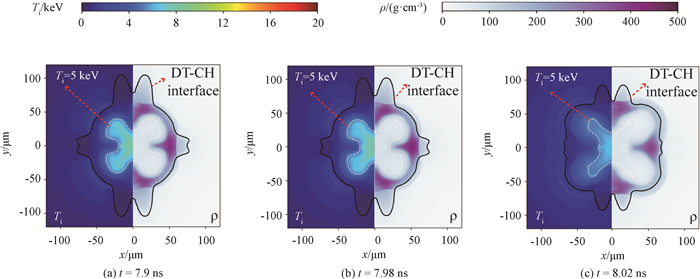
图9 1 200 μm焦斑尺寸条件下燃料层和热斑密度温度分布
Fig.9 The ion temperature contour and the density contour of the fuel and hotspot under the condition of 1 200 μm focal spot radius

图10 (a) 1 400 μm和(b) 1 500 μm焦斑尺寸壳层和热斑密度温度分布
Fig.10 The ion temperature contour and the density contour of the fuel and hotspot (a) 1 400 μm; (b) 1 500 μm
| timp/ns | Vimp/(km · s-1) | Adiabat | Bangtime/ns | Stagnation time/ns | at the stagnation time | Neutron yield | Yield/MJ | ||
| Phs/Gbar | Tihs/keV | ρRfuel/(g · cm-2) | |||||||
| 7.88 | 420 | 3.35 | 8.17 | 8.12 | 609 | 5.9 | 1.18 | 4.9 × 1018 | 13.8 |
表3 优化设计靶内爆参数
Table 3 Implosion parameters of the optimized design
| timp/ns | Vimp/(km · s-1) | Adiabat | Bangtime/ns | Stagnation time/ns | at the stagnation time | Neutron yield | Yield/MJ | ||
| Phs/Gbar | Tihs/keV | ρRfuel/(g · cm-2) | |||||||
| 7.88 | 420 | 3.35 | 8.17 | 8.12 | 609 | 5.9 | 1.18 | 4.9 × 1018 | 13.8 |
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| [1] | 李纪伟, 王立锋, 李志远, 陈耀桦, 许琰, 何民卿, 李斌, 吴俊峰, 叶文华, 贺贤土. 混合驱动下高熵高内爆速度中心点火靶设计[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(2): 181-188. |
| [2] | 谷建法, 葛峰峻, 戴振生, 康洞国, 邹士阳. 氘氘冰层贯穿性缺陷对ICF冷冻靶内爆性能的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(3): 268-276. |
| [3] | 谷建法, 葛峰峻, 戴振生, 邹士阳. 靶丸支撑膜对ICF内爆性能影响的模拟研究[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(6): 631-638. |
| [4] | 于承新, 范征锋, 刘杰, 贺贤土. 惯性约束聚变中内爆混合的模型构建[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 379-386. |
| [5] | 谷建法, 戴振生, 古培俊, 叶文华, 郑无敌, 邹士阳. 点火靶驱动不对称性与表面粗糙度的模耦合模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(6): 645-651. |
| [6] | 谷建法, 戴振生, 叶文华, 古培俊, 郑无敌. 点火靶高熵内爆的数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2015, 32(6): 662-668. |
| [7] | 李欣, 吴畅书, 邹士阳, 赵益清, 李敬宏, 古培俊, 郑无敌, 裴文兵. 点火黑腔二维模拟设计[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(3): 371-378. |
| [8] | 李树, 田东风, 邓力. 利用超高能中子诊断惯性约束聚变的燃烧[J]. 计算物理, 2012, 29(1): 82-86. |
| [9] | 曾清红, 裴文兵, 成娟, 勇珩. 多块结构网格上的Kershaw扩散格式[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(5): 641-648. |
| [10] | 李寿佛, 叶文华, 张瑗, 舒适, 肖爱国. 高阶FD-WENO格式在数值求解Rayleigh-Taylor不稳定性问题中的应用[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(4): 379-386. |
| [11] | 葛全文. 惯性约束聚变激光烧蚀驱动内界面不稳定性数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2004, 21(3): 294-304. |
| [12] | 齐进, 叶文华. 三维激光烧蚀瑞利-泰勒不稳定性并行计算[J]. 计算物理, 2002, 19(5): 388-392. |
| [13] | 陈光南, 常铁强, 张钧, 张兴宏, 裴文兵, 尤希文. 激光与靶非平衡耦合的数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 1998, 15(4): 409-418. |
| [14] | 叶文华, 张维岩, 陈光南, 晋长秋, 张钧. Rayleigh-Taylor和Richtmyer-Meshkov不稳定性的FCT方法数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 1998, 15(3): 277-282. |
| [15] | 江少恩, 刘忠礼, 李楠, 郑志坚, 唐道源, 丁永坤, 胡昕. 惯性约束聚变靶三维成象数值研究[J]. 计算物理, 1997, 14(3): 361-367. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
