计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 770-778.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8653
收稿日期:2022-10-18
出版日期:2023-11-25
发布日期:2024-01-22
通讯作者:
邹艳丽
作者简介:邵贝贝(1995-), 女, 安徽阜阳人, 硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为智能电网优化控制, E-mail: 3087498355@qq.com
基金资助:
Beibei SHAO( ), Yanli ZOU(
), Yanli ZOU( ), Shaoyan HONG, Chanjuan LIANG
), Shaoyan HONG, Chanjuan LIANG
Received:2022-10-18
Online:2023-11-25
Published:2024-01-22
Contact:
Yanli ZOU
摘要:
为探究较优的电网结构, 减小Braess悖论现象的发生概率, 采用二阶类Kuramoto相振子模型对电网进行合理建模, 参照IEEE14、IEEE30和IEEE39标准测试网络的拓扑结构, 保留网络节点数和连边数不变, 采用ER随机模型生成同样大小的随机网络。通过在随机网络中增加发电机节点个数, 改变发电机位置等方式, 研究不同结构下电网中新增传输线路导致的Braess悖论发生概率。研究表明: 适当增加电网中发电机节点个数可以减少电网中Braess悖论发生概率, 且以大度节点作为发电机节点有利于提高电网同步能力, 降低Braess悖论发生概率。本研究对电网的拓扑设计和优化具有一定指导意义。
中图分类号:
邵贝贝, 邹艳丽, 洪少燕, 梁婵娟. 基于复杂网络拓扑的电网Braess悖论现象研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(6): 770-778.
Beibei SHAO, Yanli ZOU, Shaoyan HONG, Chanjuan LIANG. Study on Braess Paradox of Power Grid Based on Complex Network Topology[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(6): 770-778.
| 新增传输线路编号 | 稳态频偏 | 临界同步耦合强度 |
| 原网络 | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| (1, 3) | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| (1, 4) | 0.0 | 2.2 |
| (2, 7) | 2.6 | 2.4 |
| (3, 10) | 2.6 | 2.5 |
| (3, 14) | 0.0 | 2.2 |
| (5, 8) | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| (5, 11) | 2.6 | 2.5 |
| (6, 8) | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| (8, 14) | 0.0 | 1.9 |
表1 IEEE14系统原网络及新增部分传输线路后网络的稳态频偏和临界同步耦合强度
Table 1 The steady state frequency offset and the critical synchronous coupling strength of the original network of IEEE14 system and the network after the addition of some transmission lines
| 新增传输线路编号 | 稳态频偏 | 临界同步耦合强度 |
| 原网络 | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| (1, 3) | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| (1, 4) | 0.0 | 2.2 |
| (2, 7) | 2.6 | 2.4 |
| (3, 10) | 2.6 | 2.5 |
| (3, 14) | 0.0 | 2.2 |
| (5, 8) | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| (5, 11) | 2.6 | 2.5 |
| (6, 8) | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| (8, 14) | 0.0 | 1.9 |
| 系统 | 总节点数 | 连边数 | 网络节点平均度 |
| IEEE14 | 14 | 20 | 2.857 1 |
| IEEE30 | 30 | 41 | 2.733 3 |
| IEEE39 | 39 | 46 | 2.359 0 |
表2 三种标准测试系统特性参数
Table 2 Three kinds of standard test system characteristics parameters
| 系统 | 总节点数 | 连边数 | 网络节点平均度 |
| IEEE14 | 14 | 20 | 2.857 1 |
| IEEE30 | 30 | 41 | 2.733 3 |
| IEEE39 | 39 | 46 | 2.359 0 |
| 14节点网络 | ||||
| 发电机节点个数 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| 负载节点个数 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
表3 14节点的网络中发电机和负载节点个数分配表
Table 3 Allocation of the number of generators and load nodes in a 14-node network
| 14节点网络 | ||||
| 发电机节点个数 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| 负载节点个数 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 7 |
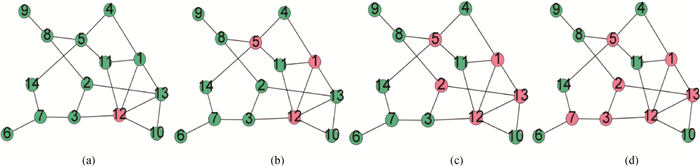
图2 大度节点作为发电机的网络拓扑图, (a)、(b)、(c)、(d)对应网络含1个、3个、5个、7个发电机节点
Fig.2 Topology of large degree nodes as generators (a), (b), (c) and (d) corresponding to a network with one, three, five and seven generator nodes, respectively
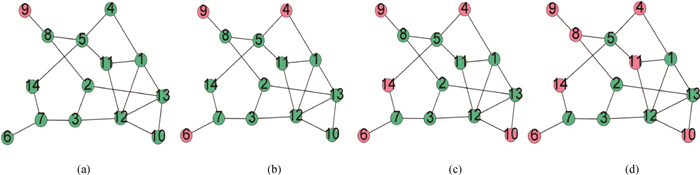
图3 小度节点作为发电机的网络拓扑图, (a)、(b)、(c)、(d)对应网络分别含1个、3个、5个、7个发电机节点
Fig.3 Topology of small degree nodes as generators, (a), (b), (c) and (d) corresponding to a network with one, three, five and seven generator nodes, respectively

图4 14节点网络新增一条传输线路后Kc增加、减小或者保持不变时的线路比例随发电机节点个数变化(a)14节点网络中大度节点作为发电机;(b)14节点网络中小度节点作为发电机
Fig.4 The proportion of lines with Kc increasing, decreasing or unchanging after adding a new transmission line to a 14-node network varies with the number of generator nodes (a) large degree nodes as generators in a 14-node network; (b) small degree nodes as generators in a 14-node network
| 30节点网络 | ||||
| 发电机节点个数 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 15 |
| 负载节点个数 | 27 | 25 | 23 | 15 |
表4 30节点的网络中发电机和负载节点个数分配表
Table 4 Allocation of the number of generators and load nodes in a 30-node network
| 30节点网络 | ||||
| 发电机节点个数 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 15 |
| 负载节点个数 | 27 | 25 | 23 | 15 |
| 39节点网络 | ||||
| 发电机节点个数 | 3 | 7 | 12 | 19 |
| 负载节点个数 | 36 | 32 | 27 | 20 |
表5 39节点的网络中发电机和负载节点个数分配表
Table 5 Allocation of the number of generators and load nodes in a 39-node network
| 39节点网络 | ||||
| 发电机节点个数 | 3 | 7 | 12 | 19 |
| 负载节点个数 | 36 | 32 | 27 | 20 |
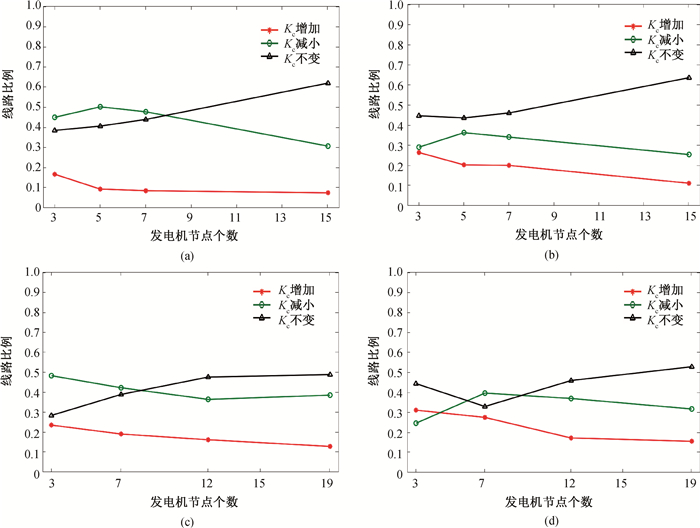
图5 30和39节点网络新增一条传输线路后Kc增加、减小或者保持不变的线路比例随发电机节点个数的变化(a)30节点网络中大度节点作为发电机;(b)30节点网络中小度节点作为发电机;(c)39节点网络中大度节点作为发电机;(d)39节点网络中小度节点作为发电机
Fig.5 The proportion of lines with Kc increasing, decreasing or unchanging after adding a new transmission line to a 30-node or a 39-node network varies with the number of generator nodes (a)large degree nodes as generators in a 30-node network; (b)small degree nodes as generators in a 30-node network; (c)large degree nodes as generators in a 39-node network; (d)small degree nodes as generators in a 39-node network
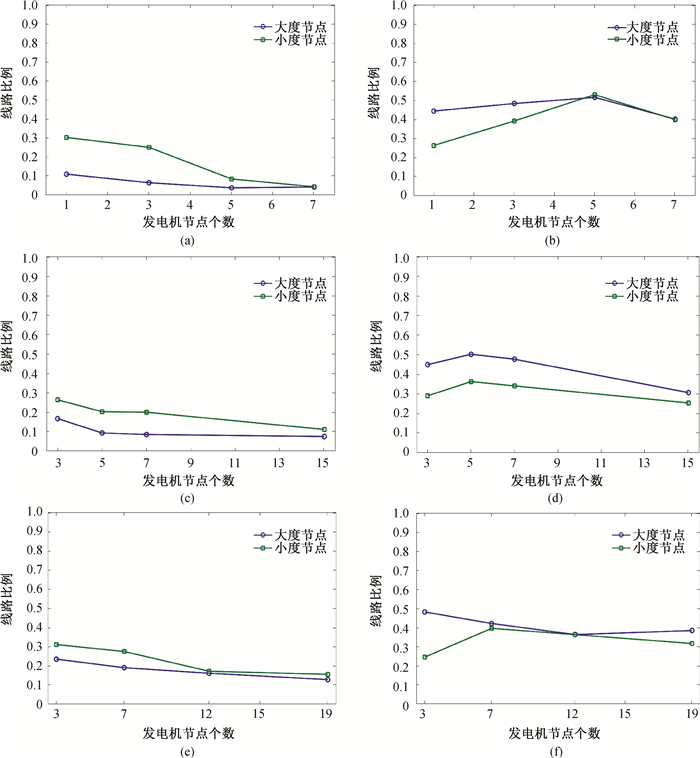
图6 14、30、39节点网络中分别以大度节点和小度节点作为发电机新增一条传输线路后Kc增加和减小的线路比例随发电机个数的变化(a)、(c)、(e)表示Kc增加的线路比例;(b)、(d)、(f)表示Kc减小的线路比例;((a)、(b)为14节点网络;(c)、(d)为30节点网络;(e)、(f)为39节点网络)
Fig.6 The proportion of lines with Kc increasing and decreasing varies with the number of generators after adding a new transmission line in 14, 30, and 39-node networks, where generators are on large degree nodes or small degree nodes, respectively (a), (c) and (e) denote the proportion of lines with Kc increasing; (b), (d) and (f)denote the proportion of lines with Kc deceasing ((a) and (b)14-node network. (c) and (d)30-node network. (e) and (f)39-node network)
| 1 |
BRAESS D . Vber ein paradoxon aus der verkehrsplanung[J]. Mathematical Methods of Operational Research, 1968, 12 (1): 258- 268.
DOI |
| 2 | ZHAO C X . Braess' paradox and robustness of traffic network under dynamic equilibrium[J]. WSEAS Transactions on Systems and Control, 2017, 12, 288- 296. |
| 3 |
赵春雪, 傅白白, 王天明. 拥挤交通网络的Braess'悖论现象[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2012, 12 (4): 155- 160.
DOI |
| 4 |
MA J , LI D W , C L , et al. Link restriction: Methods of testing and avoiding Braess paradox in networks considering traffic demands[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2018, 144 (2): 04017076.
DOI |
| 5 |
WANG A H , TANG Y H , MOHMAND Y T , et al. Modifying link capacity to avoid Braess paradox considering elastic demand[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2022, 605, 127951.
DOI |
| 6 |
COLETTA T , JACQUOD P . Linear stability and the Braess paradox in coupled Oscillators networks and electric power grids[J]. Physical Review E, 2016, 93 (3): 032222.
DOI |
| 7 | 张玥, 谢光龙, 张全, 等. 美国得州2 ·15大停电事故分析及对中国电力发展的启示[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (4): 192-198+206. |
| 8 | 卢恩, 鲁晓军, 龙霏, 等. 电力系统停电风险评估指标及方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2015, 35 (3): 68- 74. |
| 9 | WITTHAUT D , TIMME M . Nonlocal failures in complex supply networks by single link additions[J]. The European Physical Journal B, 2013, 86 (9): 1- 12. |
| 10 |
CHAO Y , YI C , LI P , et al. Impact of the network structure on transmission dynamics in complex networks[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2013, 46 (13): 218- 223.
DOI |
| 11 |
CETINAY H , KUIPERS F A , Van MIEGHEM P . A topological investigation of power flow[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12 (3): 2524- 2532.
DOI |
| 12 |
FAZLYAB M , DÖRFLER F , PRECIADO V M . Optimal network design for synchronization of coupled oscillators[J]. Automatica, 2017, 84, 181- 189.
DOI |
| 13 |
TCHAWOU T E B , GOMILA D , PERE C , et al. Curing Braess' paradox by secondary control in power grids[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2018, 20 (8): 083005.
DOI |
| 14 |
YANG L X , JIANG J , LIU X J . Influence of edge additions on the synchronizability of oscillatory power networks[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2016, 41, 11- 18.
DOI |
| 15 |
YANG L X , JIANG J . Impacts of link addition and removal on synchronization of an elementary power network[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2017, 479, 99- 107.
DOI |
| 16 | KAISER F N. Resilience of power grids and other supply networks: Structural stability, cascading failures and optimal topologies[D]. Koln: Universität zu Köln, 2022. |
| 17 |
ZOU Y L , WANG R R , GAO Z . Improve synchronizability of a power grid through power allocation and topology adjustment[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2020, 548, 122956.
DOI |
| 18 |
ZOU Y L , L H Q . Study on power grid partition and attack strategies based on complex networks[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2022, 9, 790218.
DOI |
| 19 | 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣. 复杂网络理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006. |
| 20 | 蔡泽祥, 王星华, 任晓娜. 复杂网络理论及其在电力系统中的应用研究综述[J]. 电网技术, 2012, 36 (11): 114- 121. |
| 21 | 魏震波, 苟竞. 复杂网络理论在电网分析中的应用与探讨[J]. 电网技术, 2015, 39 (1): 279- 287. |
| 22 | LI H Q , ZOU Y L , ZHANG S Z , et al. Robustness of power grids structure and braess paradox phenomenon: A complex network theory study[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38 (4): 470- 478. |
| 23 | ZOU Y L , WANG R R , WU L J , et al. Optimization of synchronization performance in power grids with local order parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 36 (4): 498- 504. |
| 24 | FILATRELLA G , NIELSEN A H , PEDERSEN N F . Analysis of a power grid using a Kuramoto-like model[J]. European Physical Journal B Condensed Matter, 2008, 61 (4): 485- 491. |
| 25 | ZHANG S Z , ZOU Y L , TAN S Y , et al. Study of Braess paradox in an interconnected power grid based on complex network theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39 (2): 233- 243. |
| 26 | GILBERT E N . Random graphs[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1959, 30 (4): 1141- 1144. |
| [1] | 付韬, 邬龙, 李晨光. 基于生成函数方法的现实网络座键渗流建模[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 212-222. |
| [2] | 张少泽, 邹艳丽, 谭秫毅, 李浩乾, 刘欣妍. 基于复杂网络理论的互联电网Braess悖论现象分析[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 233-243. |
| [3] | 李浩乾, 邹艳丽, 张少泽, 刘欣妍, 谭秫毅. 基于复杂网络的电网结构健壮性及Braess悖论现象研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 470-478. |
| [4] | 王意, 邹艳丽, 黄李, 李可. 综合考虑局部和全局特性的电网关键节点识别[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(1): 119-126. |
| [5] | 安海岗. 基于复杂网络的时间序列双变量联动波动[J]. 计算物理, 2014, 31(6): 742-750. |
| [6] | 王晓霞, 赵立华, 邹平华, 高云飞. 基于图论的空间热网拓扑结构[J]. 计算物理, 2014, 31(2): 207-215. |
| [7] | 范文礼, 刘志刚. 一种基于效率矩阵的网络节点重要度评价算法[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(5): 714-719. |
| [8] | 唐圣学, 陈丽, 黄姣英. 关联复杂网络建模及辨识研究[J]. 计算物理, 2012, 29(2): 308-316. |
| [9] | 党会学, 陈志敏, 杨智春. 不同分离距离的涡对融合[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(3): 259-262. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
