计算物理 ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 233-243.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8387
收稿日期:2021-04-28
出版日期:2022-03-25
发布日期:2022-06-24
通讯作者:
邹艳丽
作者简介:张少泽(1995-),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为复杂网络理论及其应用
基金资助:
Shaoze ZHANG, Yanli ZOU*( ), Shuyi TAN, Haoqian LI, Xinyan LIU
), Shuyi TAN, Haoqian LI, Xinyan LIU
Received:2021-04-28
Online:2022-03-25
Published:2022-06-24
Contact:
Yanli ZOU
摘要:
为了探究互联电力网络中的Braess悖论现象, 采用二阶类Kuramoto相振子模型对电网进行动力学建模, 将两个子网通过大度节点相连构建互联电网。当两个子网间有功率传输时, 分别在两个子网内部新增传输线路探究互联电网发生Braess悖论现象的概率并分析其原因。研究发现: 当互联电网中两个子网间的功率传输达到某一临界值时, 受电子网的同步能力远优于供电子网的同步能力, 供电子网新增传输线路引起互联电网发生Braess悖论的概率远高于受电子网新增传输线路引发的Braess悖论概率。通过定义子网序参数对上述现象的产生进行深入分析。本研究对互联电网的拓扑优化具有重要意义。
张少泽, 邹艳丽, 谭秫毅, 李浩乾, 刘欣妍. 基于复杂网络理论的互联电网Braess悖论现象分析[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 233-243.
Shaoze ZHANG, Yanli ZOU, Shuyi TAN, Haoqian LI, Xinyan LIU. Analysis of Braess Paradox in an Interconnected Power Grid Based on Complex Network Theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(2): 233-243.
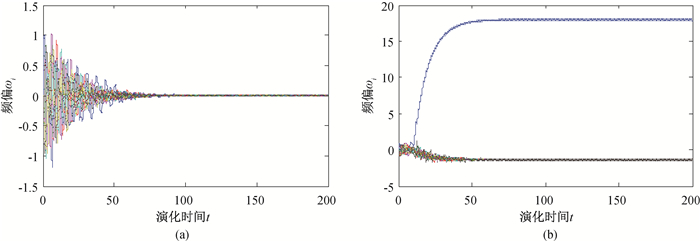
图1 IEEE14系统原网络及新增传输线路后网络频偏随时间的演化(a)原网络;(b)新增(1, 11)传输线路后网络
Fig.1 Frequency offset evolution of the original network of IEEE14 system and the network adding a new transmission line (a) original network; (b) network adding (1, 11) transmission line
| 网络 | 稳态频偏 |
| 原网络 | 0.00 |
| 新增(1, 11)传输线路 | 2.57 |
表1 IEEE14系统原网络及新增(1, 11)传输线路后网络的稳态频偏
Table 1 Steady state frequency offset of the original network and the network adding (1, 11) transmission line in IEEE14 system
| 网络 | 稳态频偏 |
| 原网络 | 0.00 |
| 新增(1, 11)传输线路 | 2.57 |
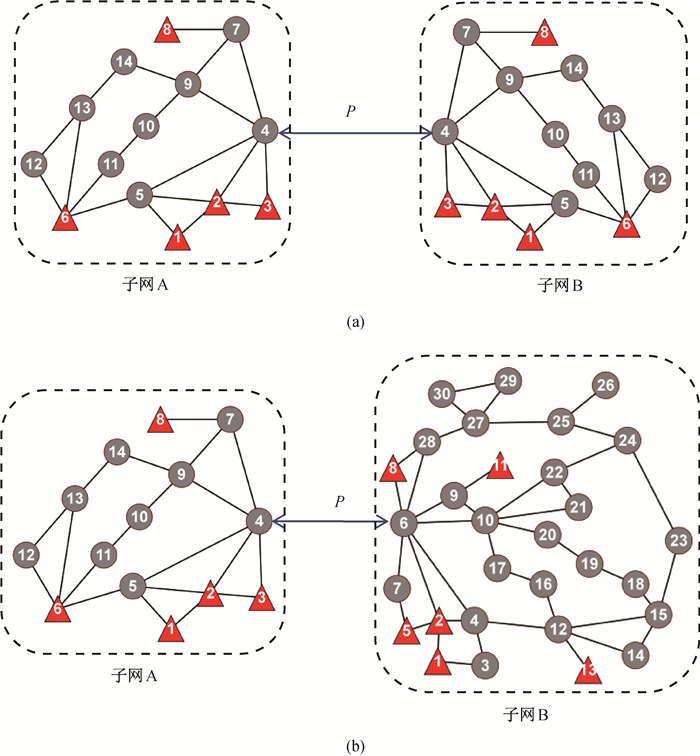
图2 互联电网拓扑图(a)IEEE14-14互联电网;(b)IEEE14-30互联电网
Fig.2 Topology of interconnected power grids (a) IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid; (b) IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid

图3 互联电网中子网新增传输线路发生Braess悖论现象的概率随传输功率变化(a)IEEE14-14子网A;(b)IEEE14-14子网B;(c)IEEE14-30子网A;(d)IEEE14-30子网B
Fig.3 Probability of Braess paradox phenomenon as adding a transmission line in a subnet in an interconneted power grid as functions of transmission power (a)IEEE14-14 subnet A; (b)IEEE14-14 subnet B; (c)IEEE14-30 subnet A; (d)IEEE14-30 subnet B
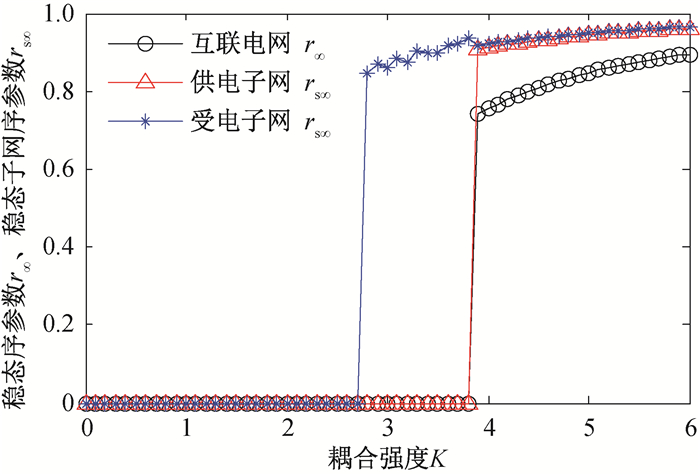
图4 IEEE14-14互联电网稳态序参数以及供电、受电子网的稳态序参数随耦合强度的变化
Fig.4 Steady state order parameters of IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid, the power supply subnet and the power receiving subnet as functions of the coupling strength
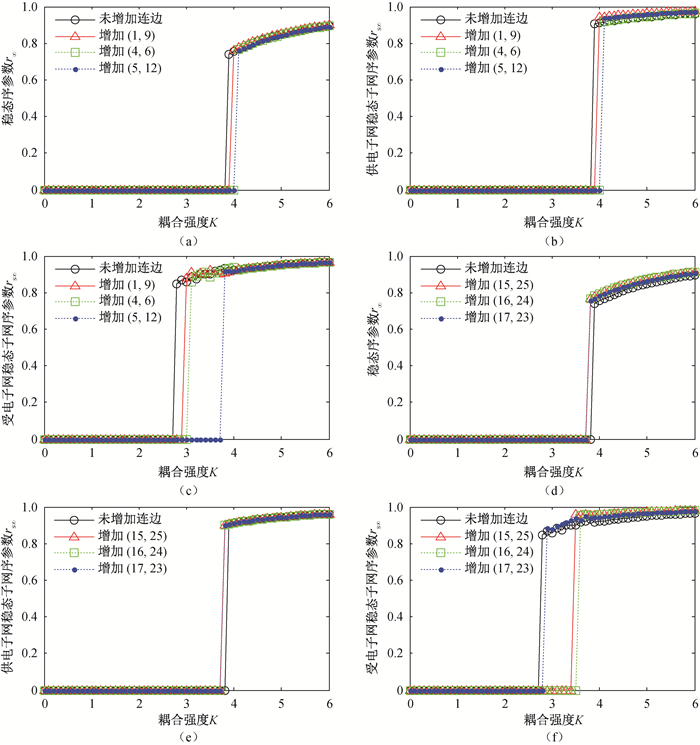
图5 分别在供电子网和受电子网新增传输线路,IEEE14-14互联电网同步情况((a)、(b)、(c)在供电子网新增传输线路,(d)、(e)、(f)在受电子网新增传输线路。) (a)IEEE14-14互联电网;(b)IEEE14-14供电子网;(c)IEEE14-14受电子网;(d)IEEE14-14互联电网;(e)IEEE14-14供电子网;(f)IEEE14-14受电子网
Fig.5 Synchronizability of IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid with a new transmission line in the power supply subnet and in the power receiving subnet, respectivlely (In (a), (b) and (c) the new transmission line is added in the power supply subnet, and in (d), (e) and (f) the new transmission line is added in the power receiving subnet.) (a) IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid; (b) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-14; (c) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-14; (d) IEEE14-14 interconnected power grid; (e) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-14; (f) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-14
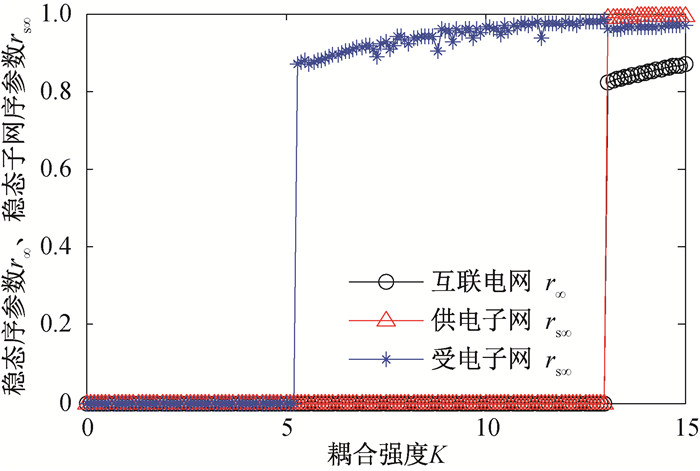
图6 IEEE14-30互联电网稳态序参数以及供电、受电子网的稳态子网序参数随耦合强度的变化
Fig.6 Steady state order parameter of IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid, the power supply subnet and the power receiving subnet as functions of the coupling strength
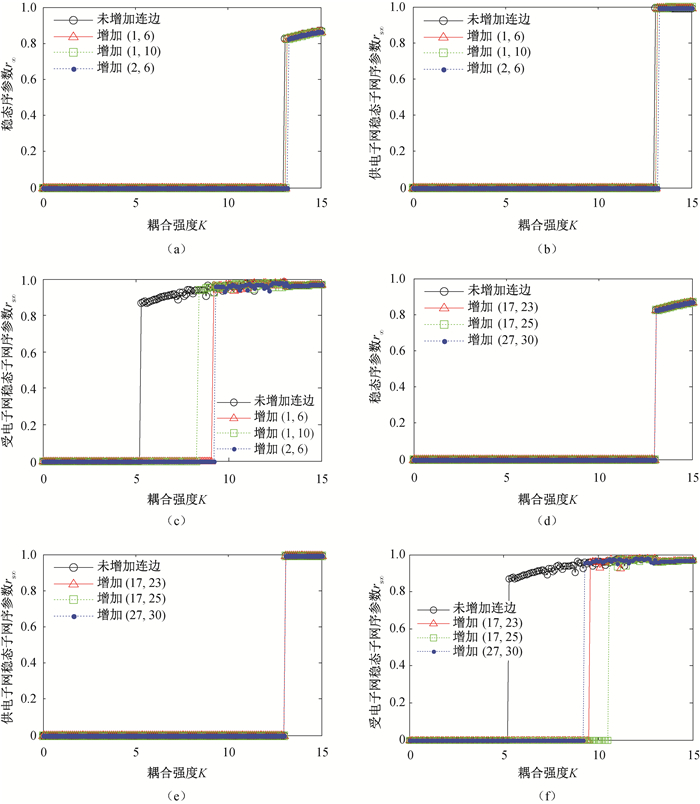
图7 分别在供电子网和受电子网新增传输线路,IEEE14-30互联电网同步情况((a)、(b)、(c)在供电子网新增传输线路,(d)、(e)、(f)在受电子网新增传输线路。) (a)IEEE14-30互联电网;(b)IEEE14-30供电子网;(c)IEEE14-30受电子网;(d)IEEE14-30互联电网;(e)IEEE14-30供电子网;(f)IEEE14-30受电子网
Fig.7 Synchronizability of IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid with a new transmission line in the power supply subnet and in the power receiving subnet, respectivlely (In (a), (b) and (c) the new transmission line is addded in the power supply subnet, and in (d), (e) and (f) the new transmission line is added in the power receiving subnet.) (a) IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid; (b) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-30; (c) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-30, (d) IEEE14-30 interconnected power grid; (e) Power supply subnet of IEEE14-30; (f) Power receiving subnet of IEEE14-30
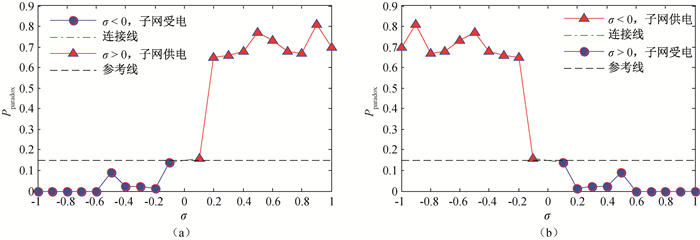
图8 互联电网中子网新增传输线路发生Braess悖论现象的概率随传输功率变化 (a)IEEE57-57子网A;(b)IEEE57-57子网B
Fig.8 Probability of the Braess paradox phenomenon with a transmission line in a subnent in an interconneted power grid as functions of the transmission power (a) IEEE57-57 subnet A; (b) IEEE57-57 subnet B
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
鲁丛林, 蔡宁. Braess's paradox的博弈论分析[J]. 交通科学与工程, 2003, 19 (3): 69- 72.
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
XUE J, GEHLOT H, UKKUSURI S V. Braess's paradox in scale-free networks[C]. The 8th International Symposium on Dynamic Traffic Assignment, 2020.
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
张国宝. "西电东送"工程: 中国电力史上的重要篇章[J]. 中国经济周刊, 2019, 1 (12): 48- 52.
|
| 8 |
李飏, 周永章. 珠江流域"西电东送"能源空间配置的综合效益分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2008, (3): 147- 151.
DOI |
| 9 |
朱法华, 王圣, 刘思湄. 中国电力规划环评的发展与建议[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2007, 23 (5): 9- 13.
DOI |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
BAILLIEUL J, ZHANG B, WANG S. The Kirchhoff-Braess paradox and its implications for smart microgrids[C]. 2015 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2015: 6556-6563.
|
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
WANG X, KOC Y, KOOIJ R E, et al. A network approach for power grid robustness against cascading failures[J]. Physics and Society, 2015, arXiv: 1505.06312.
|
| 16 |
FAZLYAB M, DORFLER F, PRECIADO V M, et al. Optimal network design for synchronization of Kuramoto oscillators[J]. Optimization and Control, 2015, arXiv: 1503.07154.
|
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣. 复杂网络理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006.
|
| 20 |
方锦清. 非线性网络的动力学复杂性研究的若干进展[J]. 自然科学进展, 2007, 17 (7): 841- 857.
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| [1] | 高正, 邹艳丽, 胡均万, 姚高华, 刘唐慧美. 基于复杂网络理论的电网耦合强度分配策略[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 579-588. |
| [2] | 刘凯歌, 韦笃取. 基于WOA-ESN的电机系统混沌振荡预测[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 498-504. |
| [3] | 付韬, 邬龙, 李晨光. 基于生成函数方法的现实网络座键渗流建模[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 212-222. |
| [4] | 李浩乾, 邹艳丽, 张少泽, 刘欣妍, 谭秫毅. 基于复杂网络的电网结构健壮性及Braess悖论现象研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 470-478. |
| [5] | 邹艳丽, 高正, 梁明月, 李志慧, 何铭. 基于潮流追踪的电网同步性能优化及鲁棒性分析[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 623-630. |
| [6] | 石建平, 李培生, 刘国平. 基于改进克隆选择算法的统一混沌系统同步控制与参数辨识[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 240-252. |
| [7] | 钟国翔, 韦笃取, 张波. 分布式发电系统感性负载的远程混沌同步[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(6): 719-725. |
| [8] | 邹艳丽, 王瑞瑞, 吴凌杰, 姚飞, 汪洋. 基于局部序参数的电网同步性能优化[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(4): 498-504. |
| [9] | 石建平, 杨兰天, 刘丹. 基于量子粒子群算法的混沌系统同步控制及参数辨识[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(2): 236-244. |
| [10] | 查进道, 李春彪. 基于引力场理论的混沌同步[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 737-749. |
| [11] | 刘利花, 韦笃取, 张波. 基于动力中继的小世界复杂电机网络混沌同步控制[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 750-756. |
| [12] | 王意, 邹艳丽, 黄李, 李可. 综合考虑局部和全局特性的电网关键节点识别[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(1): 119-126. |
| [13] | 钱慧, 于洪洁. SC混沌比例投影同步方法在保密通信中的应用[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(1): 117-126. |
| [14] | 安海岗. 基于复杂网络的时间序列双变量联动波动[J]. 计算物理, 2014, 31(6): 742-750. |
| [15] | 范文礼, 刘志刚. 一种基于效率矩阵的网络节点重要度评价算法[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(5): 714-719. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
