计算物理 ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 361-370.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8245
李鹏迪1,2( ), 刘俊2,3, 郑淇蓉2,3, 张传国2,3, 李永钢2,3,*(
), 刘俊2,3, 郑淇蓉2,3, 张传国2,3, 李永钢2,3,*( ), 张永胜2,3, 赵高峰1,*(
), 张永胜2,3, 赵高峰1,*( ), 曾雉2,3
), 曾雉2,3
收稿日期:2020-06-22
出版日期:2021-05-25
发布日期:2021-09-30
通讯作者:
李永钢,赵高峰
作者简介:李鹏迪(1995-), 女, 硕士研究生, 研究方向为半导体辐照的理论模拟, E-mail: pdli@theory.issp.ac.cn
基金资助:
Pengdi LI1,2( ), Jun LIU2,3, Qirong ZHENG2,3, Chuanguo ZHANG2,3, Yonggang LI2,3,*(
), Jun LIU2,3, Qirong ZHENG2,3, Chuanguo ZHANG2,3, Yonggang LI2,3,*( ), Yongsheng ZHANG2,3, Gaofeng ZHAO1,*(
), Yongsheng ZHANG2,3, Gaofeng ZHAO1,*( ), Zhi ZENG2,3
), Zhi ZENG2,3
Received:2020-06-22
Online:2021-05-25
Published:2021-09-30
Contact:
Yonggang LI, Gaofeng ZHAO
摘要:
为准确描述硼离子注入硅后缺陷/杂质的动力学物理过程,获得硼浓度空间分布及其演化行为,构建一个跨尺度带电缺陷动力学模型,考虑离子注入缺陷的产生及其演化的多种微观过程,包括缺陷电荷态和带电缺陷间的反应、硼-自间隙团簇(BICs)演化以及缺陷与载流子相互作用等物理过程。模拟得到与实验一致的硼浓度深度分布。结果表明:BICs对硼浓度的深度分布起主要作用,而间隙硼(BI)导致硼浓度分布向深处扩展;计及缺陷的不同电荷态修正自间隙(I)和硼间隙(BI)的扩散系数,从而更准确地描述硼浓度分布。模型揭示了硼离子注入硅发生的物理过程和微观机理,证明BICs和缺陷真实的电荷态是描述硼浓度分布的重要因素,为半导体器件制造与研发提供理论指导。
中图分类号:
李鹏迪, 刘俊, 郑淇蓉, 张传国, 李永钢, 张永胜, 赵高峰, 曾雉. 硅中硼离子注入的带电缺陷动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(3): 361-370.
Pengdi LI, Jun LIU, Qirong ZHENG, Chuanguo ZHANG, Yonggang LI, Yongsheng ZHANG, Gaofeng ZHAO, Zhi ZENG. Dynamics Modeling of Charged Defects in Si under B Ion Implantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(3): 361-370.
| 反应事件(不含团簇) | 反应事件(含团簇) |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| |
表1 模型中考虑的缺陷反应事件
Table 1 Defect reaction events considered in the model
| 反应事件(不含团簇) | 反应事件(含团簇) |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| 缺陷类型 | Ef/eV | D0/(cm2·s-1) | Em/eV | ΔEe/eV | ΔEh/eV | σe/cm2 | σh/cm2 | θ |
| I2- | 5.37 | 10-3 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 3×10-14 | |||
| I- | 4.61 | 10-3 | 0.54 | 0.26 | 1.01 | 3×10-16 | 3×10-14 | |
| I0 | 4.06 | 10-3 | 0.40 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 3×10-15 | 3×10-15 | |
| I+ | 3.73 | 10-3 | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 3×10-14 | 3×10-16 | |
| I2+ | 3.68 | 10-3 | 1.10 | 0.65 | 3×10-14 | |||
| V2- | 4.33 | 1.5×10-2 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 3×10-14 | |||
| V- | 3.87 | 1.3×10-3 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 1.03 | 3×10-16 | 3×10-14 | |
| V0 | 3.69 | 1.3×10-3 | 0.36 | 1.07 | 0.72 | 3×10-15 | 3×10-15 | |
| V+ | 4.07 | 9.6×10-3 | 0.44 | 0.99 | 0.05 | 3×10-14 | 3×10-16 | |
| V2+ | 4.55 | 9.6×10-3 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 3×10-14 | |||
| BS- | 0 | 1.075 | 3×10-14 | 1 | ||||
| BS0 | 0 | 0.045 | 1×10-20 | 4 | ||||
| BI- | 0.72 | 1.2×10-3 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 3×10-14 | |||
| BI0 | 0.63 | 1.2×10-3 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.75 | 3×10-15 | 3×10-15 | |
| BI+ | 1.13 | 1.2×10-3 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 3×10-14 | |||
| I2 | 6.52 | |||||||
| V2 | 5.57 | |||||||
| BI2 | 5.4 | |||||||
| B2 | 0.9 | |||||||
| BI2 | 2.2 | |||||||
| B2I2 | 4.4 |
表2 缺陷和电荷反应物理参数(Ef为缺陷形成能,D0为扩散前置因子,Em为扩散迁移能,ΔEe/h为发射电子/空穴所需激活能,σe/h为缺陷捕获电子/空穴截面,θ为电荷态简并度。)
Table 2 Physical parameters of defect and charge reactions in Si (Ef defect formation energy, D0 diffusion pre-exponential factor, Em migration energy, ΔEe/h activation energy for electron/hole emission, σe/h capture cross section, θ defect-state degeneracy.)
| 缺陷类型 | Ef/eV | D0/(cm2·s-1) | Em/eV | ΔEe/eV | ΔEh/eV | σe/cm2 | σh/cm2 | θ |
| I2- | 5.37 | 10-3 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 3×10-14 | |||
| I- | 4.61 | 10-3 | 0.54 | 0.26 | 1.01 | 3×10-16 | 3×10-14 | |
| I0 | 4.06 | 10-3 | 0.40 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 3×10-15 | 3×10-15 | |
| I+ | 3.73 | 10-3 | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 3×10-14 | 3×10-16 | |
| I2+ | 3.68 | 10-3 | 1.10 | 0.65 | 3×10-14 | |||
| V2- | 4.33 | 1.5×10-2 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 3×10-14 | |||
| V- | 3.87 | 1.3×10-3 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 1.03 | 3×10-16 | 3×10-14 | |
| V0 | 3.69 | 1.3×10-3 | 0.36 | 1.07 | 0.72 | 3×10-15 | 3×10-15 | |
| V+ | 4.07 | 9.6×10-3 | 0.44 | 0.99 | 0.05 | 3×10-14 | 3×10-16 | |
| V2+ | 4.55 | 9.6×10-3 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 3×10-14 | |||
| BS- | 0 | 1.075 | 3×10-14 | 1 | ||||
| BS0 | 0 | 0.045 | 1×10-20 | 4 | ||||
| BI- | 0.72 | 1.2×10-3 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 3×10-14 | |||
| BI0 | 0.63 | 1.2×10-3 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.75 | 3×10-15 | 3×10-15 | |
| BI+ | 1.13 | 1.2×10-3 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 3×10-14 | |||
| I2 | 6.52 | |||||||
| V2 | 5.57 | |||||||
| BI2 | 5.4 | |||||||
| B2 | 0.9 | |||||||
| BI2 | 2.2 | |||||||
| B2I2 | 4.4 |
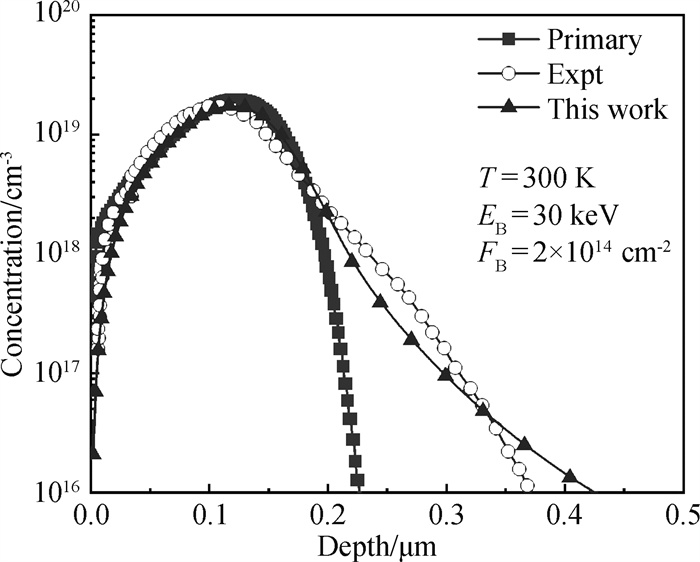
图5 300 K下,注入量为2×1014 cm-2的30 keV硼离子注入硅后硼浓度深度分布的模拟与实验结果[4]
Fig.5 Depth distribution of B concentration in Si in simulation and experiment[4] under 30 keV B ion implantation with fluence of 2×1014 cm-2 at 300 K (Black line is the depth distribution of initial B concentration.)
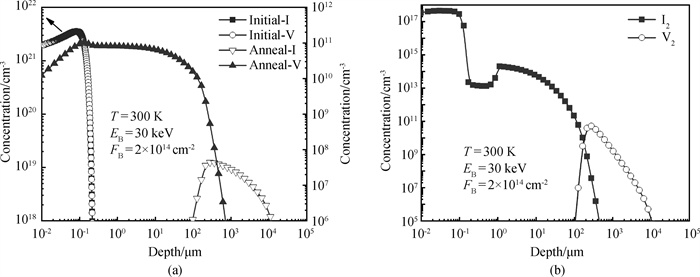
图7 (a) 30 keV,2×1014 cm-2硼离子注入硅, 初始时刻和常温退火后点缺陷深度分布;(b) 常温退火后点缺陷团簇的浓度分布
Fig.7 (a) Depth distributions of point defect concentration in Si before and after annealing to equilibrium; (b) Depth distributions of cluster concentration after annealing to equilibrium, under 30 keV B ion implantation with fluence of 2×1014 cm-2 at room temperature
| 1 | PELAZ L, MARQUÉS L A, ABOY M, et al. Front-end process modeling in silicon[J]. Eur Phys J B, 2009, 72 (3): 323- 359. |
| 2 |
ZOGRAPHOS N, ZECHNERB C, IMARTIN-BRAGADOC G, et al. Multiscale modeling of doping processes in advanced semiconductor devices[J]. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2017, 62, 49- 61.
DOI |
| 3 | YUAN G W, HANG X D, et al. Progress in numerical methods for radiation diffusion equations[J]. Chinese J Comput Phys, 2009, 26 (4): 475- 500. |
| 4 | ZHANG R, TANG Z P. Multiscale simulation of time and space in damage of a pre-tensioned aluminum plate under laser irradiation[J]. Chinese J Comput Phys, 2009, 26 (5): 743- 750. |
| 5 |
MATHIOT D, PFISTER J C. Dopant diffusion in silicon A consistent view involving nonequilibrium defects[J]. J Appl Phys, 1984, 55 (10): 3518.
DOI |
| 6 |
SOLMI S, BARUFFALDI F, CANTERI R. Diffusion of boron in silicon during post-implantation annealing[J]. J Appl Phys, 1991, 69 (4): 2135.
DOI |
| 7 |
COWERN N E, WALLE G F, ZALM P C, et al. Reactions of point defects and dopant atoms in silicon[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 69 (1): 116- 119.
DOI |
| 8 |
ZHU J, RUBIA T D D R, YANG L H Y. Ab initio pseudopotential calculations of B diffusion and pairing in Si[J]. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54 (7): 4741- 4747.
DOI |
| 9 |
SADIGH B, LENOSKY T J, THEISS S K, et al. Mechanism of boron diffusion in silicon: An ab initio and kinetic Monte Carlo study[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 83 (21): 4341- 4344.
DOI |
| 10 |
NAPOLITANI E, de SALVADOR D, STORTI R, et al. Room temperature migration of boron in crystalline silicon[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 93 (5): 055901.
DOI |
| 11 |
JÄGER H U. Point defect-based modeling of diffusion and electrical activation of ion implanted boron in crystalline silicon[J]. J Appl Phys, 1995, 78 (1): 176.
DOI |
| 12 |
FAHEY P M, GRIFFIN P B, PLUMMER J D. Point defects and dopant diffusion in silicon[J]. Rev Mod Phys, 1989, 61 (2): 289- 384.
DOI |
| 13 |
BACCUS B, WADA T, SHIGYO N. A study of nonequilibrium diffusion modeling-applications to rapid thermal annealing and advanced bipolar technologies[J]. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1992, 39 (3): 648.
DOI |
| 14 |
UEMATSU M. Simulation of boron, phosphorus, and arsenic diffusion in silicon based on an integrated diffusion model, and the anomalous phosphorus diffusion mechanism[J]. J Appl Phys, 1997, 82 (5): 2228.
DOI |
| 15 | PICHLER P. Intrinsic point defects, impurities, and their diffusion in silicon[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 2004: 1- 554. |
| 16 |
ORTIZ C J, CRISTIANOB F, COLOMBEAU B. Modeling of extrinsic extended defect evolution in ion-implanted silicon upon thermal annealing[J]. Mater Sci Eng B, 2004, 114-115, 184- 192.
DOI |
| 17 |
MARTIN-BRAGADO I, CASTRILLO P, JARAIZ M, et al. Fermi-level effects in semiconductor processing: A modeling scheme for atomistic kinetic Monte Carlo simulators[J]. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98 (5): 053709.
DOI |
| 18 |
WINDL W, BUNEA M M, STUMPF R, et al. First principles study of boron diffusion in silicon[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 83 (21): 4345- 4348.
DOI |
| 19 |
CENTONI S A, SADIGH B, GILMER G H, et al. First principles calculation of intrinsic defect formation volumes in silicon[J]. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72 (19): 195206.
DOI |
| 20 | ZHANG J, ASHIZAWA Y, OKA H. Barrier to migration of the intrinsic defects in silicon in different charged system using First-principles calculations[J]. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc, 2005, 864, E9.17.1. |
| 21 |
WRIGHT A F. Density-functional-theory calculations for the silicon vacancy[J]. Phys Rev B, 2006, 74 (16): 165116.
DOI |
| 22 |
GANCHENKOVA M G, SUPRYADKINA I A, ABGARYAN K K, et al. Influence of the ab-initio calculation parameters on prediction of energy of point defects in silicon[J]. Modern Electronic Materials, 2015, 1, 103- 108.
DOI |
| 23 |
ABOY M, SANTOS I, PELAZ L, et al. Modeling of defects dopant diffusion and clustering in silicon[J]. J Comput Electron, 2014, 13 (1): 40- 58.
DOI |
| 24 | TANG P F, ZHENG Q R, LI Y G, et al. Cluster dynamics modeling with spatial correlations in cascades[J]. Chinese J Comput Phys, 2019, 36 (5): 586- 594. |
| 25 | LI Y G, ZHOU W H, NING R H, et al. A cluster dynamics model for accumulation of helium in tungsten under helium ions and neutron irradiation[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 2012, 11 (5): 1547- 1568. |
| 26 |
HU L, LI Y G, ZHANG C G, et al. Cluster dynamics simulation of deuterium retention behaviors in irradiated beryllium[J]. Rsc Advances, 2015, 5 (81): 65750- 65756.
DOI |
| 27 |
MARTIN-BRAGADO I, BORGES R, BALBUENA J P, et al. Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation for semiconductor processing: A review[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 2018, 92, 1- 32.
DOI |
| 28 |
SILLS R B AND CAI W. Efficient time integration in dislocation dynamics[J]. Modelling Simul Mater Sci Eng, 2014, 22 (2): 025003.
DOI |
| 29 |
LI Y G, YANG Y, SHORT M P, et al. IM3D: A parallel Monte Carlo code for efficient simulations of primary radiation displacements and damage in 3D geometry[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5, 18130.
DOI |
| 30 |
MYERS S M, COOPER P J, WAMPLER W R. Model of defect reactions and the influence of clustering in pulse-neutron-irradiated Si[J]. J Appl Phys, 2008, 104 (4): 044507.
DOI |
| 31 |
WAMPLER W R, MYERS S M. Model for transport and reaction of defects and carriers within displacement cascades in gallium arsenide[J]. J Appl Phys, 2015, 117 (4): 045707.
DOI |
| 32 | SEEBAUER E G, KRATZER M C. Charged point defects in semiconductors[J]. Mater Sci Eng R, 2006, 55, 51- 149. |
| 33 | JEONG J-W, OSHIYAMA A. Atomic and electronic structures of a boron impurity and its diffusion pathways in crystalline Si[J]. Phys Rev B, 2001, 64 (23): 235204. |
| 34 | SADIGH B, LENOSKY T J, THEISS S K. Mechanism of boron diffusion in silicon: An ab initio and kinetic Monte Carlo study[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 83 (21): 4341- 4344. |
| 35 | MIRABELLA S, DE SALVADOR D, NAPOLITANI E. Mechanisms of boron diffusion in silicon and germanium[J]. J Appl Phys, 2013, 113 (3): 031101. |
| [1] | 尹海峰, 曾春花, 陈文经. 二维二元碳化硅纳米结构的等离激元激发[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(5): 603-609. |
| [2] | 王凤娟, 王刚, 余宁梅. 同轴-环形TSV电学性能[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(2): 242-252. |
| [3] | 马建立, 付志粉, 李洋, 唐旭东, 张鹤鸣. 单轴[110]应力硅电子迁移率[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 483-488. |
| [4] | 周爽, 刘贵立, 姜艳, 宋媛媛. P掺杂单壁硅纳米管Mg原子吸附性能的第一性原理研究[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(5): 554-560. |
| [5] | 柳福提, 程艳, 羊富彬, 程晓洪, 陈向荣. 硅纳米结点电子输运性质的计算[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(6): 943-948. |
| [6] | 张岩, 董刚, 杨银堂, 王宁. 考虑通孔横向热传输效应的三维集成电路热分析[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(5): 753-758. |
| [7] | 马海珠, 林敏, 陈禹宏, 刘倩, 江谦. 聚有机硅结构和规整性对链柔性和极性的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2013, 30(3): 447-453. |
| [8] | 王凤娟, 朱樟明, 杨银堂, 王宁. 考虑硅通孔的三维集成电路最高层温度模型[J]. 计算物理, 2012, 29(4): 580-584. |
| [9] | 吕少波, 蔺增, 巴德纯, 王庆. 射频辉光放电CH4等离子体一维流体动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(3): 329-340. |
| [10] | 王平, 杨银堂, 刘增基, 尚韬, 郭立新. 4H-SiC金属-半导体场效应晶体管大信号I-V特性和小信号参数的计算[J]. 计算物理, 2011, 28(1): 145-151. |
| [11] | 丁瑞雪, 杨银堂, 刘帘曦. 新型NO2化学传感器:碳化硅纳米管[J]. 计算物理, 2010, 27(5): 779-784. |
| [12] | 沈海军, 史友进. 加氢单壁硅纳米管的热稳定性与拉伸力学特性[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25(1): 92-96. |
| [13] | 王平, 杨银堂, 杨燕. SiC电子霍耳迁移率的计算[J]. 计算物理, 2006, 23(1): 80-86. |
| [14] | 王平, 杨银堂, 屈汉章, 杨燕, 李跃进, 贾护军. SiC电子输运特性的Monte Carlo数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2005, 22(3): 245-250. |
| [15] | 杨林安, 张义门, 于春利, 杨永民, 张玉明. 表面态对碳化硅功率金-半场效应管特性的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2003, 20(5): 418-422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
