计算物理 ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 535-546.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8733
• • 上一篇
熊思恒1( ), 段欢欢2, 崔国民1,*(
), 段欢欢2, 崔国民1,*( ), 肖媛1, 易智康1
), 肖媛1, 易智康1
收稿日期:2023-03-21
出版日期:2024-07-25
发布日期:2024-08-24
通讯作者:
崔国民
作者简介:熊思恒(1998-),男,硕士研究生,E-mail:q.xiongsh@qq.com
基金资助:
Siheng XIONG1( ), Huanhuan DUAN2, Guomin CUI1,*(
), Huanhuan DUAN2, Guomin CUI1,*( ), Yuan XIAO1, Zhikang YI1
), Yuan XIAO1, Zhikang YI1
Received:2023-03-21
Online:2024-07-25
Published:2024-08-24
Contact:
Guomin CUI
摘要:
本文分析了惩罚函数法处理传质约束对质量交换网络优化带来的消极影响,提出一种传质负荷动态调控策略,采用不同的调控方式处理单元传质约束,即衰减违反传质约束单元的传质负荷或消除单元,以保证结构中的传质单元不违反约束。通过两个质量交换网络算例进行验证,所得结果相比文献最优结果分别下降2 943 $·a-1和1 697 $·a-1,且结构中传质单元数量增加,证明了策略的有效性。
中图分类号:
熊思恒, 段欢欢, 崔国民, 肖媛, 易智康. 质量交换网络传质负荷不可行处理及动态调控策略[J]. 计算物理, 2024, 41(4): 535-546.
Siheng XIONG, Huanhuan DUAN, Guomin CUI, Yuan XIAO, Zhikang YI. Mass Exchange Network Mass Transfer Load Infeasibility Treatment and Dynamic Regulation Strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(4): 535-546.
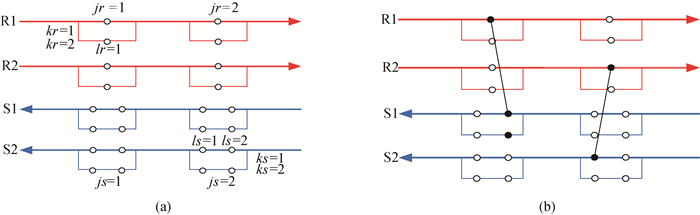
图1 有分流节点非结构模型 (a)初始空结构;(b)匹配结构
Fig.1 Schematic of nodes-based non-structural model with streams split (a) initial empty structure; (b) matching structures
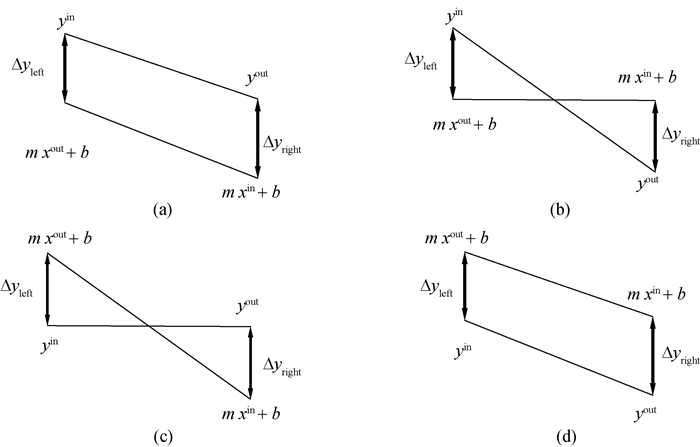
图3 传质单元左右两端传质驱动力的4种情况 (a) Δyleft > 0, Δyright > 0;(b) Δyleft > 0, Δyright < 0; (c) Δyleft < 0, Δyright > 0;(d) Δyleft < 0, Δyright < 0
Fig.3 Four cases of mass transfer driving forces of the mass exchange unit (a) Δyleft > 0, Δyright > 0; (b) Δyleft > 0, Δyright < 0;(c) Δyleft < 0, Δyright > 0;(d) Δyleft < 0, Δyright < 0
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 0.9 | 0.07 | 0.000 3 | |||
| R2 | 0.1 | 0.051 | 0.000 1 | |||
| S1 | 2.3 | 0.000 6 | 0.031 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.004 |
| S2 | ∞ | 0.000 2 | 0.003 5 | 0.26 | 0 | 0.006 |
表1 算例1的流股数据
Table 1 Stream data of Case 1
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 0.9 | 0.07 | 0.000 3 | |||
| R2 | 0.1 | 0.051 | 0.000 1 | |||
| S1 | 2.3 | 0.000 6 | 0.031 | 1.45 | 0 | 0.004 |
| S2 | ∞ | 0.000 2 | 0.003 5 | 0.26 | 0 | 0.006 |
| IT/106 | C1 | C2 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
| 1 | 3 115 | 11 | 10 122 | 630 | 2 037 |
| 2 | 6 589 | 31 | 20 179 | 1 205 | 2 873 |
| 3 | 10 087 | 71 | 30 109 | 1 935 | 4 070 |
| 4 | 13 679 | 105 | 40 142 | 2 456 | 5 068 |
| 5 | 16 045 | 158 | 49 967 | 3 014 | 5 794 |
表2 两种差解出现的频次
Table 2 Frequency of occurrence of two difference imperfect solutions
| IT/106 | C1 | C2 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
| 1 | 3 115 | 11 | 10 122 | 630 | 2 037 |
| 2 | 6 589 | 31 | 20 179 | 1 205 | 2 873 |
| 3 | 10 087 | 71 | 30 109 | 1 935 | 4 070 |
| 4 | 13 679 | 105 | 40 142 | 2 456 | 5 068 |
| 5 | 16 045 | 158 | 49 967 | 3 014 | 5 794 |
| 文献 | 单元数 | 总塔板数/块 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 5 | 25 | 313 292 | 431 613 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 326 700 | 422 293 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 24 | 311 297 | 420 545 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 20 | 317 986 | 412 500 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 314 114 | 409 704 |
| 5 | 21 | 314 777 | 410 369 | |
| 6 | 20 | 315 757 | 406 761 |
表3 算例1的结果对比
Table 3 Result comparison of Case 1
| 文献 | 单元数 | 总塔板数/块 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 5 | 25 | 313 292 | 431 613 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 326 700 | 422 293 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 24 | 311 297 | 420 545 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 20 | 317 986 | 412 500 |
| Ref.[ | 4 | 21 | 314 114 | 409 704 |
| 5 | 21 | 314 777 | 410 369 | |
| 6 | 20 | 315 757 | 406 761 |
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 2 | 0.050 | 0.010 | |||
| R2 | 1 | 0.030 | 0.006 | |||
| S1 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| S2 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.030 | 1.53 | 0 | 0 |
| S3 | ∞ | 0.001 3 | 0.015 | 0.71 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
表4 算例2的流股数据
Table 4 Steam data of Case 2
| 流股 | 最大流量/(kg·s-1) | 入口溶度/(kg·kg-1) | 目标溶度/(kg·kg-1) | m | b | CO/($·kg-1) |
| R1 | 2 | 0.050 | 0.010 | |||
| R2 | 1 | 0.030 | 0.006 | |||
| S1 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| S2 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.030 | 1.53 | 0 | 0 |
| S3 | ∞ | 0.001 3 | 0.015 | 0.71 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 文献 | 单元数 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | 投资费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 218 225 | 127 456 | 345 681 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 217 960 | 159 320 | 345 416 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 210 446 | 132 008 | 342 174 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 223 840 | 115 739 | 339 579 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 219 816 | 118 352 | 338 168 |
| 6 | 223 531 | 114 039 | 337 570 | |
| 8 | 198 453 | 138 018 | 336 471 |
表5 算例2的结果对比
Table 5 Result comparison of Case 2
| 文献 | 单元数 | 操作费用/($·a-1) | 投资费用/($·a-1) | TAC/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 218 225 | 127 456 | 345 681 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 217 960 | 159 320 | 345 416 |
| Ref.[ | 7 | 210 446 | 132 008 | 342 174 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 223 840 | 115 739 | 339 579 |
| Ref.[ | 6 | 219 816 | 118 352 | 338 168 |
| 6 | 223 531 | 114 039 | 337 570 | |
| 8 | 198 453 | 138 018 | 336 471 |
| 1 |
SHORT M , ISAFIADE A J . Thirty years of mass exchanger network synthesis-A systematic review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 304, 127112.
DOI |
| 2 |
杨友麒. 质量交换网络[J]. 化工进展, 2007, 26 (2): 284- 289.
DOI |
| 3 |
薛东峰, 陈理, 袁一, 等. 质量交换网络综合[J]. 现代化工, 2001, 21 (6): 16-19, 21.
DOI |
| 4 |
WANG Bohong , ZHANG Sheng , GUO Lianghui , et al. Graphical approaches for cleaner production and sustainability in process systems[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 366, 132790.
DOI |
| 5 |
FARRAG N M , KAMEL D A , GHALLAB A O , et al. Graphical design and analysis of mass exchange networks using composition driving forces[J]. South African Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 36, 94- 104.
DOI |
| 6 | CHEN Chengliang , HUNG P S . Simultaneous synthesis of mass exchange networks for waste minimization[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2005, 29 (7): 1561- 1576. |
| 7 |
ISAFIADE A J , FRASER D M . Interval based MINLP superstructure synthesis of mass exchange networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2008, 86 (8): 909- 924.
DOI |
| 8 | 易智康, 崔国民, 周志强, 等. 棋盘模型同步优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40 (4): 500- 510. |
| 9 |
ZHOU Zhiqiang , CUI Guoming , XIAO Yuan . A novel node-based non-structural model for mass exchanger network synthesis using a stochastic algorithm[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 376, 134227.
DOI |
| 10 | GARRARD A , FRAGA E S . Mass exchange network synthesis using genetic algorithms[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 1998, 22 (12): 1837- 1850. |
| 11 |
李绍军, 阳永荣. 利用改进的遗传算法进行质量交换网络的最优综合[J]. 化工学报, 2002, (1): 60- 65.
DOI |
| 12 |
都健, 高志辉, 陈理, 等. 采用浓度差同步优化的质量交换网络设计[J]. 化工学报, 2007, (7): 1768- 1775.
DOI |
| 13 |
谢会, 史彬, 鄢烈祥, 等. 列队竞争算法综合质量交换网络[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2010, 27 (12): 1617- 1620.
DOI |
| 14 | TAO Shaohui , JIANG Mengmeng , LIU Mingyue , et al. a mixed discrete PSO algorithm for synthesis of mass exchange network with incompatible multicomponent[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2017, 61, 709- 714. |
| 15 | 马秀宝, 盖照亮, 崔国民, 等. 基于强制进化随机游走算法的质量交换网络综合[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39 (4): 479- 490. |
| 16 | 马秀宝, 崔国民, 周志强, 等. 带有个体淘汰的强制进化随机游走算法优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40 (3): 376- 388. |
| 17 |
XIAO Yuan , CUI Guomin . A novel random walk algorithm with compulsive evolution for heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 115, 1118- 1127.
DOI |
| 18 | PAPALEXANDRI K P , PISTIKOPOULOS E N , FLOUDAS A . Mass exchange networks for waste minimization: A simultaneous approach: Process design[J]. Chemical Engineering Research & Design, 1994, 72 (3): 279- 294. |
| 19 | YEE T F , GROSSMANN I E . Simultaneous optimization models for heat integration-Ⅱ. Heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 1990, 14 (10): 1165- 1184. |
| 20 |
XU Yue , KAYANGE H A , CUI Guomin . A nodes-based non-structural model considering a series structure for heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Processes, 2020, 8 (6): 695.
DOI |
| 21 |
SHENOY U V , FRASER D M . A new formulation of the Kremser equation for sizing mass exchangers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58 (22): 5121- 5124.
DOI |
| 22 |
EL-HALWAGI M M , MANOUSIOUTHAKIS V . Synthesis of mass exchange networks[J]. AIChE Journal, 1989, 35 (8): 1233- 1244.
DOI |
| 23 | AZEEZ O S , ISAFIADE A J , FRASER D M . Supply-based superstructure synthesis of heat and mass exchange networks[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2013, 56, 184- 201. |
| 24 | HALLALE N , FRASER D M . Capital and total cost targets for mass exchange networks: Part 1: Simple capital cost models[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2000, 23 (11/12): 1661- 1679. |
| 25 |
王江峰, 沈静珠, 李有润, 等. 多目标模糊评价遗传算法综合质量交换网络[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2002, 16 (5): 549- 554.
DOI |
| 26 | 高志辉. 费用最小的质量交换网络综合研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2007. |
| 27 | SINGH D , KHANAM S . Synthesis of mass exchanger network considering piping and pumping costs using process integration principles[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering & Process Technology, 2017, 8 (1): 1000322. |
| 28 | 侯创. 基于污染物排放最小化的化工工艺质量交换网络的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2020. |
| [1] | 金广林, 崔国民, 肖媛, 刘洪彬, 付寅瑞, 张志坤. 质量交换网络的个体重构优化方法[J]. 计算物理, 2024, 41(2): 245-257. |
| [2] | 易智康, 崔国民, 周志强, 肖媛, 熊思恒, 马秀宝. 棋盘模型同步优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 500-510. |
| [3] | 马秀宝, 崔国民, 周志强, 肖媛, 徐玥, 杨其国. 带有个体淘汰的强制进化随机游走算法优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(3): 376-388. |
| [4] | 马秀宝, 盖照亮, 崔国民, 周志强, 韩新宇, 杨其国. 基于强制进化随机游走算法的质量交换网络综合[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 479-490. |
| [5] | 韩正恒, 崔国民, 章伟杰, 赵倩倩, 肖媛, 张冠华. 基于节点非结构模型的换热网络结构多样性分析及改进优化策略[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 479-488. |
| [6] | 金艳, 崔国民, 曹美, 沈昊, 陈子禾. 周期优势结构提炼与搜索路径强化结合提升换热网络结构进化能力[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(6): 725-733. |
| [7] | 姜逸文, 崔国民, 鲍中凯, 刘火林, 周金佳. 一种内部公用工程进化的换热网络优化策略[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(3): 341-351. |
| [8] | 苏戈曼, 崔国民, 鲍中凯, 肖媛, 岑镇宇. 换热网络中温度交叉结构的分析与处理[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(1): 107-118. |
| [9] | 鲍中凯, 崔国民, 曹冲, 任杰, 李梦红. 基于公用工程内置策略的换热网络优化[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(6): 707-718. |
| [10] | 邓炜栋, 崔国民, 朱玉双. 应用固定投资费用松弛策略的换热网络优化[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(5): 610-620. |
| [11] | 李剑, 崔国民, 陈家星, 肖媛. 采用三层保护策略的强制进化随机游走算法同步综合换热网络[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(1): 69-79. |
| [12] | 邓炜栋, 崔国民, 肖媛. 一种适用于复杂换热网络优化的耦合联动进化策略[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 675-684. |
| [13] | 朱玉双, 崔国民, 肖媛, 陈家星. 采用单元进化限制策略的RWCE算法优化换热网络[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(5): 593-602. |
| [14] | 于盛男, 崔国民, 肖媛, 周剑卫. 应用于换热网络优化的RWCE算法接受差解策略分析与改进[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 445-452. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
