Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 159-168.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8602
Special Issue: 贺贤土院士从事科学研究工作60周年暨激光聚变相关研究进展专刊
• The 60th Anniversary of Academician He Xiantu's Scientific Research Work: A Special Issue of Research Progress in Laser Fusion • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hongbo CAI1,2( ), Yupei XU3, Peilin YAO4, Enhao ZHANG3, Hanxiao HUANG5, Shaoping ZHU1,3, Xiantu HE1,2
), Yupei XU3, Peilin YAO4, Enhao ZHANG3, Hanxiao HUANG5, Shaoping ZHU1,3, Xiantu HE1,2
Received:2022-07-29
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-07-05
Hongbo CAI, Yupei XU, Peilin YAO, Enhao ZHANG, Hanxiao HUANG, Shaoping ZHU, Xiantu HE. Hybrid Fluid-PIC Modeling and Its Application in Laser Fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(2): 159-168.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8602
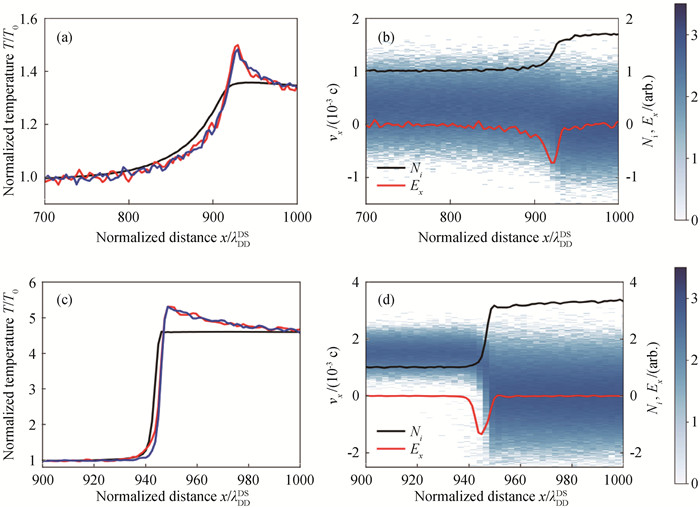
Fig.2 (a), (c) Electron and ion temperature profile in plasma shock wave with Mach number (a) M = 1.43 and (c) M = 3.79 (Black, red, and blue solid lines denote the electron, D+ and 3He2+ respectively.); (b), (d) Ion phase space of the shock (The black solid line denotes the ion density profile and the red solid line denotes the electric field.)
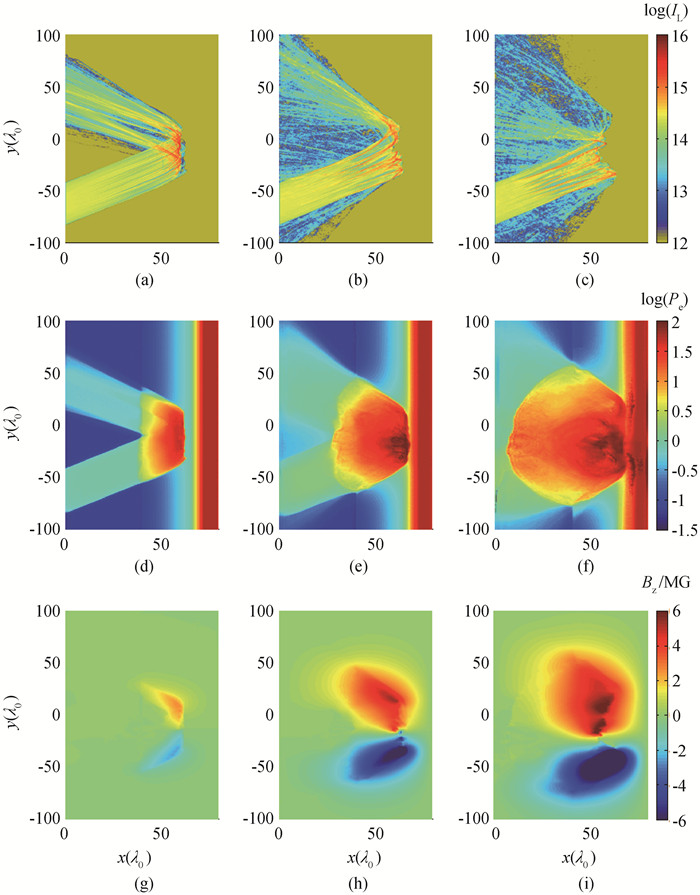
Fig.4 Profiles of Laser intensity, electron pressure, and self-generated magnetic fields at different times (a), (d), (g) t=2 500 T0; (b), (e), (h) t=10 000 T0; (c), (f), (i) t=20 000 T0
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
宋鹏, 翟传磊, 李双贵, 等. 激光间接驱动惯性约束聚变二维总体程序——LARED集成程序[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27, 032007.
DOI |
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
张钧, 常铁强. 激光核聚变靶物理基础[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2004.
|
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| [1] | Zongduo WU, Qingyang MAN, Jin YAN, Jianhua PANG, Yifang SUN. Applications of Three-component Mie-GrüNeisen Mixture Model in Underwater Explosion Mitigation Problem [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 556-569. |
| [2] | Wenshuai ZHANG, Hongbo CAI, Enhao ZHANG, Bao DU, Shiyang ZOU, Shaoping ZHU. Influence of Mach Number on Structure of Collisional Plasma Shock Waves: Fully Kinetic Simulations [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(2): 199-209. |
| [3] | Shesheng XUE, Shouxian LI. Raising of Particles on a Wall Behind a Normal Shock Wave Perpendicular to the Wall [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(3): 280-288. |
| [4] | GU Jianfa, GE Fengjun, DAI Zhensheng, ZOU Shiyang. Influence of Capsule Support Tent on ICF Capsule Implosion Performance: Simulation Study [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(6): 631-638. |
| [5] | LI Xindong, ZHAO Yingkui, HU Zongmin, JIANG Zonglin. Investigation of Normal Shock Structure by Using Navier-Stokes Equations with the Second Viscosity [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(5): 505-513. |
| [6] | ZHOU Jie, XU Shengli. On SPH Method with Treatment of Gas-Liquid Interface Boundary Conditions [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(4): 409-416. |
| [7] | LI Shuanggui, HANG Xudeng, YANG Rong, SONG Peng, ZHAI Chuanlei, QI Jin. Performance Optimization of LARED-Integration Code in Radiative Transfer Calculations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(3): 320-326. |
| [8] | CHEN Yongbin, TANG Zhili, SHENG Jianda. Multi-Objective Optimization for Natural Laminar Flow Airfoil in Transonic Flow [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2016, 33(3): 283-296. |
| [9] | JIANG Hua, DONG Gang, CHEN Xiao. A Numerical Study of Interactions Between Shock Waves and Flame with GPU Acceleration [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2016, 33(1): 23-29. |
| [10] | GU Jianfa, DAI Zhensheng, YE Wenhua, GU Peijun, ZHENG Wudi. Simulation of High-Adiabat ICF Capsule Implosion [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2015, 32(6): 662-668. |
| [11] | PAN Honglu, GUAN Faming, YUAN Xiangjiang, BU Junhui. Unsteady Interaction on Flat Plate/Isolated Roughness Element in Hypersonic Flow [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2015, 32(5): 537-544. |
| [12] | ZHU Yuejin, DONG Gang. Flow Topology Study on Shock-Flame Interaction [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2015, 32(4): 403-409. |
| [13] | LI Yuan, LUO Xisheng. Numerical Study of Shock Interactions with Rectangular Density Interface in Magnetohydrodynamics [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2014, 31(6): 659-667. |
| [14] | JIANG Xinyu, LI Zhihui, WU Junlin. Application of Gas-Kinetic Unified Algorithm Covering Various Flow Regimes for Rotational Non-equilibrium Effect [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2014, 31(4): 403-411. |
| [15] | LIU Chao, FENG Qijing, QIN Chengsen, LIANG Xianhong. Maximal Penetration Depth of Micro-jet from Void Under Shock Loading [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2014, 31(1): 44-50. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
