Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 583-596.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8647
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yu LI1,2( ), Huiqing LIU1,2,*(
), Huiqing LIU1,2,*( ), Yabin FENG2, Xiaohu DONG1,2, Qing WANG2, Bo ZHANG3
), Yabin FENG2, Xiaohu DONG1,2, Qing WANG2, Bo ZHANG3
Received:2022-10-10
Online:2023-09-25
Published:2023-11-02
Contact:
Huiqing LIU
Yu LI, Huiqing LIU, Yabin FENG, Xiaohu DONG, Qing WANG, Bo ZHANG. Adsorption Behavior of Heavy Oil on Montmorillonite Surface by Typical Surfactant: Molecular Dynamics Simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 583-596.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8647
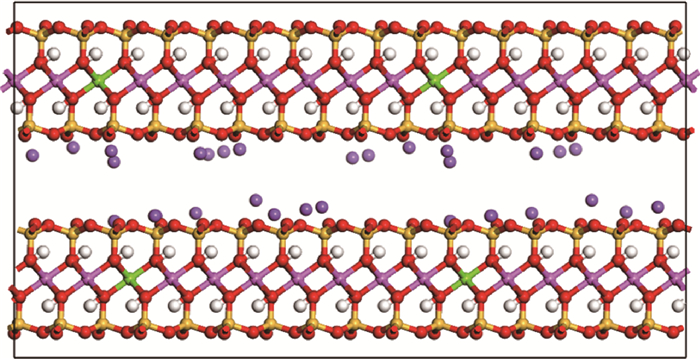
Fig.1 Ball-and-stick model of sodium-montmorillonite molecules (Yellow, red, pink, green, purple, and white are silicon, oxygen, aluminum, magnesium, sodium, and hydrogen, respectively.)
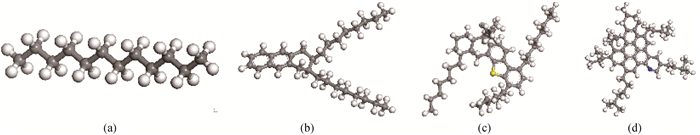
Fig.2 Ball-and-stick models of the four components in heavy oil (Gray, white, blue and yellow represent carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur atoms respectively.) (a) saturate (C12H26); (b) aromatic (C30H46); (c) resin (C50H80S); (d) asphaltene (C56H71N)
| 表活剂种类 | 数量 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 1.826 | 2.284 | 2.512 |
| 10 | 2.115 | 2.442 | 2.667 | |
| 20 | 2.229 | 2.552 | 2.732 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 1.812 | 2.244 | 2.417 |
| 10 | 2.076 | 2.375 | 2.636 | |
| 20 | 2.334 | 2.791 | 2.914 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 1.823 | 2.063 | 2.227 |
| 10 | 1.778 | 2.015 | 2.294 | |
| 20 | 1.928 | 2.284 | 2.352 | |
Table 1 Average distance das-mo (nm) between the centroid of asphaltene molecules and montmorillonite at different temperatures and surfactant concentrations
| 表活剂种类 | 数量 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 1.826 | 2.284 | 2.512 |
| 10 | 2.115 | 2.442 | 2.667 | |
| 20 | 2.229 | 2.552 | 2.732 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 1.812 | 2.244 | 2.417 |
| 10 | 2.076 | 2.375 | 2.636 | |
| 20 | 2.334 | 2.791 | 2.914 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 1.823 | 2.063 | 2.227 |
| 10 | 1.778 | 2.015 | 2.294 | |
| 20 | 1.928 | 2.284 | 2.352 | |
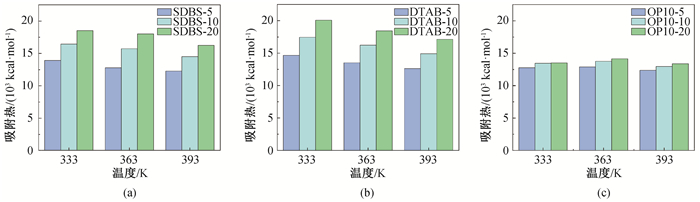
Fig.5 Adsorption heat of ternary adsorption system on the surface of montmorillonite (a)adsorption heat of SDBS system; (b)adsorption heat of DTAB system; (b)adsorption heat of OP-10 system
| 表活剂类型 | 333 K | 363 K | 393 K |
| SDBS | 0.092 9 | 0.104 0 | 0.116 1 |
| DTAB | 0.086 5 | 0.084 9 | 0.085 5 |
| OP-10 | 0.273 2 | 0.311 4 | 0.342 5 |
Table 2 Self-diffusivity of different types of surfactant, D(10-8 m2·s-1)
| 表活剂类型 | 333 K | 363 K | 393 K |
| SDBS | 0.092 9 | 0.104 0 | 0.116 1 |
| DTAB | 0.086 5 | 0.084 9 | 0.085 5 |
| OP-10 | 0.273 2 | 0.311 4 | 0.342 5 |
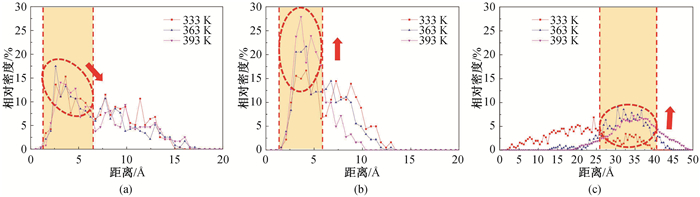
Fig.9 Relative concentrations of different types of surfactant molecules on montmorillonite surface (number of surfactant molecules 10) (a)SDBS; (b)DTAB; (c)OP-10
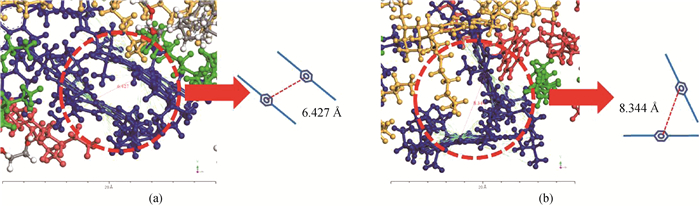
Fig.10 The accumulative configuration of asphaltene molecules at equilibrium (number of DTAB surfactant molecules 5) (a) staggered face-to-face stacking (F-shaped); (b) side to side stacking (T-shape)
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 0.896 | 1.045 | 1.232 |
| 10 | 0.935 | 1.127 | 1.288 | |
| 20 | 0.976 | 1.195 | 1.372 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 0.903 | 1.011 | 1.247 |
| 10 | 1.017 | 1.178 | 1.294 | |
| 20 | 1.252 | 1.367 | 1.433 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 |
| 10 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
| 20 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
Table 3 Average distance din (nm) between the center of mass of asphaltene molecules at different temperatures and surfactant concentrations
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 0.896 | 1.045 | 1.232 |
| 10 | 0.935 | 1.127 | 1.288 | |
| 20 | 0.976 | 1.195 | 1.372 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 0.903 | 1.011 | 1.247 |
| 10 | 1.017 | 1.178 | 1.294 | |
| 20 | 1.252 | 1.367 | 1.433 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 |
| 10 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
| 20 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
| 表活剂类型 | 温度/K | 沥青质吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | 表活剂吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | |||
| 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | |||
| SDBS | 333 | -265 | -420 | -6 000 | 82 | |
| 363 | -255 | -380 | -6 035 | 85 | ||
| 393 | -223 | -329 | -6 001 | 86 | ||
| DTAB | 333 | -259 | -442 | -5 661 | 16 | |
| 363 | -242 | -377 | -5 760 | 33 | ||
| 393 | -217 | -280 | -5 804 | 47 | ||
| OP-10 | 333 | -366 | -553 | 0 | 0 | |
| 363 | -356 | -333 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 393 | -344 | -273 | 0 | 0 | ||
Table 4 Van der Waal energy and electrostatic potential energy of asphaltenes and surfactants on montmorillonite surface
| 表活剂类型 | 温度/K | 沥青质吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | 表活剂吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | |||
| 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | |||
| SDBS | 333 | -265 | -420 | -6 000 | 82 | |
| 363 | -255 | -380 | -6 035 | 85 | ||
| 393 | -223 | -329 | -6 001 | 86 | ||
| DTAB | 333 | -259 | -442 | -5 661 | 16 | |
| 363 | -242 | -377 | -5 760 | 33 | ||
| 393 | -217 | -280 | -5 804 | 47 | ||
| OP-10 | 333 | -366 | -553 | 0 | 0 | |
| 363 | -356 | -333 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 393 | -344 | -273 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 198 | 207 | 214 |
| 10 | 220 | 227 | 233 | |
| 20 | 267 | 276 | 281 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 226 | 220 | 218 |
| 10 | 254 | 247 | 242 | |
| 20 | 288 | 271 | 263 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 187 | 195 | 208 |
| 10 | 185 | 196 | 210 | |
| 20 | 184 | 196 | 211 | |
Table 5 The number of hydrogen bonds between water molecules and montmorillonite
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 198 | 207 | 214 |
| 10 | 220 | 227 | 233 | |
| 20 | 267 | 276 | 281 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 226 | 220 | 218 |
| 10 | 254 | 247 | 242 | |
| 20 | 288 | 271 | 263 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 187 | 195 | 208 |
| 10 | 185 | 196 | 210 | |
| 20 | 184 | 196 | 211 | |
| 1 |
曹仁义, 黄涛, 程林松, 等. 水驱油藏中原油极性物质对吸附和润湿性影响的分子模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38 (5): 595- 602.
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
张雪芳, 刘宗宾, 刘超, 等. 辽东湾坳陷X油田黏土矿物对注水开发储层物性的影响[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2017, 36 (5): 62- 67.
DOI |
| 4 |
刘刚, 侯吉瑞, 李秋言, 等. 二类油层中三元复合驱体系的损耗及有效作用距离[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39 (6): 171- 177.
DOI |
| 5 |
刘慧卿, 东晓虎. 稠油热复合开发提高采收率技术现状与趋势[J]. 石油科学通报, 2022, 7 (2): 174- 184.
|
| 6 |
杜春泽, 刘卫东, 孙灵辉, 等. 黏土矿物对化学驱提高采收率的影响[J]. 应用化工, 2018, 47 (11): 2314- 2316.
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
柴汝宽, 刘月田, 王俊强, 等. 分子动力学模拟方解石和白云石润湿性[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36 (4): 474- 482.
DOI |
| 11 |
于维钊, 乔贵民, 张军, 等. 沥青质在石英表面吸附行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2012, 28 (1): 76- 82.
DOI |
| 12 |
宋圣晗. 稠油中沥青质与表面活性剂相互作用的分子模拟[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019: 21-36.
|
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
郭东红, 李森, 袁建国. 表面活性剂驱的驱油机理与应用[J]. 精细石油化工, 2002, (7): 36- 41.
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
杨胜来, 魏俊之. 油层物理学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2013: 159- 166.
|
| 19 |
黄小娟, 徐加放, 丁廷稷, 等. 有机胺抑制蒙脱石水化机理的分子模拟[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2017, 39 (4): 442- 448.
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
吕兆兰. 超临界二氧化碳在页岩黏土矿物中吸附行为的分子模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2020: 22-24.
|
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
熊凯阳. 烷烃与CO2在不同岩石孔内吸附及驱替特性的分子动力学模拟[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2020: 17-20.
|
| 24 |
刘霞, 陈敬中, 韩炜. 纳米级蒙脱石晶胞参数计算与研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2003, (5): 13- 17.
|
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
王子军. 石油沥青质的化学和物理Ⅱ沥青质的化学组成和结构[J]. 石油沥青, 1996, (1): 26- 36.
|
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
纪德罗. 沥青质在亲水/亲油表面吸附的分子动力学模拟[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020: 18-21.
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
王鹏, 黄世军, 赵凤兰, 等. 沥青质微观聚集特征的分子动力学研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28 (4): 77- 85.
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
苑世领, 张恒, 张冬菊. 分子模拟—理论与实验[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2017: 86- 89.
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
柴汝宽, 刘月田, 杨莉, 等. 两种不同极性有机小分子在方解石(104)面吸附的密度泛函研究[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37 (2): 221- 230.
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
蔡新恒, 龙军, 任强, 等. 沥青质分子聚集体的解离对策[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2020, 36 (5): 889- 898.
|
| 45 |
|
| [1] | Zhaozhao WEI, Kai LIU, Huijun LI. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Deformation Behavior of NiAl Nanowire Under Bending [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 425-435. |
| [2] | Zhaoyang HOU, Yuan NIU, Qixin XIAO, Zhen WANG, Qingtian DENG. Simulation of Mechanical Behavior and Deformation Mechanism of Al Nanowires Along Different Crystal Orientations [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(3): 341-351. |
| [3] | Hubao A, Zhibing YANG, Ran HU, Yifeng CHEN. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Capillary Dynamics at the Nanoscale [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(5): 603-611. |
| [4] | WANG Guohua, CUI Yaru, YANG Ze, LI Xiaoming, TANG Hongliang, YANG Shufeng. Potential Function and Molecular Dynamics Simulation for FexO-SiO2-CaO-MgO-“NiO” Nickel Slag [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(2): 215-223. |
| [5] | WANG Xuemei, DONG Bin, ZHU Ziliang, YANG Junsheng. Interfacial Interaction and Diffusion Properties of Functionalized CNT/Polymer Systems: Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(5): 589-594. |
| [6] | HE Erbin, LUO Zhirong, ZHU Liuhua. Atomistic Analysis of Myoglobin Mechanical Unfolding [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(2): 205-211. |
| [7] | ZHOU Lu, MA Honghe. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on Crystallization Kinetics of Sodium Sulfate in Supercritical Water [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(2): 212-220. |
| [8] | CHAI Rukuan, LIU Yuetian, WANG Junqiang, XIN Jing, PI Jian, LI Changyong. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Wettability of Calcite and Dolomite [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(4): 474-482. |
| [9] | WANG Shuaichuang, ZHANG Gongmu, SUN Bo, SONG Haifeng, TIAN Mingfeng, FANG Jun, LIU Haifeng. Quantum Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Transport Properties of Liquid Plutonium [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(3): 253-258. |
| [10] | LIANG Hua, LI Maosheng. Molecular Dynamics Study of Mechanical Properties of Single Crystal Aluminum with Voids and Vacancies [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(2): 211-218. |
| [11] | ZHANG Haiyan, YIN Xinchun. Molecular Dynamics Study on Growth Mechanism of Pure Metals Solid-Liquid Interface During Solidification [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(1): 80-88. |
| [12] | YANG Shaodong, YE Xuemin, LI Chunxi. Effect of Surfactant Concentration Distribution on Film Drainage [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(5): 577-586. |
| [13] | QI Meiling, YANG Qiong, WANG Canglong, TIAN Yuan, YANG Lei. Parallel Algorithm on GPU and Optimization for Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Irradiation Damage of Structure Materials [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(4): 461-467. |
| [14] | LIU Hao, CHENG Linsong, YANG Zhijun, HUANG Shijun, LI Chunlan, ZHANG Zhongyi. A Recovery Prediction Model for Solvent Enhanced Steam Flooding in Thin Heavy Oil Reservoirs [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2017, 34(2): 183-192. |
| [15] | LI Chunxi, YANG Baocai, YE Xuemin. Stability of Liquid Droplet Containing Surfactant over Corrugated Topography Surface under Disjoining Pressure [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2015, 32(4): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
