Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 453-464.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8435
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu-lin DU1( ), Lin-song CHENG1, Lang-yu NIU1, Yu-ming CHEN2, Ren-yi CAO1,*(
), Lin-song CHENG1, Lang-yu NIU1, Yu-ming CHEN2, Ren-yi CAO1,*( ), Yong-hong XIE3
), Yong-hong XIE3
Received:2021-08-16
Online:2022-07-25
Published:2022-11-17
Contact:
Ren-yi CAO
Xu-lin DU, Lin-song CHENG, Lang-yu NIU, Yu-ming CHEN, Ren-yi CAO, Yong-hong XIE. Numerical Simulation of 3D Discrete Fracture Networks Considering Dynamic Closure of Hydraulic Fractures and Natural Fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(4): 453-464.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8435
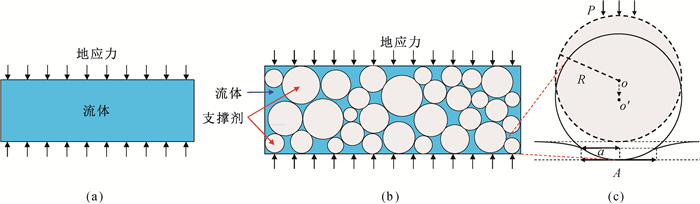
Fig.1 Surface stress analysis of natural fracture and hydraulic fracture (a) natural fractures; (b) hydraulic fractures; (c) embedment of proppant particles
| k1 | m1 | m2 | m3 | m4 | s1 | w1 | |
| 棕砂 | 0.000 089 | 2.34 | 2 550 | 2.23 × 10-6 | 0 | 22 000 | 0.116 9 |
| 白砂 | 0.000 15 | 2.28 | 3 150 | 1.4 × 10-7 | 0.5 | 27 000 | 0.116 4 |
| 高密度陶粒 | 0.000 021 | 2.6 | 3 800 | 3 × 10-6 | 0 | 45 000 | 0.098 |
Table 1 Regression coefficients in Barree model for different proppants[10]
| k1 | m1 | m2 | m3 | m4 | s1 | w1 | |
| 棕砂 | 0.000 089 | 2.34 | 2 550 | 2.23 × 10-6 | 0 | 22 000 | 0.116 9 |
| 白砂 | 0.000 15 | 2.28 | 3 150 | 1.4 × 10-7 | 0.5 | 27 000 | 0.116 4 |
| 高密度陶粒 | 0.000 021 | 2.6 | 3 800 | 3 × 10-6 | 0 | 45 000 | 0.098 |
| 物理量 | 参数 | 物理量 | 参数 | |
| 原油标况密度/(kg·m-3) | 820 | 原油黏度/(mPa·s) | 2 | |
| 基质孔隙度 | 0.13 | 基质渗透率/mD | 0.1 | |
| 水力压裂缝孔隙度 | 0.4 | 水力压裂缝初始渗透率/mD | 20 000 | |
| 水力压裂缝长度/m | 200 | 水力压裂缝初始开度/m | 0.01 | |
| 水力压裂缝间距/m | 200 | 束缚水饱和度 | 0.3 | |
| 原始油藏压力/MPa | 20 | 井底流压/MPa | 10 |
Table 2 Basic parameters in model verification
| 物理量 | 参数 | 物理量 | 参数 | |
| 原油标况密度/(kg·m-3) | 820 | 原油黏度/(mPa·s) | 2 | |
| 基质孔隙度 | 0.13 | 基质渗透率/mD | 0.1 | |
| 水力压裂缝孔隙度 | 0.4 | 水力压裂缝初始渗透率/mD | 20 000 | |
| 水力压裂缝长度/m | 200 | 水力压裂缝初始开度/m | 0.01 | |
| 水力压裂缝间距/m | 200 | 束缚水饱和度 | 0.3 | |
| 原始油藏压力/MPa | 20 | 井底流压/MPa | 10 |
| 地层压力/MPa | 水力压裂缝传导率/(mD·m) |
| 20 | 86.14 |
| 18 | 79.95 |
| 16 | 74.05 |
| 14 | 68.48 |
| 12 | 63.24 |
| 11 | 60.74 |
Table 3 Conductivity change of hydraulic fracture
| 地层压力/MPa | 水力压裂缝传导率/(mD·m) |
| 20 | 86.14 |
| 18 | 79.95 |
| 16 | 74.05 |
| 14 | 68.48 |
| 12 | 63.24 |
| 11 | 60.74 |
| 支撑剂浓度/(g·cm-2) | 支撑剂颗粒的中值直径/μm | 支撑剂类型 | |
| 方案一 | 0.5 | 300 | 棕砂 |
| 方案二 | 2 | 300 | 棕砂 |
| 方案三 | 0.5 | 450 | 棕砂 |
| 方案四 | 0.5 | 300 | 高密度陶粒 |
Table 4 Conductivity change of hydraulic fracture
| 支撑剂浓度/(g·cm-2) | 支撑剂颗粒的中值直径/μm | 支撑剂类型 | |
| 方案一 | 0.5 | 300 | 棕砂 |
| 方案二 | 2 | 300 | 棕砂 |
| 方案三 | 0.5 | 450 | 棕砂 |
| 方案四 | 0.5 | 300 | 高密度陶粒 |
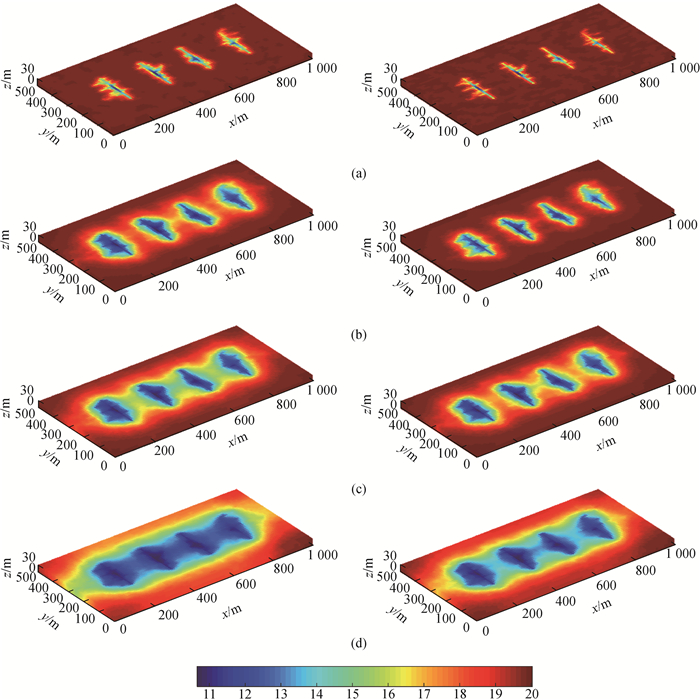
Fig.12 Pressure distributions of static fracture networks (left) and dynamic fracture networks (right) in different periods(a) 30 days; (b) 100 days; (c) 300 days; (d) 1000 days
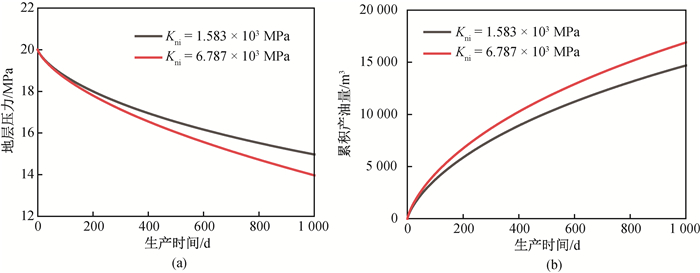
Fig.14 Formation pressure and production of natural fractures with different initial normal stiffness (a) formation pressure; (b) cumulative oil production
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
曹仁义, 程林松, 杜旭林, 等. 致密油藏渗流规律及数学模型研究进展[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43 (5): 113- 136.
|
| 3 |
王友净, 宋新民, 田昌炳, 等. 动态裂缝是特低渗透油藏注水开发中出现的新的开发地质属性[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42 (2): 222- 228.
|
| 4 |
张景, 王颖, 范希彬, 等. 致密砂砾岩储层应力敏感性评价研究[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32 (3): 105- 110.
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
EVANS K F, KOHL T, HOPKIRK R J, et al. Modeling of energy production from hot dry rock systems[C]. ETH Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 1992.
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
BARREE R D, MISKIMINS J L, CONWAY M W, et al. Generic correlations for proppant-pack conductivity[C]. SPE-179135-MS, 2017.
|
| 11 |
HUANG J, SAFARI R, PEREZ O, et al. Reservoir depletion-induced proppant embedment and dynamic fracture closure[C]. SPE-195135-MS, 2019.
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
方思冬, 王卫红, 吴永辉, 等. 基于改进格林元的压裂水平井动态分析方法[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37 (1): 73- 82.
|
| 16 |
王志凯, 程林松, 曹仁义, 等. 三维压裂缝网不稳定压力半解析求解方法[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53 (08): 2246- 2256.
|
| 17 |
戴城, 胡小虎, 方思冬, 等. 基于微地震数据和嵌入式离散裂缝的页岩气开发渗流数值模拟[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9 (5): 74- 81.
|
| 18 |
饶翔, 程林松, 曹仁义, 等. 适用于任意形状倾斜裂缝面的三维嵌入式离散裂缝模型前处理算法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20 (3): 1035- 1043.
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
杜红莉, 张薇, 马峰, 等. 水力压裂支撑剂的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017, 8 (36): 112- 117.
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
WANG J, ELSWORTH D. Conductivity evolution of proppant-filled hydraulic fractures[C]. ARMA 18-111, 2018.
|
| 23 |
GHANIZADEH A, CLARKSON C R, DEGLINT H, et al. Unpropped/propped fracture permeability and proppant embedment evaluation: A rigorous core-analysis/imaging methodology[C]. Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, 2016.
|
| [1] | Li LIU, Shengli NIU, Jinhui ZHU, Yinghong ZUO, Honggang XIE, Peng SHANG. Numerical Simulation of Debris Motion from a Near-space Nuclear Detonation [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 521-528. |
| [2] | Liyuan WU, Suying ZHANG. Ground State of Bose-Einstein Condensates in a Spin-dependent Optical Lattice [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 617-623. |
| [3] | Tengfei ZHAO, Hua ZHANG. Analysis of Deformation and Breakage During Bubble Collision [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(1): 41-52. |
| [4] | Furong GUAN, Chengqian LI, Minyi DENG. Spiral Wave Dynamics of Excited Medium: Effect of Relative Refractory [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(6): 749-756. |
| [5] | Junjie WANG, Jisheng KOU, Jianchao CAI, Yixin PAN, Zhen ZHONG. Tolman Length-based Modified Lucas-Washburn Capillary-driven Model and Numerical Simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(5): 521-533. |
| [6] | Zhankang YANG, Yi NIU. Influence of Temperature, Enclosure and Ventilation on Radon Concentration Distribution in a Blind Roadway [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(4): 456-464. |
| [7] | HU Shaoliang, XU Xiaowen, ZHENG Yuteng, ZHAO Zhenguo, WANG Weijie, XU Ran, AN Hengbin, MO Zeyao. Algorithms in Linear Solver for Large-scale Time-harmonic Maxwell's Equations in SiP Applications: State-of-the-art and Challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(2): 131-145. |
| [8] | CHEN Hao, CAI Ruming. Shape Optimization of Stratosphere Airship with Propeller [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(5): 562-570. |
| [9] | WANG Zimo, LI Ling. Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Fast Phase Change in Ultrashort Laser Drilling [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(3): 299-306. |
| [10] | WANG Zhi, ZOU Gaoyu, GONG Jing, BAI Jianfeng, ZHAI Bowen. A Pressure-based Algorithm for Numerical Simulation of One-dimensional Two-phase Flow [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(4): 413-420. |
| [11] | ZHANG Longhui, YOU Changfu. A Fictitious Domain Method Based on Finite Volume Scheme for Particulate Flows [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(3): 291-297. |
| [12] | XU Chengjun, XU Shengli. Sufficient Conditions and Numerical Validations for Smooth Functions in Particle Approximation of SPH Scheme [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(1): 25-38. |
| [13] | WANG Ye, WANG Yi, HU Wenting, WANG Liangbi. Application of POD Reduced-order Model in Heat Transfer Performance of Flat Tube Bank Fin Heat Exchanger [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(5): 587-596. |
| [14] | SUN Tingting, HAN Saisai, XU Mingtian. A Modified Finite Integration Method for Convection-Diffusion-Reaction Problems [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(3): 269-274. |
| [15] | LU Min, DONG Boheng, ZHANG Ying, ZENG Liang, LIN Xiangquan, DU Peng. Numerical Simulation of Free-Rising of Bubbles in a Tube with Fins Using Front Tracking Method [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(1): 47-54. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
