Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 403-417.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8737
Previous Articles Next Articles
Runzhang MAO1,2( ), Hao DU3, Hongyun TIAN2, Silu HUANG2, Peng ZHANG2,4, Xiaowen XU2,4,*(
), Hao DU3, Hongyun TIAN2, Silu HUANG2, Peng ZHANG2,4, Xiaowen XU2,4,*( )
)
Received:2023-03-23
Online:2024-07-25
Published:2024-08-24
Contact:
Xiaowen XU
CLC Number:
Runzhang MAO, Hao DU, Hongyun TIAN, Silu HUANG, Peng ZHANG, Xiaowen XU. Analysis of Parallel Scalability Bottleneck for Algebraic Multigrid in Typical Real Applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(4): 403-417.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8737
| 算法步骤 | 组件模块 | 内涵 | 计算模式① | 通信模式 |
| 1.1 | Coarsen | 选择粗变量集合 | 图遍历 | 聚合通信,点对点通信 |
| 1.2 | BuildInterp | 构造插值算子 | 图遍历 | 点对点通信 |
| 1.3 | RAP | 三个矩阵相乘 | SpGeMM② | 聚合通信、点对点通信 |
| 2.1 | Smooth | 前光滑、后光滑 | SpTrSV③ | 点对点通信 |
| 2.2 | Restrict | 残差限制 | SpMV④、SpMTV⑤ | 点对点通信 |
| 2.3 | CoarsestSolver | 最粗层求解器 | LU分解 | 点对点通信 |
| 2.4 | Prolong | 插值校正 | SpMV | 点对点通信 |
| 2.6 | ResidualNorm | 计算残差 | SpMV、内积 | 聚合通信、点对点通信 |
Table 1 Component modules, implications, computational patterns, and communication patterns involved in the AMG algorithm
| 算法步骤 | 组件模块 | 内涵 | 计算模式① | 通信模式 |
| 1.1 | Coarsen | 选择粗变量集合 | 图遍历 | 聚合通信,点对点通信 |
| 1.2 | BuildInterp | 构造插值算子 | 图遍历 | 点对点通信 |
| 1.3 | RAP | 三个矩阵相乘 | SpGeMM② | 聚合通信、点对点通信 |
| 2.1 | Smooth | 前光滑、后光滑 | SpTrSV③ | 点对点通信 |
| 2.2 | Restrict | 残差限制 | SpMV④、SpMTV⑤ | 点对点通信 |
| 2.3 | CoarsestSolver | 最粗层求解器 | LU分解 | 点对点通信 |
| 2.4 | Prolong | 插值校正 | SpMV | 点对点通信 |
| 2.6 | ResidualNorm | 计算残差 | SpMV、内积 | 聚合通信、点对点通信 |
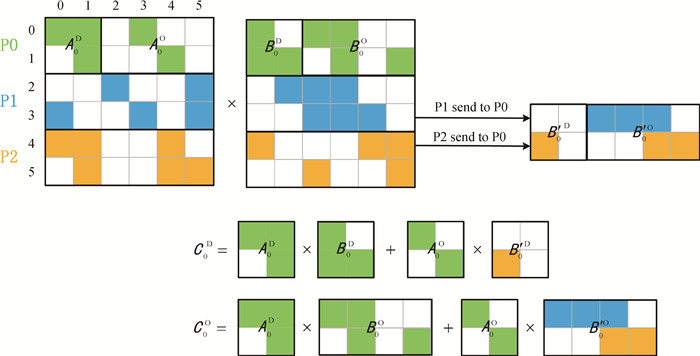
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of point-to-point communication mode for sparse matrix multiplication C=AB (The specific implementation process is demonstrated using process 0 as an example. The sparse matrix A and B is partitioned by rows and assigned to each process. Green, blue, and orange represent the matrix elements owned by processes 0, 1, and 2, respectively.)
| 算例名 | 应用领域 | 偏微分方程 | 网格类型 | 离散方法 |
| RHD-1T | 辐射流体力学流体不稳定性 | 三维辐射扩散方程 | 结构网格 | 有限体积7点格式 |
| RHD-3T | 辐射流体力学流体不稳定性 | 三维三温能量方程 | 结构网格 | 有限体积7点格式 |
| SM-LXJ | 离心机装置结构力学分析 | 三维线弹性方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
| SM-C | 接触问题结构力学分析 | 三维线弹性方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
| HF-S | 航空发动机整机静力学分析 | 三维线弹性方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
| HF-C | 航空发动机燃烧室仿真 | 三维压力方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
Table 2 Application background of test examples
| 算例名 | 应用领域 | 偏微分方程 | 网格类型 | 离散方法 |
| RHD-1T | 辐射流体力学流体不稳定性 | 三维辐射扩散方程 | 结构网格 | 有限体积7点格式 |
| RHD-3T | 辐射流体力学流体不稳定性 | 三维三温能量方程 | 结构网格 | 有限体积7点格式 |
| SM-LXJ | 离心机装置结构力学分析 | 三维线弹性方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
| SM-C | 接触问题结构力学分析 | 三维线弹性方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
| HF-S | 航空发动机整机静力学分析 | 三维线弹性方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
| HF-C | 航空发动机燃烧室仿真 | 三维压力方程 | 非结构网格 | 有限元 |
| 算例名 | 阶数 | 非零元数 | 平均每行非零元数 | 稠密度 | 带宽 |
| RHD-1T | 2 097 152 | 14 581 760 | 6.95 | 3.32×10-6 | 16 384 |
| RHD-3T | 6 291 456 | 52 133 888 | 8.29 | 1.32×10-6 | 49 152 |
| SM-LXJ | 83 073 | 2 826 927 | 34.03 | 4.10×10-4 | 45 426 |
| SM-C | 12 075 090 | 655 371 242 | 54.27 | 4.49×10-6 | 12 075 079 |
| HF-S | 2 081 541 | 71 033 481 | 34.13 | 1.63×10-5 | 733 683 |
| HF-C | 19 637 808 | 97 535 370 | 4.97 | 2.53×10-7 | 18 234 897 |
Table 3 Basic algebraic characteristics of test examples
| 算例名 | 阶数 | 非零元数 | 平均每行非零元数 | 稠密度 | 带宽 |
| RHD-1T | 2 097 152 | 14 581 760 | 6.95 | 3.32×10-6 | 16 384 |
| RHD-3T | 6 291 456 | 52 133 888 | 8.29 | 1.32×10-6 | 49 152 |
| SM-LXJ | 83 073 | 2 826 927 | 34.03 | 4.10×10-4 | 45 426 |
| SM-C | 12 075 090 | 655 371 242 | 54.27 | 4.49×10-6 | 12 075 079 |
| HF-S | 2 081 541 | 71 033 481 | 34.13 | 1.63×10-5 | 733 683 |
| HF-C | 19 637 808 | 97 535 370 | 4.97 | 2.53×10-7 | 18 234 897 |
| 网格层 | L0 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 |
| RHD-1T | 17.0 | 48.3 | 119.2 | 220.7 | 309.1 | 142.4 | 42.4 | |
| RHD-3T | 17.0 | 48.5 | 120.6 | 223.1 | 333.3 | 174.9 | 50.4 | |
| SM-LXJ | 160.2 | 274.2 | 275.3 | 196.3 | 98.3 | 38.1 | 12.2 | |
| SM-C | 127.4 | 103.9 | 107.5 | 150.6 | 180.3 | 25.7 | ||
| HF-S | 189.8 | 244.1 | 273.1 | 272.5 | 229.9 | 128.4 | 38.3 | 12.5 |
| HF-C | 848.9 | 853.0 | 860.5 | 865.4 | 840.9 | 599.0 | 200.7 | 32.6 |
Table 4 Average matrix communication domain of examples at each grid layer (L0 represents the finest grid layer with 2 048 processes.)
| 网格层 | L0 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 |
| RHD-1T | 17.0 | 48.3 | 119.2 | 220.7 | 309.1 | 142.4 | 42.4 | |
| RHD-3T | 17.0 | 48.5 | 120.6 | 223.1 | 333.3 | 174.9 | 50.4 | |
| SM-LXJ | 160.2 | 274.2 | 275.3 | 196.3 | 98.3 | 38.1 | 12.2 | |
| SM-C | 127.4 | 103.9 | 107.5 | 150.6 | 180.3 | 25.7 | ||
| HF-S | 189.8 | 244.1 | 273.1 | 272.5 | 229.9 | 128.4 | 38.3 | 12.5 |
| HF-C | 848.9 | 853.0 | 860.5 | 865.4 | 840.9 | 599.0 | 200.7 | 32.6 |
| 插值类型 | 粗化类型 | 光滑类型 | 强连通阈值 | 最粗层矩阵规模阈值 |
| 修正的经典插值[ | HMIS[ | 混合对称的Gauss-Seidel[ | 0.25 | 100 |
Table 5 Test parameters of AMG solver
| 插值类型 | 粗化类型 | 光滑类型 | 强连通阈值 | 最粗层矩阵规模阈值 |
| 修正的经典插值[ | HMIS[ | 混合对称的Gauss-Seidel[ | 0.25 | 100 |

Fig.8 Time trend chart of 4 communication functions in the FIS module of Coarsen component with number of processes (a)RHD-1T; (b)RHD-3T; (c)SM-LXJ; (d)SM-C; (e)HF-S; (f)HF-C
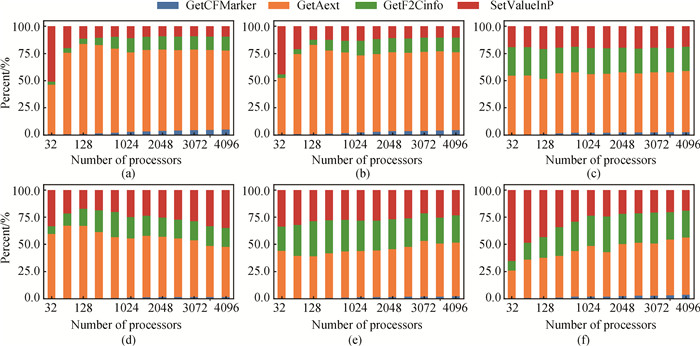
Fig.10 The percentage of time of the four modules in the BuildInterp component with number of processes (a)RHD-1T; (b)RHD-3T; (c)SM-LXJ; (d)SM-C; (e)HF-S; (f)HF-C
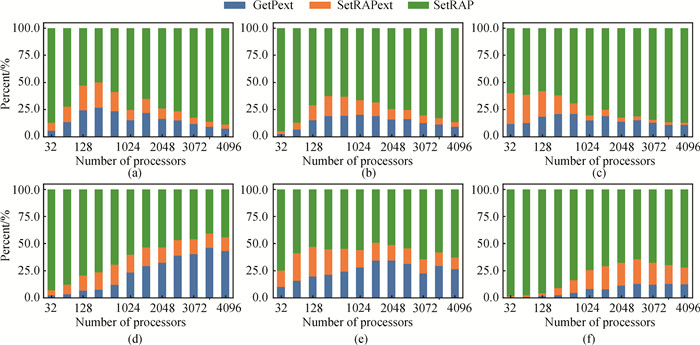
Fig.11 The percentage of time of the three modules in the RAP component with number of processes (a)RHD-1T; (b)RHD-3T; (c)SM-LXJ; (d)SM-C; (e)HF-S; (f)HF-C
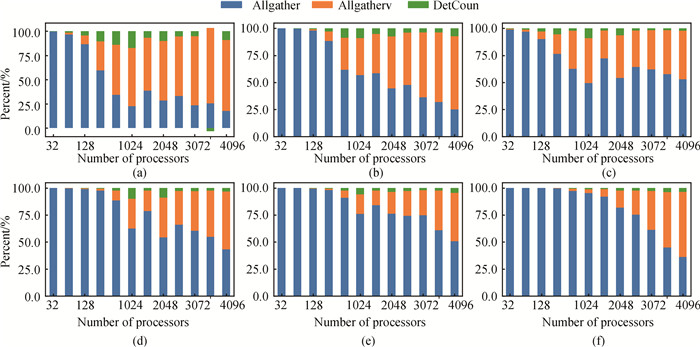
Fig.12 The time percentage of the CPkg module in the RAP component for each example with number of processes (a)RHD-1T; (b)RHD-3T; (c)SM-LXJ; (d)SM-C; (e)HF-S; (f)HF-C
| 层号 | L0 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 |
| RHD-1T | 6 | 16 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 42.4 |
| RHD-3T | 7 | 16 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 6 | |
| SM-LXJ | 14 | 20 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 4 | |
| SM-C | 12 | 13 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 1 | |
| HF-S | 16 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 5 |
| HF-C | 4 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 5 |
Table 6 Maximum number of non-zero elements per row of interpolation operator for each example at each grid level (L0 represents the finest grid layer and the number of processes is 4 096.)
| 层号 | L0 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 |
| RHD-1T | 6 | 16 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 42.4 |
| RHD-3T | 7 | 16 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 6 | |
| SM-LXJ | 14 | 20 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 4 | |
| SM-C | 12 | 13 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 1 | |
| HF-S | 16 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 5 |
| HF-C | 4 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 5 |
| 1 | BRANDT A. Multi-Level adaptive techniques (MLAT) for partial differential equations: ideas and software[M]//RICE J R. Mathematical Software. New York: Academic Press, 1977: 277-318. |
| 2 | 徐小文, 莫则尧, 安恒斌. 求解大规模稀疏线性代数方程组序列的自适应AMG预条件策略[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2016, 46 (10): 1411- 1420. |
| 3 |
徐小文, 莫则尧, 安恒斌. 求解二维三温辐射扩散方程组的一种代数两层迭代方法[J]. 计算物理, 2009, 26 (1): 1- 8.
DOI |
| 4 |
QIAO Changhe , WU Shuhong , XU Jinchao , et al. Analytical decoupling techniques for fully implicit reservoir simulation[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 336, 664- 681.
DOI |
| 5 |
CHEN Junqing , CHEN Zhiming , CUI Tao , et al. An adaptive finite element method for the eddy current model with circuit/field couplings[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2010, 32 (2): 1020- 1042.
DOI |
| 6 |
周志阳, 徐小文, 舒适, 等. 二维三温辐射扩散方程组两层预条件子的自适应求解[J]. 计算物理, 2012, 29 (4): 475- 483.
DOI |
| 7 |
HENSON V E , YANG U M . BoomerAMG: A parallel algebraic multigrid solver and preconditioner[J]. Applied Numerical Mathematics, 2002, 41 (1): 155- 177.
DOI |
| 8 |
BELL N , OLSON L N , SCHRODER J . PyAMG: Algebraic multigrid solvers in python[J]. Journal of Open Source Software, 2022, 7 (72): 4142.
DOI |
| 9 |
XU Xiaowen , YUE Xiaoqiang , MAO Runzhang , et al. JXPAMG: a parallel algebraic multigrid solver for extreme-scale numerical simulations[J]. CCF Transactions on High Performance Computing, 2023, 5 (1): 72- 83.
DOI |
| 10 |
NAUMOV M , ARSAEV M , CASTONGUAY P , et al. AmgX: A library for GPU accelerated algebraic multigrid and preconditioned iterative methods[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2015, 37 (5): S602- S626.
DOI |
| 11 | HÄFNER F. Simulation and parameter identification of Oswald's saltpool experiments with the SAMG multigrid-solver in the transport code MODCALIF[C]//Proceedings of the Conference "Finite-Element Models, MODFLOW, and More", 2004: 13-16. |
| 12 | 徐小文. 并行代数多重网格算法: 大规模计算应用现状与挑战[J]. 数值计算与计算机应用, 2019, 40 (4): 243- 260. |
| 13 | YANG U M. Parallel algebraic multigrid methods-high performance preconditioners[M]//Bruaset A M, Tveito A. Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations on Parallel Computers. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 209-236. |
| 14 |
MO Zeyao , XU Xiaowen . Relaxed RS0 or CLJP coarsening strategy for parallel AMG[J]. Parallel Computing, 2007, 33 (3): 174- 185.
DOI |
| 15 | GAHVARI H, GROPP W, JORDAN K E, et al. Modeling the performance of an algebraic multigrid cycle using hybrid MPI/OpenMP[C]//2012 41st International Conference on Parallel Processing. Pittsburgh: IEEE, 2012: 128-137. |
| 16 |
BIENZ A , FALGOUT R D , GROPP W , et al. Reducing parallel communication in algebraic multigrid through sparsification[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2016, 38 (5): S332- S357.
DOI |
| 17 |
MASCAGNI M , BIENZ A , GROPP W D , et al. Reducing communication in algebraic multigrid with multi-step node aware communication[J]. International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications, 2020, 34 (5): 547- 561.
DOI |
| 18 | BAKER A H, SCHULZ M, YANG U M. On the performance of an algebraic multigrid solver on multicore clusters[M]//PALMA J M L M, DAYDÉ M, MARQUES O. High Performance Computing for Computational Science-VECPAR 2010. Berlin: Springer, 2010: 102-115. |
| 19 | BAKER A H, GAMBLIN T, SCHULZ M, et al. Challenges of scaling algebraic multigrid across modern multicore architectures[C]//2011 IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium. Anchorage: IEEE, 2011: 275-286. |
| 20 | PARK J, SMELYANSKIY M, YANG U M, et al. High-performance algebraic multigrid solver optimized for multi-core based distributed parallel systems[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. Austin, Texas: Association for Computing Machinery, 2015: 54. |
| 21 |
BRANNICK J J , FALGOUT R D . Compatible relaxation and coarsening in algebraic multigrid[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2010, 32 (3): 1393- 1416.
DOI |
| 22 |
徐小文, 莫则尧. 并行代数多重网格算法可扩展性能分析[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24 (4): 387- 394.
DOI |
| 23 | 徐小文, 莫则尧, 曹小林. HYPRE中多重网格解法器的并行可扩展性能分析[J]. 软件学报, 2009, 20 (Z1): 8- 14. |
| 24 | 田鸿运. 大规模数值模拟运行时稳定性评测与诊断[D]. 北京: 中国工程物理研究院, 2022. |
| 25 | YANG U, FALGOUT R, PARK J. Algebraic Multigrid Benchmark[R]. Livermore, CA (United States): Lawrence Livermore National Lab (LLNL), 2017. |
| 26 |
FALGOUT R D , JONES J E , YANG U M . Pursuing scalability for hypre's conceptual interfaces[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2005, 31 (3): 326- 350.
DOI |
| 27 |
PATARASUK P , YUAN Xin . Bandwidth optimal all-reduce algorithms for clusters of workstations[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2009, 69 (2): 117- 124.
DOI |
| 28 | 傅天豪, 田鸿运, 金煜阳, 等. 一种面向构件化并行应用程序的性能骨架分析方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48 (6): 1- 9. |
| 29 |
ADVE V , SAKELLARIOU R . Application representations for multiparadigm performance modeling of large-scale parallel scientific codes[J]. International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications, 2000, 14 (4): 304- 316.
DOI |
| 30 | SODHI S, SUBHLOK J. Skeleton based performance prediction on shared networks[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid, 2004. CCGrid 2004. Chicago: IEEE, 2004: 723-730. |
| 31 |
SODHI S , SUBHLOK J , XU Qiang . Performance prediction with skeletons[J]. Cluster Computing, 2008, 11 (2): 151- 165.
DOI |
| 32 |
VETTER J S , MCCRACKEN M O . Statistical scalability analysis of communication operations in distributed applications[J]. ACM SIGPLAN Notices, 2001, 36 (7): 123- 132.
DOI |
| 33 | DE STERCK H , FALGOUT R D , NOLTING J W , et al. Distance-two interpolation for parallel algebraic multigrid[J]. Numerical Linear Algebra With Applications, 2008, 15 (2/3): 115- 139. |
| 34 | DE STERCKH H , YANG U M , HEYS J J . Reducing complexity in parallel algebraic multigrid preconditioners[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2006, 27 (4): 1019- 1039. |
| 35 | 徐小文, 莫则尧, 武林平. 迭代方法中基于渐近规模的通信与计算比分析[J]. 计算机学报, 2013, 36 (4): 782- 789. |
| [1] | Shi SHU, Xiaoqiang YUE, Jianmeng HE, Xiaowen XU, Zeyao MO. Feature-driven Parallel Algebraic Multigrid Methods for Multi-group Radiation Diffusion Problems [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(1): 87-97. |
| [2] | Chunsheng FENG, Shizhe LI, Shenghao LIU, Chensong ZHANG, Li ZHAO. Application-oriented Preconditioning of Seepage Mechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(1): 98-109. |
| [3] | Yue HAO, Silu HUANG, Xiaowen XU. Convergence Estimation and Characteristic Analysis of A Two-level Iterative Algorithm for Discretized Three-temperature Energy Linear Systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(1): 122-130. |
| [4] | Shaoliang HU, Kailong XU, Ran XU, Zaigang LIU, Xiaowen XU, Hengbin AN, Ronghong FAN, Zhenyu WANG, Wei WANG. A Algebraic Multigrid Algorithm Based on Hybrid Coarsening for Pressure Poisson Equation [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 527-534. |
| [5] | Yi HU, Hengbin AN. Algorithms for Solving Electronic Continuity Equation in Numerical Simulation of Semiconductor Devices [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 570-582. |
| [6] | ZUO Fengli, LIU Xu, ZHANG Baoyin, HU Xiaoyan. Parallel Implementation of Fast Multipole Methods for Three-dimensional Potential Fields on JASMIN [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2013, 30(1): 140-147. |
| [7] | ZHOU Zhiyang, XU Xiaowen, SHU Shi, FENG Chunsheng, MO Zeyao. An Adaptive Two-level Preconditioner for 2-D 3-T Radiation Diffusion Equations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2012, 29(4): 475-483. |
| [8] | CHENG Jie, ZHANG Linbo. A Scalable Parallel Algorithm for Three-dimensional Semiconductor Device Simulation [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2012, 29(3): 439-448. |
| [9] | XU Xiaowen, MO Zeyao, AN Hengbin. Algebraic Two-level Iterative Method for 2-D 3-T Radiation Diffusion Equations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2009, 26(1): 1-8. |
| [10] | XU Xiaowen, MO Zeyao. Scalability Analysis for Parallel Algebraic Multigrid Algorithms [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2007, 24(4): 387-394. |
| [11] | SHU Shi, HUANG Yun-qing, YANG Ying, YU Xi-jun, XIAO Ying-xiong. A Class of Algebraic Multigrid Algorithms with Three-Dimensional Equal Algebraic Structures [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2005, 22(6): 18-22. |
| [12] | Mo Zeyao, Xu Linbao, Zhang Baolin, Shen Longjun. Parallel computing and performance analysis for 2-dimensional plasma simulations with particle clouds in cells methods [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1999, 16(5): 496-504. |
| [13] | Fu Hanqing, Chang Qianshun. Application of Algebraic Multigrid Method to Solve the Splitting Scheme of One-dimensional Euler Equations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1997, 14(1): 19-25. |
| [14] | Chang Qianshun, Li Zhengfeng. NEW INTERPOLATION FORMULA IN ALGEBRAIC MULTIGRID METHOD [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 1990, 7(4): 453-460. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
