Since a quantum system is inevitably influenced by some unpredictable perturbations, we thereby conclude that all the experimental realizations of Grover quantum search algorithm reported were, in fact, achieved in a three-dimensional complex subspace. We also prove that in a two-dimensional complex subspace, for any given initial superposition of basis states|
γ0>=cos
β0|
α>+sin
β0e
iζ|
β)(
β0 is a small positive real number,
ζ is an arbitrary real number), there exists a set of solutions
Fj={(
θj,
θj-1,…,
θ1),(
φj,
φj-1,…,
φ1)} such that a desired state can be found with certainty for some positive integer j≥2, where the phase rotation angles
θl and
θt are real numbers but not equal to 2
k'π,1 ≤ 1 ≤
j,k'is an arbitrary integer. If it is only required that a desired state can be found with high success probability, then as the total number of the desired and undesired states in an unsorted database is sufficiently large the above set of solutions
Fj can be written in the form
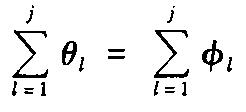
for a relatively small positive integer
j.
