计算物理 ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 333-342.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8214
收稿日期:2020-03-30
出版日期:2021-05-25
发布日期:2021-09-30
通讯作者:
崔国民
作者简介:姜逸文(1995-), 男, 硕士研究生, E-mail: jiangyiwen1995@163.com
基金资助:
Yiwen JIANG( ), Guomin CUI(
), Guomin CUI( ), Zihe CHEN, Jiaming YU, Qianqian ZHAO
), Zihe CHEN, Jiaming YU, Qianqian ZHAO
Received:2020-03-30
Online:2021-05-25
Published:2021-09-30
Contact:
Guomin CUI
摘要:
强制进化随机游走算法(RWCE)应用于换热网络优化,具有算法流程简洁、结构进化能力强等特点。其中接受差解几率对个体跳出局部最优有重要的影响。本文统计优化后期连续变量和结构变量使得年综合费用下降的次数,分析二者对优化进程的影响,讨论接受差解几率在个体优化进程中所起的作用,提出一种通过判别差解结构与原结构的异同来智能调整接受差解几率的换热网络优化方法。该策略进一步强化个体的结构进化与跳出局部极值的能力,通过算例证明了策略的有效性。
中图分类号:
姜逸文, 崔国民, 陈子禾, 俞佳明, 赵倩倩. 智能调整接受差解几率的RWCE算法[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(3): 333-342.
Yiwen JIANG, Guomin CUI, Zihe CHEN, Jiaming YU, Qianqian ZHAO. An RWCE Algorithm with Intelligently Adjusted Acceptance Probability of Improper Solutions[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(3): 333-342.
| 进口温度Ti/K | 出口温度To/K | 热容流率Fu/(kW·K-1) | 换热系数h/(kW·m-2·K-1) | |
| 热流体1 | 658 | 432 | 131.51 | 1.238 |
| 热流体2 | 789 | 316 | 1 198.96 | 0.546 |
| 热流体3 | 405 | 355 | 378.52 | 0.771 |
| 热流体4 | 364 | 333 | 589.545 | 0.859 |
| 热流体5 | 490 | 316 | 186.216 | 1 |
| 热流体6 | 922 | 316 | 116 | 1 |
| 冷流体1 | 303 | 658 | 119.1 | 1.85 |
| 冷流体2 | 372 | 744 | 191.05 | 1.129 |
| 冷流体3 | 710 | 794 | 377.91 | 0.815 |
| 冷流体4 | 351 | 691.6 | 160.43 | 1 |
| 冷流体5 | 490 | 507 | 1 297.7 | 0.443 |
| 冷流体6 | 529 | 539 | 2 753 | 2.085 |
| 冷流体7 | 322 | 422 | 197.39 | 1 |
| 冷流体8 | 332 | 436.4 | 123.156 | 1.063 |
| 冷流体9 | 436 | 922 | 95.98 | 1.81 |
| 冷流体10 | 492 | 494.3 | 1 997.5 | 1.377 |
| 热公用工程1 | 2 073 | 1 073 | 1.2 | |
| 热公用工程2 | 782 | 782 | 1.0 | |
| 冷公用工程 | 311 | 308.5 | 1.0 |
表附表 1 H6C10的物流参数
Table 附表 1 Parameters in Case H6C10
| 进口温度Ti/K | 出口温度To/K | 热容流率Fu/(kW·K-1) | 换热系数h/(kW·m-2·K-1) | |
| 热流体1 | 658 | 432 | 131.51 | 1.238 |
| 热流体2 | 789 | 316 | 1 198.96 | 0.546 |
| 热流体3 | 405 | 355 | 378.52 | 0.771 |
| 热流体4 | 364 | 333 | 589.545 | 0.859 |
| 热流体5 | 490 | 316 | 186.216 | 1 |
| 热流体6 | 922 | 316 | 116 | 1 |
| 冷流体1 | 303 | 658 | 119.1 | 1.85 |
| 冷流体2 | 372 | 744 | 191.05 | 1.129 |
| 冷流体3 | 710 | 794 | 377.91 | 0.815 |
| 冷流体4 | 351 | 691.6 | 160.43 | 1 |
| 冷流体5 | 490 | 507 | 1 297.7 | 0.443 |
| 冷流体6 | 529 | 539 | 2 753 | 2.085 |
| 冷流体7 | 322 | 422 | 197.39 | 1 |
| 冷流体8 | 332 | 436.4 | 123.156 | 1.063 |
| 冷流体9 | 436 | 922 | 95.98 | 1.81 |
| 冷流体10 | 492 | 494.3 | 1 997.5 | 1.377 |
| 热公用工程1 | 2 073 | 1 073 | 1.2 | |
| 热公用工程2 | 782 | 782 | 1.0 | |
| 冷公用工程 | 311 | 308.5 | 1.0 |
| IT/104 | N1 | ΔF1/($·a-1) | N2 | ΔF2/($·a-1) | N3 | N4 |
| 80~1 000 | 877 | 2 583 | 5 916 | 357 | 859 | 808 |
表1 不同优化形态出现次数
Table 1 Cumulative number of different optimization style
| IT/104 | N1 | ΔF1/($·a-1) | N2 | ΔF2/($·a-1) | N3 | N4 |
| 80~1 000 | 877 | 2 583 | 5 916 | 357 | 859 | 808 |
| IT/104 | δ=0.01 | δ=0.001 | δ=0.000 1 |
| 100~500 | 4 474 | 553 | 42 |
表2 不同接受差解几率的结构变异次数
Table 2 Optimization times of structural variables with different probability of accepting improper solutions
| IT/104 | δ=0.01 | δ=0.001 | δ=0.000 1 |
| 100~500 | 4 474 | 553 | 42 |
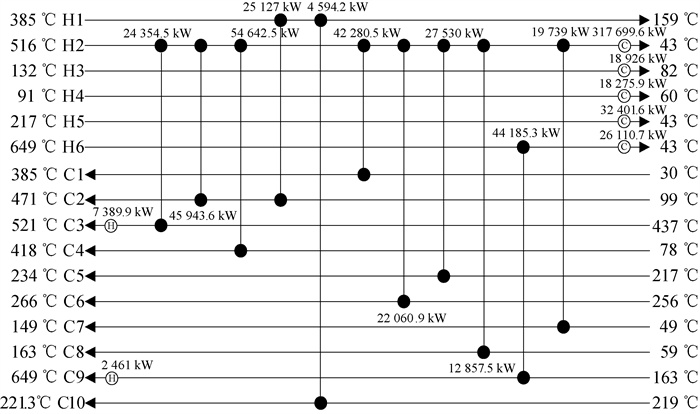
图6 采用智能调整接受差解概率RWCE算法换热网络结构图(6 829 826 $ ·a-1)
Fig.6 HEN structure obtained with RWCE in which acceptance probability of improper solutions is adjusted intelligently
| 文献 | 换热单元数 | 热公用工程/MW | 冷公用工程/MW | 年综合费用/($ ·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 18 | 66.07 | 469.62 | 7 435 740 |
| Ref.[ | 16 | 38.80 | 442.37 | 7 361 190 |
| Ref.[ | 19 | 23.79 | 427.36 | 7 212 116 |
| Ref.[ | 17 | 34.21 | 437.77 | 7 128 572 |
| Ref.[ | 18 | 9.84 | 413.34 | 6 861 111 |
| This work( | 18 | 9.84 | 413.40 | 6 829 826 |
表3 算例H6C10结果对比
Table 3 Comparison results of Case H6C10
| 文献 | 换热单元数 | 热公用工程/MW | 冷公用工程/MW | 年综合费用/($ ·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 18 | 66.07 | 469.62 | 7 435 740 |
| Ref.[ | 16 | 38.80 | 442.37 | 7 361 190 |
| Ref.[ | 19 | 23.79 | 427.36 | 7 212 116 |
| Ref.[ | 17 | 34.21 | 437.77 | 7 128 572 |
| Ref.[ | 18 | 9.84 | 413.34 | 6 861 111 |
| This work( | 18 | 9.84 | 413.40 | 6 829 826 |
| 进口温度Ti/K | 出口温度To/K | 热容流率Fu/(kW·K-1) | 换热系数h/(kW·m-2·K-1) | |
| 热流体1 | 576 | 437 | 23.1 | 0.06 |
| 热流体2 | 599 | 399 | 15.22 | 0.06 |
| 热流体3 | 530 | 382 | 15.15 | 0.06 |
| 热流体4 | 449 | 237 | 14.76 | 0.06 |
| 热流体5 | 368 | 177 | 10.7 | 0.06 |
| 热流体6 | 121 | 114 | 149.6 | 1 |
| 热流体7 | 202 | 185 | 258.2 | 1 |
| 热流体8 | 185 | 113 | 8.38 | 1 |
| 热流体9 | 140 | 120 | 59.89 | 1 |
| 热流体10 | 69 | 66 | 165.79 | 1 |
| 热流体11 | 120 | 68 | 8.74 | 1 |
| 热流体12 | 67 | 35 | 7.62 | 1 |
| 热流体13 | 1 034.5 | 576 | 21.3 | 0.06 |
| 冷流体1 | 123 | 343 | 10.61 | 0.06 |
| 冷流体2 | 20 | 156 | 6.65 | 1.2 |
| 冷流体3 | 156 | 157 | 3 291 | 2 |
| 冷流体4 | 20 | 182 | 26.63 | 1.2 |
| 冷流体5 | 182 | 318 | 31.19 | 1.2 |
| 冷流体6 | 318 | 320 | 4 011.83 | 2 |
| 冷流体7 | 322 | 923.78 | 17.6 | 0.06 |
| 热公用工程 | 927 | 927 | 5 | |
| 冷公用工程 | 9 | 17 | 1 |
表附表 2 算例H13C7的物流参数
Table 附表 2 Parameters in Case H13C7
| 进口温度Ti/K | 出口温度To/K | 热容流率Fu/(kW·K-1) | 换热系数h/(kW·m-2·K-1) | |
| 热流体1 | 576 | 437 | 23.1 | 0.06 |
| 热流体2 | 599 | 399 | 15.22 | 0.06 |
| 热流体3 | 530 | 382 | 15.15 | 0.06 |
| 热流体4 | 449 | 237 | 14.76 | 0.06 |
| 热流体5 | 368 | 177 | 10.7 | 0.06 |
| 热流体6 | 121 | 114 | 149.6 | 1 |
| 热流体7 | 202 | 185 | 258.2 | 1 |
| 热流体8 | 185 | 113 | 8.38 | 1 |
| 热流体9 | 140 | 120 | 59.89 | 1 |
| 热流体10 | 69 | 66 | 165.79 | 1 |
| 热流体11 | 120 | 68 | 8.74 | 1 |
| 热流体12 | 67 | 35 | 7.62 | 1 |
| 热流体13 | 1 034.5 | 576 | 21.3 | 0.06 |
| 冷流体1 | 123 | 343 | 10.61 | 0.06 |
| 冷流体2 | 20 | 156 | 6.65 | 1.2 |
| 冷流体3 | 156 | 157 | 3 291 | 2 |
| 冷流体4 | 20 | 182 | 26.63 | 1.2 |
| 冷流体5 | 182 | 318 | 31.19 | 1.2 |
| 冷流体6 | 318 | 320 | 4 011.83 | 2 |
| 冷流体7 | 322 | 923.78 | 17.6 | 0.06 |
| 热公用工程 | 927 | 927 | 5 | |
| 冷公用工程 | 9 | 17 | 1 |
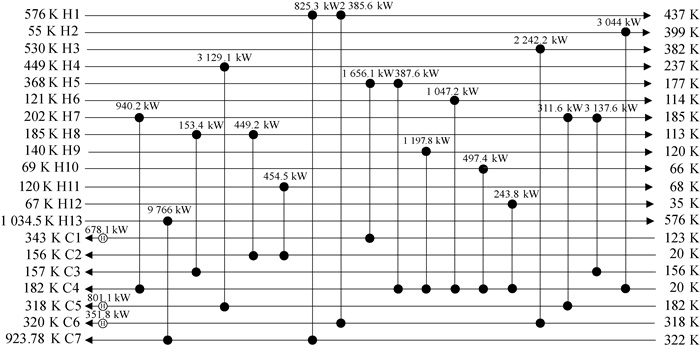
图8 采用智能调整接受差解概率RWCE算法换热网络结构图(1 399 751 $ ·a-1)
Fig.8 HEN structure obtained with RWCE in which acceptance probability of improper solutions is adjusted intelligently
| 文献 | 换热单元数 | 热公用工程/kW | 冷公用工程/kW | 年综合费用/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 21 | 1 938 | 107 | 1 537 086 |
| Ref.[ | 22 | 1 827 | 0 | 1 418 977 |
| Ref.[ | 22 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 418 981 |
| Ref.[ | 21 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 413 807 |
| Ref.[ | 22 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 401 958 |
| This work( | 21 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 399 751 |
表4 H13C7算例的优化结果与文献结果对比
Table 4 Comparison results of Case H13C7
| 文献 | 换热单元数 | 热公用工程/kW | 冷公用工程/kW | 年综合费用/($·a-1) |
| Ref.[ | 21 | 1 938 | 107 | 1 537 086 |
| Ref.[ | 22 | 1 827 | 0 | 1 418 977 |
| Ref.[ | 22 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 418 981 |
| Ref.[ | 21 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 413 807 |
| Ref.[ | 22 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 401 958 |
| This work( | 21 | 1 831 | 0 | 1 399 751 |
| 1 |
RUDD D F. The synthesis of system designs: I. Elementary decomposition theory[J]. Aiche Journal, 1968, 14 (2): 343- 349.
DOI |
| 2 | 李志红, 华贲, 尹清华, 等. 人工智能与数学规划的集成用于换热网络最优合成设计的研究[J]. 石油化工, 1998, 9, 36- 44. |
| 3 | BJÖRK K M, WESTERLUND T. Global optimization of heat exchanger network synthesis problems with and without the isothermal mixing assumption[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2002, 26, 1581- 1593. |
| 4 | FURMAN K C, SAHINIDIS N V. Approximation algorithms for the minimum number of matches problem in heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2004, 43 (14): 3554- 3565. |
| 5 |
CHOI S H, MANOUSIOUTHAKIS V. Global optimization methods for chemical process design: Deterministic and stochastic approaches[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2002, 19 (2): 227- 232.
DOI |
| 6 |
RAVAGNANI M A S S, SILVA A P, ARROYO P A, et al. Heat exchanger network synthesis and optimisation using genetic algorithm[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2005, 25 (7): 1003- 1017.
DOI |
| 7 |
YERRAMSETTY K M, MURTY C V S. Synthesis of cost-optimal heat exchanger networks using differential evolution[J]. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2008, 32 (8): 1861- 1876.
DOI |
| 8 | SILVA A P, RAVAGNANI M A S S, BISCAIA E C, et al. Optimal heat exchanger network synthesis using[J]. Optimization & Engineering, 2010, 11 (3): 459- 470. |
| 9 | 肖媛, 崔国民, 李帅龙. 一种新的用于换热网络全局优化的强制进化随机游走算法[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67 (12): 5140- 5147. |
| 10 | VITORPAVÃO L, COSTA C B B, SÁRAVAGNANI M A S, et al. Large-scale heat exchanger networks synthesis using simulated annealing and the novel rocket fireworks optimization[J]. AIChE Journal, 2016, 63 (5) |
| 11 | LUCAS F S, et al. Synthesis and optimization of work and heat exchanger networks using an MINLP model with a reduced number of decision variables[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, (262) |
| 12 | YU S, CUI G, XIAO Y, et al. An improved accepting imperfect network strategy for RWCE algorithm in heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 34 (4): 445- 452. |
| 13 | 孙涛, 崔国民, 肖媛. 采用结构进化增强策略的RWCE算法优化换热网络[J]. 热能动力工程, 2019, 34 (8): 16- 24. |
| 14 | KHORASANY R M, FESANGHARY M. A novel approach for synthesis of cost-optimal heat exchanger networks[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2009, 33 (8): 1363- 1370. |
| 15 |
HUO Z, ZHAO L, YIN H, et al. Simultaneous synthesis of structural-constrained heat exchanger networks with and without stream splits[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2013, 91 (5): 830- 842.
DOI |
| 16 | ZHANG H, CUI G, XIAO Y, et al. A novel simultaneous optimization model with efficient stream arrangement for heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 110, 1659- 1673. |
| 17 |
VITORPAVÃO L, COSTA C B B, SRAVAGNANI M A S. Heat exchanger network synthesis without stream splits using parallelized and simplified simulated annealing and particle swarm optimization[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 158, 96- 107.
DOI |
| 18 |
ZHANG H, CUI G. Optimal heat exchanger network synthesis based on improved cuckoo search via Lévy flights[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2018, 134, 62- 79.
DOI |
| 19 | SORSAK A, KRAVANJA Z. MINLP retrofit of heat exchanger networks comprising different exchanger types[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2004, 28 (1/2): 235- 251. |
| 20 | ESCOBAR M, TRIERWEILER J O. Optimal heat exchanger network synthesis: A case study comparison[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 51 (1/2): 801- 826. |
| 21 | BAO Z, CUI G, CAO C, et al. Heat exchanger network optimization based on inner utility placement strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 36 (6): 707- 718. |
| 22 | SU G, CUI G, BAO Z, et al. Analysis and treatment on structures with temperature cross in heat exchanger network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2020, 37 (1): 107- 118. |
| 23 | 陈子禾, 崔国民, 陈家星, 等. 参数寻优的多个体平行搜索法应用于换热网络全局最优化[J]. 热能动力工程, 2019, 34 (6): 11- 21. |
| [1] | 韩新宇, 段欢欢, 崔国民, 肖媛, 杨其国, 张冠华. 公用工程灵活匹配的节点非结构拓展模型[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(6): 707-716. |
| [2] | 马秀宝, 盖照亮, 崔国民, 周志强, 韩新宇, 杨其国. 基于强制进化随机游走算法的质量交换网络综合[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 479-490. |
| [3] | 刘凯歌, 韦笃取. 基于WOA-ESN的电机系统混沌振荡预测[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 498-504. |
| [4] | 张璐, 崔国民, 刘薇薇, 肖媛, 徐玥, 张冠华. 基于小负荷换热单元保护的松弛策略优化换热网络[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(3): 352-360. |
| [5] | 刘薇薇, 崔国民, 肖媛, 徐玥, 赵倩倩, 张冠华. 一种采用优势个体多方向强制搜索策略的换热网络优化方法[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(1): 60-70. |
| [6] | 韩新宇, 崔国民, 肖媛, 张冠华, 高远. 动态区域禁忌匹配策略提高新生换热单元竞争力[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(1): 71-82. |
| [7] | 韩正恒, 崔国民, 章伟杰, 赵倩倩, 肖媛, 张冠华. 基于节点非结构模型的换热网络结构多样性分析及改进优化策略[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 479-488. |
| [8] | 赵倩倩, 崔国民, 韩正恒, 肖媛, 徐玥. RWCE算法中选择性接受差解策略优化换热网络[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 489-497. |
| [9] | 屠丽娟, 周恩泽, 吴雪飞, 杨琪, 丁雪峰. 基于流量测点的热网变动阻力系数优化辨识[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 498-504. |
| [10] | 瞿悦呈, 陈家星, 崔国民. 加权差分进化算法应用于换热网络综合[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(1): 79-88. |
| [11] | 张丁太, 崔国民, 李万总, 徐玥. 保护有效结构的整型/连续变量分离优化策略改进RWCE算法[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(1): 89-98. |
| [12] | 徐玥, 崔国民. 应用结构摄动策略的有分流换热网络优化[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(6): 734-744. |
| [13] | 陈皓, 蔡汝铭. 平流层飞艇气动外形优化设计:螺旋桨的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 562-570. |
| [14] | 李万总, 崔国民, 孙涛, 肖媛. 垂直非结构模型应用于换热网络优化[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(4): 448-458. |
| [15] | 姜逸文, 崔国民, 鲍中凯, 刘火林, 周金佳. 一种内部公用工程进化的换热网络优化策略[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(3): 341-351. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
