计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 14-28.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8546
收稿日期:2022-04-22
出版日期:2023-01-25
发布日期:2023-07-04
通讯作者:
尚月强
作者简介:王湛煌,男,硕士研究生,研究方向为偏微分方程数值解与计算流体力学,E-mail:wangzhanhuang1997@163.com
基金资助:
Zhanhuang WANG( ), Bo ZHENG, Yueqiang SHANG*(
), Bo ZHENG, Yueqiang SHANG*( )
)
Received:2022-04-22
Online:2023-01-25
Published:2023-07-04
Contact:
Yueqiang SHANG
摘要:
使用标准的有限元方法求解非定常Navier-Stokes方程所得速度误差常受压力误差影响,且误差随粘性系数的减少而增大。为了增强压力的鲁棒性,本文引入grad-div稳定项,以提高近似解的精度,提出数值求解非定常Navier-Stokes方程的并行两水平grad-div稳定有限元算法,其时间和空间离散分别采用隐式Euler格式和Galerkin有限元方法。首先在全局粗网格上求解非线性grad-div稳定问题,然后在相互重叠的细网格子区域上并行求解grad-div稳定问题,以校正粗网格解。最后给出数值实验验证理论分析的正确性和算法的有效性。
王湛煌, 郑波, 尚月强. 非定常Navier-Stokes方程的并行两水平稳定有限元算法[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(1): 14-28.
Zhanhuang WANG, Bo ZHENG, Yueqiang SHANG. Parallel Two-level Stabilized Finite Element Algorithms for Unsteady Navier-Stokes Equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(1): 14-28.
| 算法 | h | H | CPU/s | Eu | Ep | 收敛阶 |
| 算法3.1 | 1/27 | 1/18 | 7.782 | 2.283 × 10-3 | 2.947 × 10-3 | |
| 1/64 | 1/32 | 23.472 | 4.923 × 10-4 | 4.444 × 10-4 | 2.044 | |
| 1/125 | 1/50 | 62.289 | 1.186 × 10-4 | 1.595 × 10-4 | 2.060 | |
| 算法3.2 | 1/27 | 1/18 | 7.553 | 2.832 × 10-3 | 2.943 × 10-3 | |
| 1/64 | 1/32 | 23.519 | 4.923 × 10-4 | 4.444 × 10-4 | 2.043 | |
| 1/125 | 1/50 | 63.909 | 1.186 × 10-4 | 1.595 × 10-4 | 2.060 | |
| 算法3.3 | 1/27 | 1/18 | 6.86 | 2.833 × 10-3 | 2.931 × 10-3 | |
| 1/64 | 1/32 | 23.222 | 4.934 × 10-4 | 4.456 × 10-4 | 2.041 | |
| 1/125 | 1/50 | 63.645 | 1.191 × 10-4 | 1.586 × 10-4 | 2.059 |
表1 算法3.1~3.3的近似解误差
Table 1 Errors of approximate solutions by Algorithms 3.1-3.3
| 算法 | h | H | CPU/s | Eu | Ep | 收敛阶 |
| 算法3.1 | 1/27 | 1/18 | 7.782 | 2.283 × 10-3 | 2.947 × 10-3 | |
| 1/64 | 1/32 | 23.472 | 4.923 × 10-4 | 4.444 × 10-4 | 2.044 | |
| 1/125 | 1/50 | 62.289 | 1.186 × 10-4 | 1.595 × 10-4 | 2.060 | |
| 算法3.2 | 1/27 | 1/18 | 7.553 | 2.832 × 10-3 | 2.943 × 10-3 | |
| 1/64 | 1/32 | 23.519 | 4.923 × 10-4 | 4.444 × 10-4 | 2.043 | |
| 1/125 | 1/50 | 63.909 | 1.186 × 10-4 | 1.595 × 10-4 | 2.060 | |
| 算法3.3 | 1/27 | 1/18 | 6.86 | 2.833 × 10-3 | 2.931 × 10-3 | |
| 1/64 | 1/32 | 23.222 | 4.934 × 10-4 | 4.456 × 10-4 | 2.041 | |
| 1/125 | 1/50 | 63.645 | 1.191 × 10-4 | 1.586 × 10-4 | 2.059 |
| ν | 算法3.1 | 无稳定项的并行算法 | |||
| Eu | Ep | Eu | Ep | ||
| 1 | 1.126 3 × 10-4 | 6.216 51 × 10-4 | 1.119 99 × 10-4 | 5.582 96 × 10-4 | |
| 10-1 | 1.175 85 × 10-4 | 2.083 03 × 10-4 | 1.126 32 × 10-4 | 2.036 05 × 10-4 | |
| 10-2 | 1.311 98 × 10-4 | 1.933 03 × 10-4 | 1.420 51 × 10-4 | 2.002 67 × 10-4 | |
| 10-3 | 3.479 11 × 10-4 | 1.946 46 × 10-4 | 6.041 92 × 10-4 | 1.984 52 × 10-4 | |
| 10-4 | 5.473 91 × 10-4 | 1.966 75 × 10-4 | 1.536 08 × 10-3 | 1.994 52 × 10-4 | |
| 10-5 | 5.915 42 × 10-4 | 1.970 91 × 10-4 | 1.937 1 × 10-3 | 1.999 92 × 10-4 | |
| 10-6 | 5.968 42 × 10-4 | 1.971 32 × 10-4 | 1.989 61 × 10-3 | 2.000 63 × 10-4 | |
表2 不同ν值下两种算法的误差
Table 2 Errors of two algorithms with different ν
| ν | 算法3.1 | 无稳定项的并行算法 | |||
| Eu | Ep | Eu | Ep | ||
| 1 | 1.126 3 × 10-4 | 6.216 51 × 10-4 | 1.119 99 × 10-4 | 5.582 96 × 10-4 | |
| 10-1 | 1.175 85 × 10-4 | 2.083 03 × 10-4 | 1.126 32 × 10-4 | 2.036 05 × 10-4 | |
| 10-2 | 1.311 98 × 10-4 | 1.933 03 × 10-4 | 1.420 51 × 10-4 | 2.002 67 × 10-4 | |
| 10-3 | 3.479 11 × 10-4 | 1.946 46 × 10-4 | 6.041 92 × 10-4 | 1.984 52 × 10-4 | |
| 10-4 | 5.473 91 × 10-4 | 1.966 75 × 10-4 | 1.536 08 × 10-3 | 1.994 52 × 10-4 | |
| 10-5 | 5.915 42 × 10-4 | 1.970 91 × 10-4 | 1.937 1 × 10-3 | 1.999 92 × 10-4 | |
| 10-6 | 5.968 42 × 10-4 | 1.971 32 × 10-4 | 1.989 61 × 10-3 | 2.000 63 × 10-4 | |
| 子区域数 | Eu | Ep |
| 2 × 2 | 2.283 21 × 10-3 | 2.947 28 × 10-3 |
| 2 × 4 | 2.554 87 × 10-3 | 2.092 27 × 10-3 |
| 4 × 4 | 2.566 64 × 10-3 | 2.133 74 × 10-3 |
表3 不同子区域下算法3.1的误差
Table 3 Errors of Algorithm 3.1 with different subdomains
| 子区域数 | Eu | Ep |
| 2 × 2 | 2.283 21 × 10-3 | 2.947 28 × 10-3 |
| 2 × 4 | 2.554 87 × 10-3 | 2.092 27 × 10-3 |
| 4 × 4 | 2.566 64 × 10-3 | 2.133 74 × 10-3 |
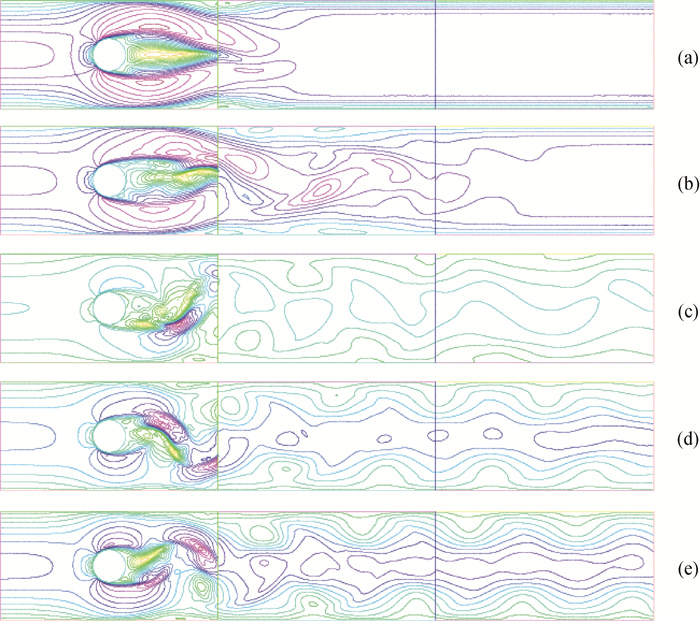
图2 圆柱绕流的速度流线u1 (a) T = 2; (b) T = 4; (c) T = 6; (d) T = 8; (e) T = 10
Fig.2 u1- velocity of a flow around a circular cylinder (a) T = 2; (b) T = 4; (c) T = 6; (d) T = 8; (e) T = 10
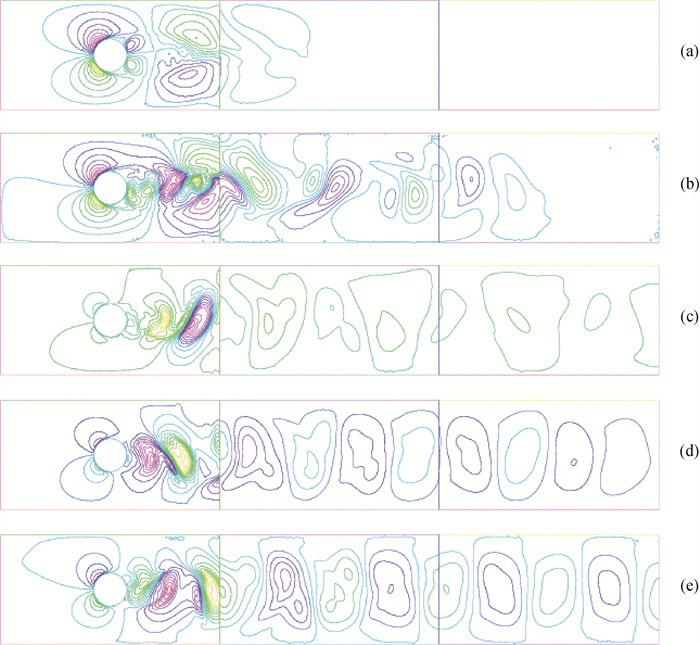
图3 圆柱绕流的速度流线u2 (a) T = 2; (b) T = 4; (c) T = 6; (d) T = 8; (e) T = 10
Fig.3 u2- velocity of a flow around a circular cylinder (a) T = 2; (b) T = 4; (c) T = 6; (d) T = 8; (e) T = 10
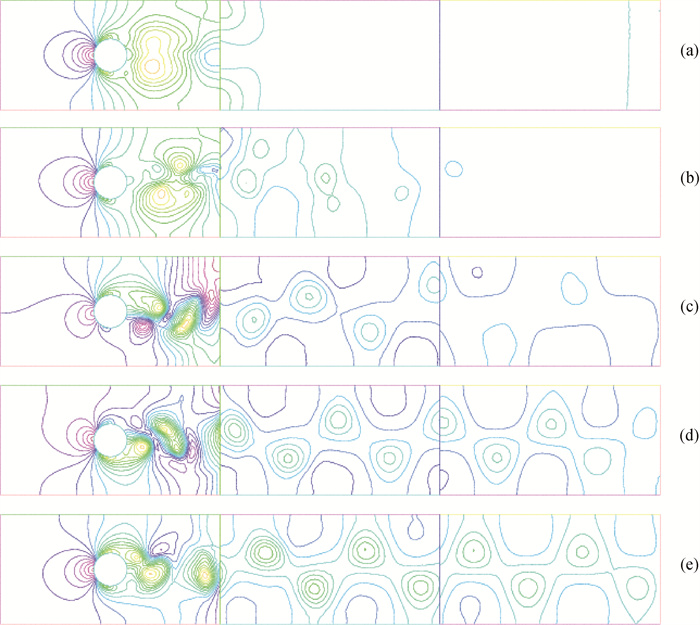
图4 圆柱绕流的等压线(a) T = 2; (b) T = 4; (c) T = 6; (d) T = 8; (e) T = 10
Fig.4 Isobars of a flow around a circular cylinder (a) T = 2; (b) T = 4; (c) T = 6; (d) T = 8; (e) T = 10
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
TEMAM R. Navier-Stokes equations [M]. North-Holland, 1984.
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
DOI |
| [1] | 王国梁, 郑波, 尚月强. 带阻尼项定常Navier-Stokes方程的并行两水平有限元算法[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(5): 535-547. |
| [2] | 胡晓燕, 范征锋. 惯性约束聚变内爆中基于多块结构网格的高效辐射扩散并行算法[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(3): 277-285. |
| [3] | 朱家莉, 尚月强. 不可压缩流的并行两水平稳定有限元算法[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(3): 309-317. |
| [4] | 蔡颖, 张存波, 刘旭, 范征锋, 刘元元, 徐小文, 张爱清. 二维球坐标系中子输运方程的一种并行SN算法[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 143-152. |
| [5] | 丁琪, 尚月强. 非定常Navier-Stokes方程基于两重网格离散的有限元并行算法[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(1): 10-18. |
| [6] | 张庆福, 姚军, 黄朝琴, 李阳, 王月英. 裂缝性介质多尺度深度学习模型[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [7] | 温小静, 屈瑜, 陈城钊. 双层开口环的圆二色性数值研究[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(3): 357-362. |
| [8] | 张守慧, 梁栋. 二维抛物型问题的Strang型交替分段区域分裂格式[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(4): 413-428. |
| [9] | 葛志昊, 吴慧丽. 体积约束的非局部扩散问题的加罚有限元方法[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(2): 161-168. |
| [10] | 杨晓成, 尚月强. 大雷诺数Navier-Stokes方程的两水平亚格子模型稳定化方法[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(6): 657-665. |
| [11] | 朱晓钢, 聂玉峰, 王俊刚, 袁占斌. 分数阶对流扩散方程的特征有限元方法[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 417-424. |
| [12] | 祁美玲, 杨琼, 王苍龙, 田园, 杨磊. 结构材料辐照损伤的分子动力学程序GPU并行化及优化[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 461-467. |
| [13] | 赵国忠, 蔚喜军, 郭怀民. 二维Lagrangian坐标系下可压气动方程组的间断Petrov-Galerkin方法[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(3): 294-308. |
| [14] | 叶珍宝, 朱剑, 周海京. 基于曲四面体单元剖分的CN E-H TDFEM方法[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(6): 652-660. |
| [15] | 叶珍宝, 周海京. 基于高阶叠层矢量基函数的E-H时域有限元方法分析谐振腔和波导结构[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(3): 333-340. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
