Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 389-400.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8567
Received:2022-05-23
Online:2023-05-25
Published:2023-07-22
Contact:
Duqu WEI
Lijun LIU, Duqu WEI. Synchronization of Memristive Rulkov Neural Networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(3): 389-400.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8567
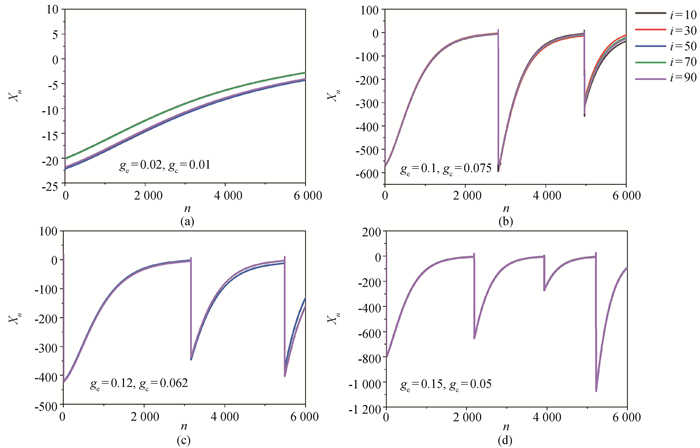
Fig.14 The waveforms of neurons (i = 10, 30, 50, 70, 90) for different ge and gc (a) ge= 0.02、gc= 0.01, (b) ge= 0.1、gc= 0.075, (c) ge= 0.12、gc= 0.062, (d) ge= 0.15、gc= 0.05
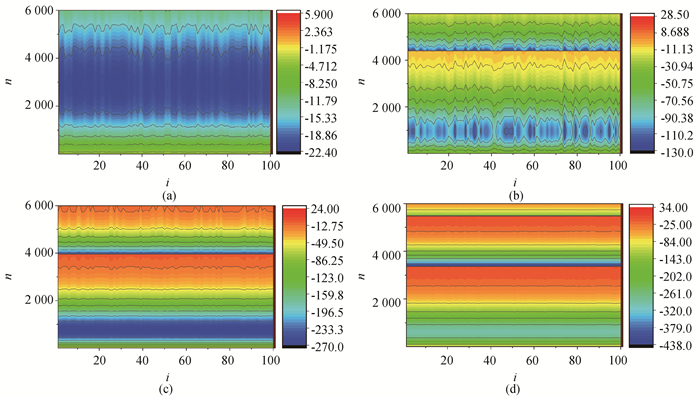
Fig.15 Developed spatial patterns of network for different ge and gc (a) ge= 0.02、gc= 0.01, (b) ge= 0.1、gc= 0.075, (c) ge= 0.12、gc= 0.062, (d) ge= 0.15、gc= 0.05
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
SINGER W. Time as coding space in neocortical processing: A hypothesis[M]. Temporal Coding in the Brain, 1994: 51-79.
|
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
DOI |
| 35 |
DOI |
| 36 |
DOI |
| 37 |
DOI |
| 38 |
DOI |
| 39 |
DOI |
| 40 |
DOI |
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
DOI |
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
DOI |
| 46 |
DOI |
| [1] | Limei LU, Duqu WEI. Firing Activity of Memristive Izhikevich Neural Network Under Electromagnetic Field Coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 490-499. |
| [2] | Weiguang LIANG, Jianbing SANG, Hongyan TIAN, Wenjie DUAN, Yaping TAO, Fengtao LI. Flow Characteristic Analysis of Pipe Flow and Turbulence Model Coefficient Correction Based on Data-driven [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(1): 57-66. |
| [3] | Liang SUN, Jia LUO, Yinhu QIAO. Initial Offset Boosting Dynamics in A Memristive Hopfield Neural Network and Its Application in Image Encryption [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(1): 106-116. |
| [4] | Guozheng WU, Fajie WANG, Suifu CHENG, Chengxin ZHANG. Numerical Simulation of Forward and Inverse Problems of Internal Sound Field Based on Physics-informed Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(6): 687-698. |
| [5] | Cong XIAO, Shicheng ZHANG, Xinfang MA, Tong ZHOU, Tengfei HOU. Model-reduced Autoregressive Neural Network for Parameter Inversion [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 564-578. |
| [6] | Lihong TANG, Zongmei HE, Yanli YAO. Magnetic Induction HR Neuron with Hidden Extreme Multistability and Its Circuit Implementation [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(5): 589-597. |
| [7] | Can HUANG, Leng TIAN, Heng-li WANG, Jia-xin WANG, Li-li JIANG. A Single Well Production Forecasting Model of Reservoir Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Net [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(4): 465-478. |
| [8] | Jian PAN, Zhaoli GUO, Songze CHEN. A Compound Neural Network for Learning Partial Differential Equations from Noisy Data [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(2): 223-232. |
| [9] | Lihong TANG, Zongmei HE, Yanli YAO. Dynamical Analysis and Circuit Implementation of a Memristive Hopfield Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(2): 244-252. |
| [10] | Hong LI, Lixin ZHANG, Yan REN, Ming GAO, Jingnan LIU. Prediction of Water Temperature of Mixed-flow Closed Cooling Tower Based on BP Neural Network and Grey Correlation Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(1): 53-59. |
| [11] | Jia LUO, Liang SUN, Yinhu QIAO. Dynamical Analysis and Circuit Implementation of a Memristor Synapse-coupled Ring Hopfield Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(1): 109-117. |
| [12] | Shuyu ZHENG, Jiazhen PENG, Xianmei ZHANG, Erbing XUE, Limin YU. Prediction of Energy Confinement Time in Tokamak Based on Neural Networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(4): 423-430. |
| [13] | ZHOU Qian, WEI Duqu. Firing Activity of Memristive Neural Network Under Field Coupling [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(6): 750-756. |
| [14] | LU Xinrui, HUANG Handong, LI Shuai, YIN Long. Salt-body Classification Method Based on U-Net [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(3): 327-334. |
| [15] | ZHOU Yuhao, LIU Huiqing, QI Peng, ZHAO Meng, CHEN Yu. Forecast of Oil Production in Fractured-Vuggy Reservoir by Using Recurrent Neural Networks [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2018, 35(6): 668-674. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.

