计算物理 ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 534-542.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8346
所属专题: 多孔介质毛细动力学研究
收稿日期:2021-02-24
出版日期:2021-09-25
发布日期:2022-03-24
作者简介:杨柳(1987-), 男(汉), 副教授, 硕士生导师, E-mail: shidayangliu@cumtb.edu.cn
基金资助:
Liu YANG1( ), Jingwei GAO1, Yuanhan ZHENG1, Xiaomei LI2, Yunfan ZHANG1
), Jingwei GAO1, Yuanhan ZHENG1, Xiaomei LI2, Yunfan ZHANG1
Received:2021-02-24
Online:2021-09-25
Published:2022-03-24
摘要:
采用随机四参数法对非均质砂质砾岩孔隙结构进行重构, 基于改进的SC-LBM(Shan-Chen格子玻尔兹曼)模型研究润湿流体在多孔介质中的渗吸行为。结果表明: 初始阶段的界面动力学与孔隙骨架的排列有很大关系, 会形成以基质为主的渗吸界面; 流体流经孔喉部分时, 流动断面瞬间缩小, 导致压力梯度和流动阻力迅速增加, 孔吼压力的存在导致流动断面瞬间缩小, 提高了流动阻力, 说明孔隙半径变化对渗吸速率影响较大; 后期阶段, 润湿流体会形成优势渗吸通道, 降低了波及面积, 大幅度降低了渗吸驱油速率。研究结果有助于理解流体在非均质孔隙中的自发渗吸规律, 对发挥裂缝性致密油藏渗吸驱油作用具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
杨柳, 高敬威, 郑元涵, 李晓梅, 张云帆. 基于LB方法的非均质砂质砾岩渗吸规律数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 534-542.
Liu YANG, Jingwei GAO, Yuanhan ZHENG, Xiaomei LI, Yunfan ZHANG. Numerical Simulation of Imbibition Law of Heterogeneous Sandy Conglomerate: Lattice Boltzmann Method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(5): 534-542.
| 岩心编号 | 直径/cm | 长度/cm | 孔隙度/% | 渗透率/mD |
| 砂砾岩1 | 2.510 | 4.511 | 6.3 | 3.08 |
| 砂砾岩2 | 2.507 | 4.983 | 3.0 | 0.262 |
| 砂砾岩3 | 2.520 | 6.742 | 7.4 | 0.878 |
| 砂砾岩4 | 3.650 | 3.458 | 5.7 | 0.386 |
表1 新疆砂砾岩样品物性特征
Table 1 Physical characteristics of sandy conglomerate samples in Xinjiang
| 岩心编号 | 直径/cm | 长度/cm | 孔隙度/% | 渗透率/mD |
| 砂砾岩1 | 2.510 | 4.511 | 6.3 | 3.08 |
| 砂砾岩2 | 2.507 | 4.983 | 3.0 | 0.262 |
| 砂砾岩3 | 2.520 | 6.742 | 7.4 | 0.878 |
| 砂砾岩4 | 3.650 | 3.458 | 5.7 | 0.386 |
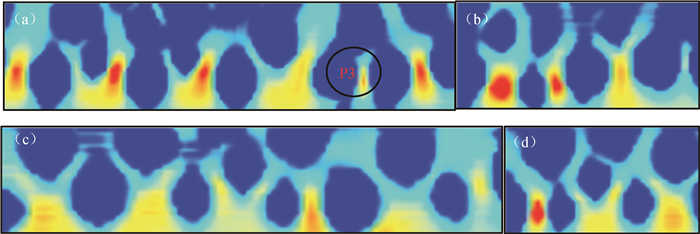
图11 不同时间步长下流体在基质中的运移渗吸行为(a)1 000;(b)10 000;(c)50 000;(d)105步长
Fig.11 Migration and imbibition behavior of fluid in the matrix at (a)1 000; (b)10 000; (c)50 000; (d)105 steps
| 1 |
STUKAN M R, LIGNEUL P, CRAWSHAW J P, et al. Spontaneous imbibition in nanopores of different roughness and wettability[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26 (16): 13342- 13352.
DOI |
| 2 | 杨文, 李建良, 刘刚, 等. 多因素影响下Y型管内流动状态数值模拟研究[J]. 油气田地面工程, 2020, 39 (03): 27- 34. |
| 3 |
YU Mengping, WU Dagang, CHEN Yanjun, et al. Electromagnetic rock properties' characterization and modeling using 3D micro-CT rock images[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 2020, 34 (8): 1073- 1089.
DOI |
| 4 |
TANG Xuelin, YANG Shangyu, WANG Fujun. Researches on two-phase flows around a hydrofoil using Shan-Chen multi-phase LBM model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2016, 30 (2): 575- 584.
DOI |
| 5 |
ABED Z, MAHNUD A. A multiple relaxation time extension of the constant speed kinetic model[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 2016, 27 (8): 1650088.
DOI |
| 6 | SHANGGUAN Yanqin, WANG Xian, LI Yueming. Hing-performance numerical simulation of jet in cross-flow based on lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2015, 32 (6): 669- 676. |
| 7 | LEI Timan, MENG Xuhui, GUO Zhaoli. Lattice Boltzmann study on influence of chemical reaction on mixing of miscible fluids with viscous instability in porous media[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 33 (4): 399- 409. |
| 8 | JU Long, ZHANG Chunhua, CHEN Songze, et al. Lattice Boltzmann study on displacement process of thermal miscible fluids in porous media[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 36 (6): 648- 658. |
| 9 | HU Yu, SUN Tao. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of dynamics characteristics of two rising bubbles with lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2020, 37 (3): 277- 283. |
| 10 | GHARIBI F, ASHRAFIZAADEH M. Simulation of high-viscosity-ratio multicomponent fluid flow using a pseudopotential model based on the nonorthogonal central-moments lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Physical Review E, 2020, 101 (4-1): 043311. |
| 11 |
MEHRDAD A, ANDREA P, PAOLO R D, et al. A lattice-Boltzmann study of permeability-porosity relationships and mineral precipitation patterns in fractured porous media[J]. Computational Geosciences, 2020, 24 (5): 1865- 1882.
DOI |
| 12 | 何雅玲, 王勇, 李庆. 格子Boltzmann方法的理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008. |
| 13 | 郭照立, 郑楚光, 李青, 等. 流体动力学的格子Boltzmann方法[M]. 武汉: 湖北科学技术出版社, 2002. |
| 14 | LI Pei, BERKOWITZ B. Characterization of mixing and reaction between chemical species during cycles of drainage and imbibition in porous media[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2019, 130 (8): 113- 128. |
| 15 |
SEBASTINE L, ANDREA P, BASTINE C, et al. Three-dimensional lattice Boltzmann method benchmarks between color-gradient and pseudo-potential immiscible multi-component models[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 2017, 28 (7): 1750085.
DOI |
| 16 | ZHANG Tao, SUN Shuyu. A coupled lattice Boltzmann approach to simulate gas flow and transport in shale reservoirs with dynamic sorption[J]. Fuel, 2019, 246 (2): 196- 203. |
| 17 | AKSHAY G, TAYFUN B, SUSSANTA S Y, et al. Pore-scale interfacial dynamics and oil-water relative permeabilities of capillary driven counter-current flow in fractured porous media[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2013, 103 (2): 106- 114. |
| 18 |
WIKLUND H S, UESAKA T. Microfluidics of imbibition in random porous media[J]. Physical Review E, 2013, 87 (2): 023006.
DOI |
| 19 | LIU Yang, CAI Jianchao, MUHAMMAD S, et al. A study of the role of microfractures in counter-current spontaneous imbibition by lattice Boltzmann simulation[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2020, 133 (5): 313- 32. |
| 20 | 张戈, 冯程远, 龚文波, 等. 粗糙元对单裂隙渗流影响的格子Boltzmann方法模拟及分析[J]. 中国科学: 物理学, 力学, 天文学, 2017, 47 (02): 68- 79. |
| 21 |
GHASEMI F, GHAEDI M, ESCROCHI M. A new scaling equation for imbibition process in naturally fractured gas reservoirs[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2020, 4 (1): 99- 106.
DOI |
| 22 |
SHENG G, SU Y, ZHAO H, et al. A unified apparent porosity/permeability model of organic porous media: Coupling complex pore structure and multi-migration mechanism[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2020, 4 (2): 115- 125.
DOI |
| 23 | CAROLINA M G, BELEN G F, DIEGO F, et al. Impact of mussel shell aggregates on air lime mortars: Pore structure and carbonation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 215 (10): 650- 668. |
| 24 |
HUANG Haibo, LI Zhitao, LIU Shuaishuai, et al. Shan-and-Chen-type multiphase lattice Boltzmann study of viscous coupling effects for two-phase flow in porous media[J]. Int J Numer Meth Fluids, 2009, 61 (3): 341- 354.
DOI |
| 25 | BAGDAGUL D, LUIS R, ROJAS S, et al. Numerical simulation of diffusion process in T-shaped micromixer using Shan-Chen lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Computers and Fluids, 2018, 167 (8): 229- 240. |
| 26 | 何雅玲, 李庆, 王勇, 等. 格子Boltzmann方法的工程热物理应用[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54 (18): 2638- 2656. |
| 27 | 赵伟峰. 格子Boltzmann方法的理论分析和边界处理[D]. 北京: 中国工程物理研究院, 2017: 139. |
| 28 | AKSHAY G, TAYFUN B, SUSANTA S R. Pore-scale interfacial dynamics and oil-water relative permeabilities of capillary driven counter-current flow in fractured porous media[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2013, 103 (3): 106- 114. |
| 29 |
李仁民, 刘松玉, 方磊, 等. 采用随机生长四参数生成法构造黏土微观结构[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2010, 44 (10): 1897- 1901.
DOI |
| 30 | 李祯. 致密储层中流体流动的LBM模拟[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2016: 73. |
| 31 | ZHENG Jiangtao, CHEN Zhiqiang, XIE Chiyu, et al. Characterization of spontaneous imbibition dynamics in irregular channels by mesoscopic modeling[J]. Computers and Fluids, 2018, 168 (9): 21- 31. |
| 32 |
YANG L, WANG S, CAI Jianchao, et al. Main controlling factors of fracturing fluid imbibition in shale fracture network[J]. Capillarity, 2018, 1 (1): 1- 10.
DOI |
| 33 | 蔡建超, 郁伯铭. 多孔介质自发渗吸研究进展[J]. 力学进展, 2012, 42 (06): 735- 754. |
| [1] | 冯舒婷, 戴厚平, 宋通政. 二维空间分数阶反应扩散方程组的格子Boltzmann方法[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(6): 666-676. |
| [2] | 刘嘉鑫, 郑林, 张贝豪. 多孔介质方腔内双扩散自然对流熵产的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 549-563. |
| [3] | 林品亮, 冯欢欢, 董宇红. 具有多孔介质覆面层的柱体绕流流场分析[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 418-426. |
| [4] | 张巧玲, 景何仿. 三维曲面腔顶盖驱动流的MRT-LBM研究[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 427-439. |
| [5] | 陈露, 高明, 梁佳, 王东民, 赵玉刚, 章立新. 润湿梯度作用下液滴在倾斜表面向上运动的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(6): 672-682. |
| [6] | 魏雪丹, 戴厚平, 李梦军, 郑洲顺. 一维空间Riesz分数阶对流扩散方程的格子Boltzmann方法[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(6): 683-692. |
| [7] | 蔡建超. 多孔介质自发渗吸关键问题与思考[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 505-512. |
| [8] | 张震杰, 冯建园, 蔡建超, 陈康力, 孟庆帮. 不同边界条件下的渗吸驱动因素[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 513-520. |
| [9] | 郑江韬, 贾宁洪, 胡慧芳, 杨勇, 鞠杨, 王沫然. 分支通道内液-液自发渗吸规律研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 543-554. |
| [10] | 朱云轩, 李治平. 彭水地区龙马溪组页岩渗吸规律及渗吸动态分布[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 555-564. |
| [11] | 郭建春, 陶亮, 陈迟, 赵玉航, 何颂根, 刘彧轩. 川南龙马溪组页岩储层水相渗吸规律[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 565-572. |
| [12] | 娄钦, 汤升, 王浩原. 基于格子Boltzmann大密度比模型的多孔介质内气泡动力学行为数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(3): 289-300. |
| [13] | 梁佳, 高明, 陈露, 王东民, 章立新. 液滴撞击不同湿润性固壁面上静止液滴的格子Boltzmann研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(3): 313-323. |
| [14] | 袁俊杰, 叶欣, 单彦广. 格子Boltzmann方法模拟填充纳米流体三角形腔内的自然对流[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(1): 57-68. |
| [15] | 冯玲玲, 徐洪涛, 王迪, 罗祝清. 活性炭吸附甲醛的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(1): 69-78. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
