Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 193-202.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8701
Previous Articles Next Articles
Boyao WEN1( ), Genying GAO2, Xi LU3, Songtao GUAN4, Zhengyuan LUO1, Bofeng BAI1,*(
), Genying GAO2, Xi LU3, Songtao GUAN4, Zhengyuan LUO1, Bofeng BAI1,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-08
Online:2024-03-25
Published:2024-04-03
Contact:
Bofeng BAI
CLC Number:
Boyao WEN, Genying GAO, Xi LU, Songtao GUAN, Zhengyuan LUO, Bofeng BAI. Ionic Regulation Mechanisms of Surfactant Desorption from the Spherical Micelles[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(2): 193-202.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8701
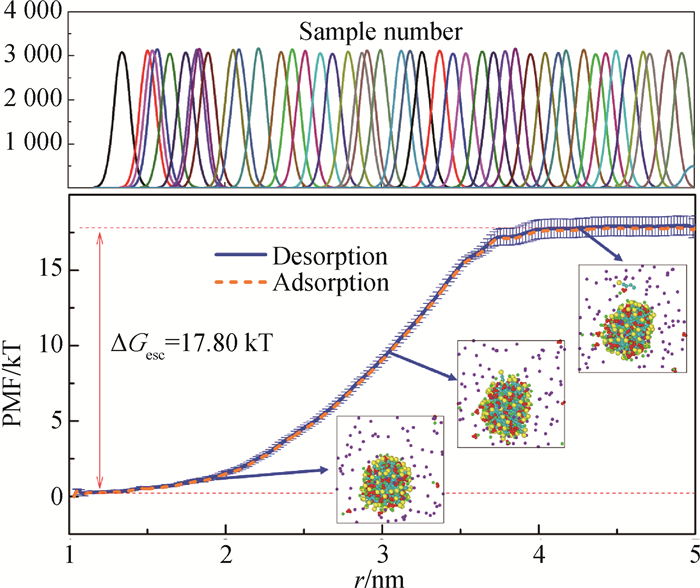
Fig.2 PMF profiles and sampling histogram of surfactant adsorption and desorption processes at or from the spherical micelle (CTAC/NaSal system, N = 80, R = 1.0)
| Rg/nm | Rs/nm | |
| Our simulation results | 1.55±0.05 | 2.00±0.06 |
| Ref.[ | 1.55±0.30 | 1.98±0.27 |
| Ref.[ | 1.50 | 1.96 |
| Ref.[ | 1.58 | 1.90 |
| Ref.[ | 1.64 | 1.99 |
| Ref.[ | 1.60±0.06 | 1.97±0.08 |
| Ref.[ | 1.54 | 2.00 |
Table 1 Structural properties of SDS spherical micelles (N = 60, R = 0)
| Rg/nm | Rs/nm | |
| Our simulation results | 1.55±0.05 | 2.00±0.06 |
| Ref.[ | 1.55±0.30 | 1.98±0.27 |
| Ref.[ | 1.50 | 1.96 |
| Ref.[ | 1.58 | 1.90 |
| Ref.[ | 1.64 | 1.99 |
| Ref.[ | 1.60±0.06 | 1.97±0.08 |
| Ref.[ | 1.54 | 2.00 |
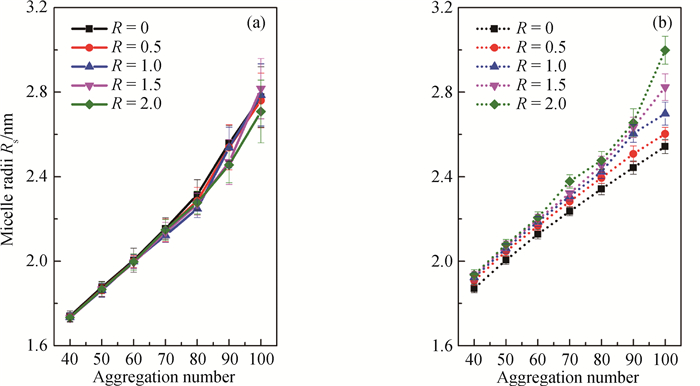
Fig.3 Micelle radius of spherical micelle with different aggregation number and salt-to-surfactant concentration ratio (a) SDS/NaCl system; (b) CTAC/NaSal system
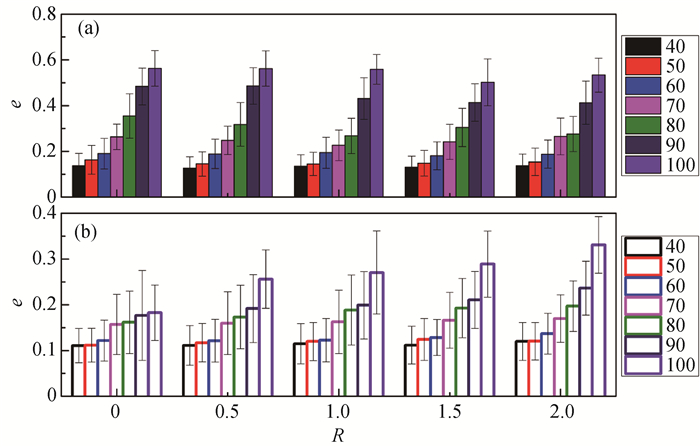
Fig.4 Eccentricities e of spherical micelles with different aggregation number and salt-to-surfactant concentration ratio (a) SDS/NaCl system; (b) CTAC/NaSal system
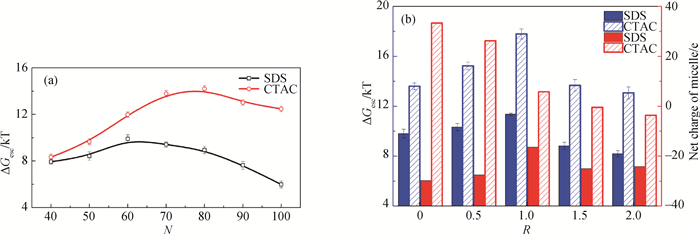
Fig.5 Desorption free energy of surfactant from spherical micelle with different aggregation number and salt-to-surfactant concentration ratio (a) aggregation number; (b) salt-to-surfactant concentration ratio on desorption free energy and net charge of micelle
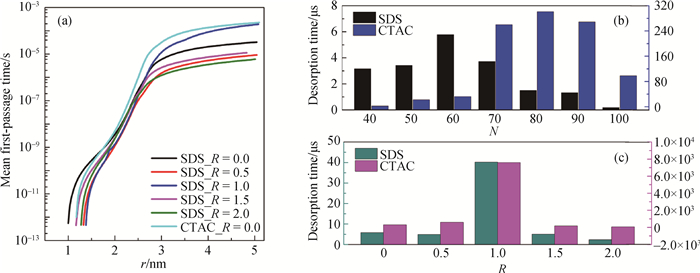
Fig.6 Mean first-passage time profiles and desorption time of SDS molecules from the interfaces (a) mean first-passage time of SDS molecules from the oil-water interfaces with different adsorbed numbers; (b) desorption time of SDS molecules from interfaces with different adsorbed numbers; (c) effects of ionic species and concentrations on the desorption time of SDS molecules
| 1 |
DHAKAL S , SURESHKUMAR R . Topology, length scales, and energetics of surfactant micelles[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 143 (2): 024905.
DOI |
| 2 | 杨少东, 叶学民, 李春曦. 活性剂浓度分布对液膜排液过程的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35 (5): 577- 586. |
| 3 |
BALLAUFF M . Self-assembly creates 2D materials[J]. Science, 2016, 352 (6286): 656- 657.
DOI |
| 4 |
LI Qintang , WANG Jiao , LEI Nana , et al. Phase behaviours of a cationic surfactant in deep eutectic solvents: From micelles to lyotropic liquid crystals[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20 (17): 12175- 12181.
DOI |
| 5 | 王雯婷, 尹慧瑾, 潘俊星, 等. 光掩膜诱导的聚合物/纳米粒子共混体系的自组装计算机模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39 (5): 598- 608. |
| 6 | LARSSON J , SANCHEZ-FERNANDEZ A , LEUNG A E , et al. Molecular structure of maltoside surfactants controls micelle formation and rheological behavior[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 581 (Pt B): 895- 904. |
| 7 |
SAMBASIVAM A , SANGWAI A V , SURESHKUMAR R . Dynamics and scission of rodlike cationic surfactant micelles in shear flow[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 114 (15): 158302.
DOI |
| 8 |
AMANN M , WILLNER L , STELLBRINK J , et al. Studying the concentration dependence of the aggregation number of a micellar model system by SANS[J]. Soft Matter, 2015, 11 (21): 4208- 4217.
DOI |
| 9 | ZANA R . Dynamics of surfactant self-assemblies: Micelles, microemulsions, vesicles and lyotropic phases[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2005. |
| 10 |
PATIST A , KANICKY J R , SHUKLA P K , et al. Importance of micellar kinetics in relation to technological processes[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 245 (1): 1- 15.
DOI |
| 11 |
OH S G , SHAH D O . Micellar lifetime: Its relevance to various technological processes[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 1994, 15 (3): 297- 316.
DOI |
| 12 |
SHCHEKIN A K , ADZHEMYAN L T , BABINTSEV I A , et al. Kinetics of aggregation and relaxation in micellar surfactant solutions[J]. Colloid Journal, 2018, 80 (2): 107- 140.
DOI |
| 13 |
WATON G . Kinetics associated with the change of the number density of micelles in solution[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1997, 101 (47): 9727- 9731.
DOI |
| 14 |
ANIANSSON E A G , WALL S N . Kinetics of step-wise micelle association[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1974, 78 (10): 1024- 1030.
DOI |
| 15 |
BECKER R , DÖRING W . Kinetische behandlung der keimbildung in übersättigten dämpfen[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1935, 416 (8): 719- 752.
DOI |
| 16 |
SHCHEKIN A K , BABINTSEV I A , ADZHEMYAN L T . Full-time kinetics of self-assembly and disassembly in micellar solution via the generalized Smoluchowski equation with fusion and fission of surfactant aggregates[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2016, 145 (17): 174105.
DOI |
| 17 | 史晓蕊, 刘振宇, 吴慧英. 纳米孔壁面作用对蛋白质过孔影响的粗粒化分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37 (1): 63- 68. |
| 18 |
SAMMALKORPI M , KARTTUNEN M , HAATAJA M . Micelle fission through surface instability and formation of an interdigitating stalk[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130 (52): 17977- 17980.
DOI |
| 19 | 曹仁义, 黄涛, 程林松, 等. 水驱油藏中原油极性物质对吸附和润湿性影响的分子模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38 (5): 595- 602. |
| 20 | 俞宏伟, 李实, 李金龙, 等. 气驱油油气混相过程的界面传质特性及其分子机制[J]. 物理化学学报, 2022, 38 (5): 2006061. |
| 21 |
BROCOS P , MENDOZA-ESPINOSA P , CASTILLO R , et al. Multiscale molecular dynamics simulations of micelles: Coarse-grain for self-assembly and atomic resolution for finer details[J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8 (34): 9005- 9014.
DOI |
| 22 |
JUSUFI A , PANAGIOTOPOULOS A Z . Explicit- and implicit-solvent simulations of micellization in surfactant solutions[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31 (11): 3283- 3292.
DOI |
| 23 |
YUAN Fang , WANG Shihu , LARSON R G . Potentials of mean force and escape times of surfactants from micelles and hydrophobic surfaces using molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31 (4): 1336- 1343.
DOI |
| 24 |
WEN Boyao , BAI Bofeng , LARSON R G . Surfactant desorption and scission free energies for cylindrical and spherical micelles from umbrella-sampling molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 599, 773- 784.
DOI |
| 25 | 温伯尧, 杨海中, 姚秀田, 等. 油水界面上表面活性剂的脱附动力学及其离子调控[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67 (25): 3088- 3096. |
| 26 |
SANGWAI A V , SURESHKUMAR R . Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations of the sphere to rod transition in surfactant micelles[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27 (11): 6628- 6638.
DOI |
| 27 |
RUSSO KRAUSS I , CAVASSO D , CICCARELLI D , et al. A hofmeister series perspective on the mixed micellization of cationic and non-ionic surfactants[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 335, 116205.
DOI |
| 28 |
SOUZA P C T , ALESSANDRI R , BARNOUD J , et al. Martini 3: A general purpose force field for coarse-grained molecular dynamics[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18 (4): 382- 388.
DOI |
| 29 | GROSSFIELD A. WHAM: The weighted histogram analysis method, version 2.0[Z]. 2018. |
| 30 |
WANG Shihu , LARSON R G . Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulation of self-assembly and surface adsorption of ionic surfactants using an implicit water model[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31 (4): 1262- 1271.
DOI |
| 31 |
PALAZZESI F , CALVARESI M , ZERBETTO F . A molecular dynamics investigation of structure and dynamics of SDS and SDBS micelles[J]. Soft Matter, 2011, 7 (19): 9148- 9156.
DOI |
| 32 |
SHANG B Z , WANG Zuowei , LARSON R G . Molecular dynamics simulation of interactions between a sodium dodecyl sulfate micelle and a poly(ethylene oxide) polymer[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2008, 112 (10): 2888- 2900.
DOI |
| 33 |
RAKITIN A R , PACK G R . Molecular dynamics simulations of ionic interactions with dodecyl sulfate micelles[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108 (8): 2712- 2716.
DOI |
| 34 |
MACKERELL A D Jr . Molecular dynamics simulation analysis of a sodium dodecyl sulfate micelle in aqueous solution: Decreased fluidity of the micelle hydrocarbon interior[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1995, 99 (7): 1846- 1855.
DOI |
| 35 |
ITRI R , AMARAL L Q . Distance distribution function of sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles by x-ray scattering[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1991, 95 (1): 423- 427.
DOI |
| 36 |
TANG Xueming , KOENIG P H , LARSON R G . Molecular dynamics simulations of sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles in water-the effect of the force field[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2014, 118 (14): 3864- 3880.
DOI |
| [1] | GAO Xudong, SUN Shuyi, WEI Wenjing, LI Gongping. A Simulation Study on Irradiation Damage of Rutile TiO2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(2): 214-221. |
| [2] | Yu LI, Huiqing LIU, Yabin FENG, Xiaohu DONG, Qing WANG, Bo ZHANG. Adsorption Behavior of Heavy Oil on Montmorillonite Surface by Typical Surfactant: Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 583-596. |
| [3] | Zhaozhao WEI, Kai LIU, Huijun LI. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Deformation Behavior of NiAl Nanowire Under Bending [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 425-435. |
| [4] | Zhaoyang HOU, Yuan NIU, Qixin XIAO, Zhen WANG, Qingtian DENG. Simulation of Mechanical Behavior and Deformation Mechanism of Al Nanowires Along Different Crystal Orientations [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(3): 341-351. |
| [5] | Xiaohui WANG, Ping ZHANG. Structural Stability and Anharmonic Effect of Metallic Hydrogen FCC Phase Under High Pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(2): 159-164. |
| [6] | Hubao A, Zhibing YANG, Ran HU, Yifeng CHEN. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Capillary Dynamics at the Nanoscale [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(5): 603-611. |
| [7] | WANG Guohua, CUI Yaru, YANG Ze, LI Xiaoming, TANG Hongliang, YANG Shufeng. Potential Function and Molecular Dynamics Simulation for FexO-SiO2-CaO-MgO-“NiO” Nickel Slag [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(2): 215-223. |
| [8] | WANG Xuemei, DONG Bin, ZHU Ziliang, YANG Junsheng. Interfacial Interaction and Diffusion Properties of Functionalized CNT/Polymer Systems: Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(5): 589-594. |
| [9] | HE Erbin, LUO Zhirong, ZHU Liuhua. Atomistic Analysis of Myoglobin Mechanical Unfolding [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(2): 205-211. |
| [10] | ZHOU Lu, MA Honghe. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on Crystallization Kinetics of Sodium Sulfate in Supercritical Water [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(2): 212-220. |
| [11] | SHI Xiaorui, LIU Zhenyu, WU Huiying. Coarse-grained MD Simulation of Nanopore Interaction Influence on Protein Translocation [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2020, 37(1): 63-68. |
| [12] | CHAI Rukuan, LIU Yuetian, WANG Junqiang, XIN Jing, PI Jian, LI Changyong. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Wettability of Calcite and Dolomite [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(4): 474-482. |
| [13] | WANG Shuaichuang, ZHANG Gongmu, SUN Bo, SONG Haifeng, TIAN Mingfeng, FANG Jun, LIU Haifeng. Quantum Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Transport Properties of Liquid Plutonium [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(3): 253-258. |
| [14] | LIANG Hua, LI Maosheng. Molecular Dynamics Study of Mechanical Properties of Single Crystal Aluminum with Voids and Vacancies [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(2): 211-218. |
| [15] | ZHANG Haiyan, YIN Xinchun. Molecular Dynamics Study on Growth Mechanism of Pure Metals Solid-Liquid Interface During Solidification [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS, 2019, 36(1): 80-88. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
