计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 490-499.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8582
收稿日期:2022-06-28
出版日期:2023-07-25
发布日期:2023-10-13
通讯作者:
韦笃取
作者简介:陆丽梅(1999-), 硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为忆阻神经网络动力学行为分析与控制
基金资助:Received:2022-06-28
Online:2023-07-25
Published:2023-10-13
Contact:
Duqu WEI
摘要:
考虑到电磁场的影响, 在Izhikevich神经元模型中引入电场变量和磁通变量, 利用电突触耦合构建神经网络, 研究电磁场耦合忆阻Izhikevich神经网络集体动力学行为。数值仿真发现: 随着电突触耦合强度的增大, 神经网络逐渐达到同步状态, 并且神经元的放电模式也会随之改变。增大磁场耦合值可以提高神经元的放电活性, 并且对网络同步也有一定的促进作用, 而增大电场则会抑制神经元的放电活动。另外, 当电突触与磁场耦合共同作用时, 磁场耦合值越小, 电突触耦合更能有效促进网络同步; 在电突触耦合强度的作用下, 电场抑制电活动的效果更明显。研究结果可望为理解神经系统中的信号编码和传递提供新的见解。
陆丽梅, 韦笃取. 电磁场耦合忆阻Izhikevich神经网络电活动研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 490-499.
Limei LU, Duqu WEI. Firing Activity of Memristive Izhikevich Neural Network Under Electromagnetic Field Coupling[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 490-499.
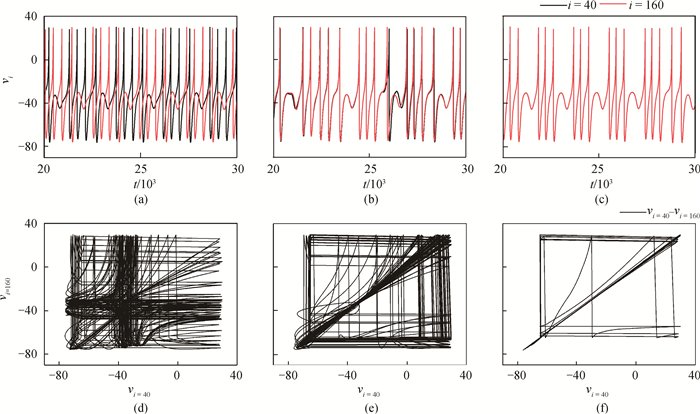
图1 不同gb值下,神经元(i=40, 160)放电活动,gc=0,r=0。(a)~(c)分别为gb=0.005,0.015,0.05时神经元的膜电位时间序列;(d)~(f)分别为gb=0.005,0.015,0.05时神经元的相平面图。
Fig.1 The firing activity of neurons (i=40, 160) for different gb with gc=0, r=0. (a)~(c) are the time series of membrane potential of neurons when gb=0.005, 0.015, 0.05, respectively. (d)~(f) are the phase plans of neurons when gb=0.005, 0.015, 0.05, respectively.
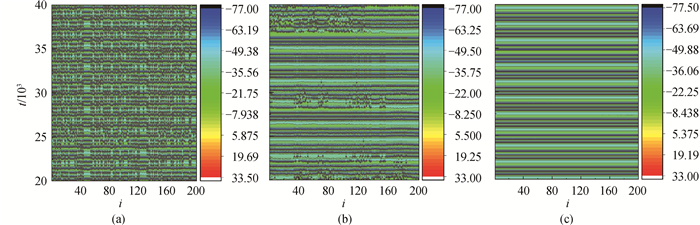
图2 不同gb值下,神经网络时空图(gc=0,r=0) (a)gb=0.005;(b)gb=0.015;(c)gb=0.05
Fig.2 Developed spatial patterns of network for different gb with gc=0, r=0 (a)gb=0.005; (b)gb=0.015; (c)gb=0.05
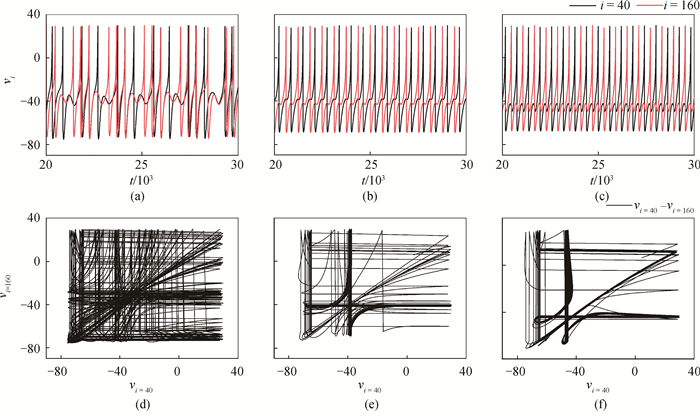
图3 不同gc值下,神经元(i=40, 160)放电活动,gb=0,r=0。(a)~(c)分别为gc=0.005,0.01,0.1时神经元的膜电位时间序列;(d)~(f)分别为gc=0.005,0.01,0.1时神经元的相平面图。
Fig.3 The firing activity of neurons (i=40, 160) for different gc with gb=0, r=0. (a)~(c) are the time series of membrane potential of neurons when gc=0.005, 0.01, 0.1, respectively; (d)~(f) are the phase plans of neurons when gc=0.005, 0.01, 0.1, respectively.
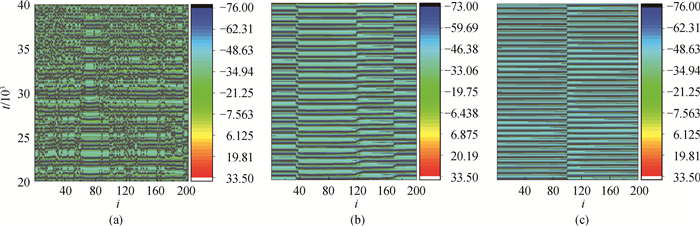
图4 不同gc值下,神经网络时空图(gb=0,r=0) (a)gc=0.005;(b)gc=0.01;(c)gc=0.1
Fig.4 Developed spatial patterns of network for different gc with gb=0, r=0 (a)gc=0.005; (b)gc=0.01; (c)gc=0.1
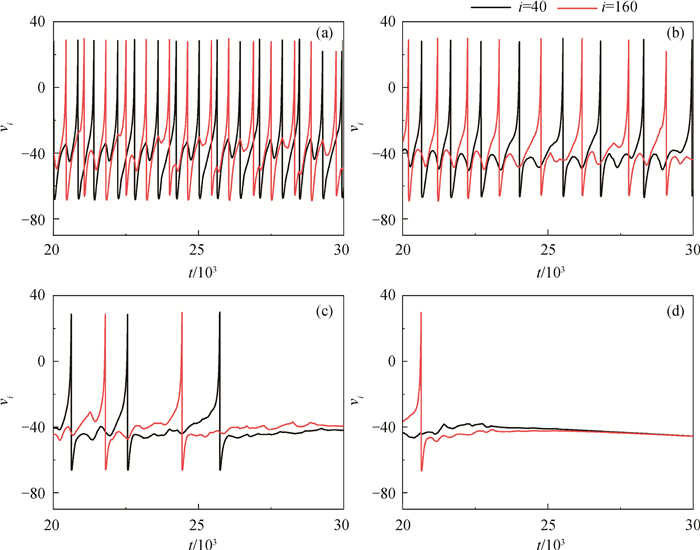
图6 不同r值下,神经元(i=40, 160)的膜电位时间序列(gb=0.02,gc=0.01) (a) r=0.000 01;(b) r=0.000 05;(c) r=0.000 08;(d) r=0.000 1
Fig.6 The time series of membrane potential of neurons(i=40, 160) for different r with gb=0.02, gc=0.01 (a) r=0.000 01; (b) r=0.000 05; (c) r=0.000 08; (d) r=0.000 1
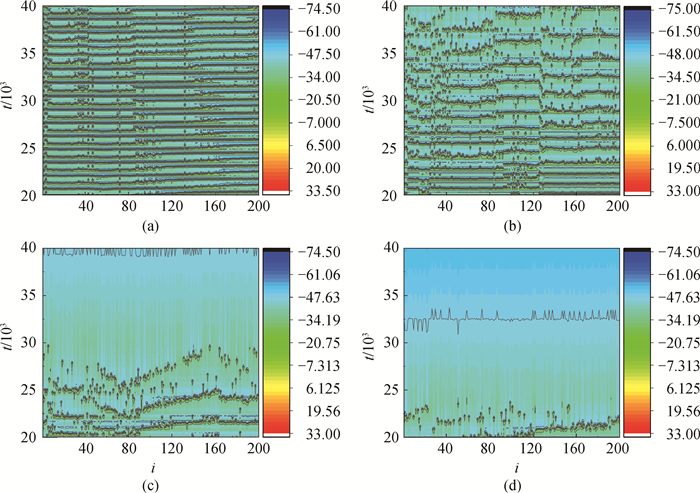
图7 不同r值下,神经网络的时空图(gb=0.02,gc=0.01) (a) r=0.000 01;(b) r=0.000 05;(c) r=0.000 08;(d) r=0.000 1
Fig.7 Developed spatial patterns of network for different r with gb=0.02, gc=0.01 (a) r=0.000 01; (b) r=0.000 05; (c) r=0.000 08; (d) r=0.000 1
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
DOI |
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
DOI |
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
DOI |
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
DOI |
| 35 |
DOI |
| 36 |
DOI |
| 37 |
DOI |
| 38 |
DOI |
| 39 |
DOI |
| 40 |
DOI |
| [1] | 李德奎, 毛北行. 时滞干扰环状网络的修正函数投影同步及仿真[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(5): 643-652. |
| [2] | 曹文鑫, 韦笃取. 基于NG-RC电机系统的混沌预测[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 519-526. |
| [3] | 马秀宝, 崔国民, 周志强, 肖媛, 徐玥, 杨其国. 带有个体淘汰的强制进化随机游走算法优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(3): 376-388. |
| [4] | 刘丽君, 韦笃取. 忆阻Rulkov神经网络同步研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(3): 389-400. |
| [5] | 李震波, 唐叶芝. 高维混沌系统的多元函数投影同步及其保密通信方案[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(1): 91-105. |
| [6] | 高正, 邹艳丽, 胡均万, 姚高华, 刘唐慧美. 基于复杂网络理论的电网耦合强度分配策略[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 579-588. |
| [7] | 刘凯歌, 韦笃取. 基于WOA-ESN的电机系统混沌振荡预测[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 498-504. |
| [8] | 张少泽, 邹艳丽, 谭秫毅, 李浩乾, 刘欣妍. 基于复杂网络理论的互联电网Braess悖论现象分析[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 233-243. |
| [9] | 邹艳丽, 高正, 梁明月, 李志慧, 何铭. 基于潮流追踪的电网同步性能优化及鲁棒性分析[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 623-630. |
| [10] | 石建平, 李培生, 刘国平. 基于改进克隆选择算法的统一混沌系统同步控制与参数辨识[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 240-252. |
| [11] | 钟国翔, 韦笃取, 张波. 分布式发电系统感性负载的远程混沌同步[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(6): 719-725. |
| [12] | 邹艳丽, 王瑞瑞, 吴凌杰, 姚飞, 汪洋. 基于局部序参数的电网同步性能优化[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(4): 498-504. |
| [13] | 石建平, 杨兰天, 刘丹. 基于量子粒子群算法的混沌系统同步控制及参数辨识[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(2): 236-244. |
| [14] | 查进道, 李春彪. 基于引力场理论的混沌同步[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 737-749. |
| [15] | 刘利花, 韦笃取, 张波. 基于动力中继的小世界复杂电机网络混沌同步控制[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 750-756. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发

