计算物理 ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 65-76.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8822
收稿日期:2023-08-28
出版日期:2025-01-25
发布日期:2025-03-08
通讯作者:
娄钦
作者简介:孙书宝, 男, 硕士研究生, 研究方向为多孔介质内反应流, E-mail: sunshubao2021@163.com
基金资助:
Shubao SUN( ), Qin LOU*(
), Qin LOU*( )
)
Received:2023-08-28
Online:2025-01-25
Published:2025-03-08
Contact:
Qin LOU
摘要:
基于格子Boltzmann方法在表征单元体积(REV)尺度下模拟串列多孔CaO颗粒吸收CO2化学反应过程, 主要研究CaO颗粒孔隙率、颗粒直径、颗粒间排列方式对颗粒转化效率和平均转化率的影响。结果表明: CaO颗粒转化效率随其孔隙率增加呈现先减小再增大的趋势, 这是由于不同的孔隙率导致颗粒初始物质的量和内部气固反应速率不同, 二者竞争进而影响转化效率。另一方面, 颗粒直径越大, 转化效率越低, 粒径50 μm的颗粒比粒径150 μm的颗粒平均转化效率提高了8.4%, 粒径150 μm的颗粒比粒径250 μm的颗粒平均转化效率提高了7.2%。研究颗粒排列方式对平均转化率的影响发现: 当颗粒间水平夹角θ=0°~10°, 由于回流涡的影响使得平均转化率随角度增加不能得到有效提升; 当θ=10°~40°, 后方CaO颗粒逐渐远离回流区, 使得平均转化率随角度增加得到显著提升; 当水平夹角大于40°时, CaO颗粒完全脱离回流区, 此时平均转化率达到最大且不随角度发生变化, 模拟结果可以为CO2捕捉提供一定的参考依据。
孙书宝, 娄钦. 表征单元体积尺度下多个CaO颗粒吸收CO2的介观数值方法[J]. 计算物理, 2025, 42(1): 65-76.
Shubao SUN, Qin LOU. Mesoscopic Simulation of CO2 Absorption by Tandem Porous CaO Particles at REV Scale[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2025, 42(1): 65-76.
| 物理量 | 物理量符号 | 物理单位 | 格子单位 | 转换因子 |
| 计算域长度 | Lx | 3.6×10-3 m | 720 | 5×10-6 m |
| 计算域高度 | Ly | 1.8×10-3 m | 360 | 5×10-6 m |
| 颗粒直径 | lp | 1.5×10-4m | 30 | 5×10-6 m |
| 入口CO2流速 | u0 | 7.4×10-3m·s-1 | 0.074(Re=20) | 0.1 m·s-1 |
| CO2浓度 | C0 | 5.64 mol·m-3 | 1 | 5.64 mol·m-3 |
| CO2密度 | ρ | 1.977 kg·m-3 | 1 | 1.977 kg·m-3 |
| CO2黏度 | v | 8.37×10-6m2·s-1 | 0.037 | 2.26×10-4 m2·s-1 |
| CaO物质的量 | n0 | 212.63 mol·m-3 | 37.7(ε=0.2) | 5.64 mol·m-3 |
表1 格子单位与物理单位转换表
Table 1 Conversion between lattice units and physical units
| 物理量 | 物理量符号 | 物理单位 | 格子单位 | 转换因子 |
| 计算域长度 | Lx | 3.6×10-3 m | 720 | 5×10-6 m |
| 计算域高度 | Ly | 1.8×10-3 m | 360 | 5×10-6 m |
| 颗粒直径 | lp | 1.5×10-4m | 30 | 5×10-6 m |
| 入口CO2流速 | u0 | 7.4×10-3m·s-1 | 0.074(Re=20) | 0.1 m·s-1 |
| CO2浓度 | C0 | 5.64 mol·m-3 | 1 | 5.64 mol·m-3 |
| CO2密度 | ρ | 1.977 kg·m-3 | 1 | 1.977 kg·m-3 |
| CO2黏度 | v | 8.37×10-6m2·s-1 | 0.037 | 2.26×10-4 m2·s-1 |
| CaO物质的量 | n0 | 212.63 mol·m-3 | 37.7(ε=0.2) | 5.64 mol·m-3 |
| ε=0.01 | ε=0.4 | ε=0.6 | ε=0.8 | |
| Ref.[ | Ref.[ | Ref.[ | Ref.[ | |
| 2.05 | 2.411 | 2.105 | 2.049 | |
| 本文 | 2.053 | 2.423 | 2.136 | 2.083 |
| 相对误差/% | 0.15 | 0.49 | 1.45 | 1.63 |
表2 阻力系数数据对比
Table 2 Comparison of resistance coefficient data
| ε=0.01 | ε=0.4 | ε=0.6 | ε=0.8 | |
| Ref.[ | Ref.[ | Ref.[ | Ref.[ | |
| 2.05 | 2.411 | 2.105 | 2.049 | |
| 本文 | 2.053 | 2.423 | 2.136 | 2.083 |
| 相对误差/% | 0.15 | 0.49 | 1.45 | 1.63 |
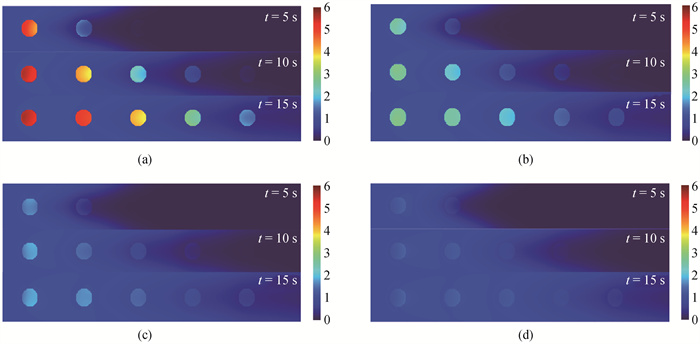
图6 CaO颗粒内部CO2气体浓度分布(a) ε=0.2;(b) ε=0.4;(c) ε=0.6;(d)ε=0.8
Fig.6 Distribution of CO2 gas concentration inside CaO particles (a) ε=0.2;(b) ε=0.4;(c) ε=0.6;(d) ε=0.8
| 颗粒直径 | 流动阻力 |
| lp= 50 μm | 4.66×10-3 |
| lp=150 μm | 8.37×10-2 |
| lp=250 μm | 3.92×10-1 |
表3 流动阻力对比
Table 3 Comparison of resistance to flow
| 颗粒直径 | 流动阻力 |
| lp= 50 μm | 4.66×10-3 |
| lp=150 μm | 8.37×10-2 |
| lp=250 μm | 3.92×10-1 |
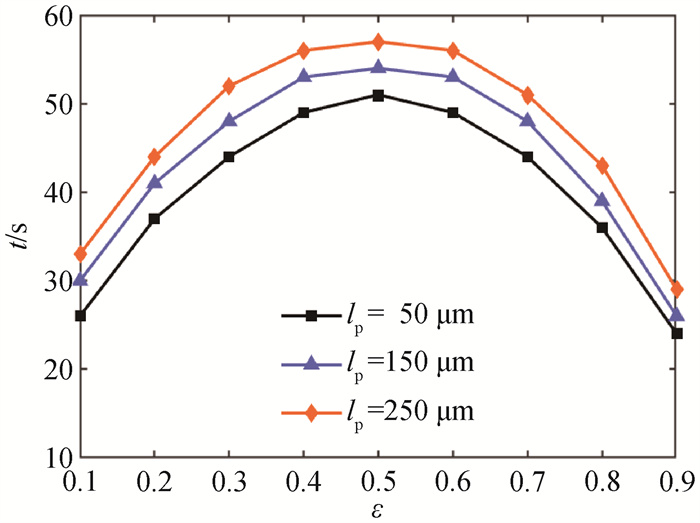
图10 孔隙率为ε在0.1~0.9不同CaO颗粒直径平均转化率达到0.8所需时间
Fig.10 Time required for average conversion rate to reach 0.8 under different CaO particle diameters with ε=0.1-0.9
| ε=0.1 | ε=0.2 | ε=0.3 | ε=0.4 | ε=0.5 | ε=0.6 | ε=0.7 | ε=0.8 | ε=0.9 | 平均 | |
| 150 μm比250 μm增量 | 9% | 6.8% | 7.7% | 5.4% | 5.3% | 5.4% | 5.9% | 9.3% | 10.3% | 7.2% |
| 50 μm比150μm增量 | 13.3% | 9.8% | 8.3% | 7.5% | 5.6% | 7.5% | 8.3% | 7.7% | 7.7% | 8.4% |
表4 不同粒径转化效率百分比增量
Table 4 Percentage increment of conversion efficiency for different particle sizes
| ε=0.1 | ε=0.2 | ε=0.3 | ε=0.4 | ε=0.5 | ε=0.6 | ε=0.7 | ε=0.8 | ε=0.9 | 平均 | |
| 150 μm比250 μm增量 | 9% | 6.8% | 7.7% | 5.4% | 5.3% | 5.4% | 5.9% | 9.3% | 10.3% | 7.2% |
| 50 μm比150μm增量 | 13.3% | 9.8% | 8.3% | 7.5% | 5.6% | 7.5% | 8.3% | 7.7% | 7.7% | 8.4% |
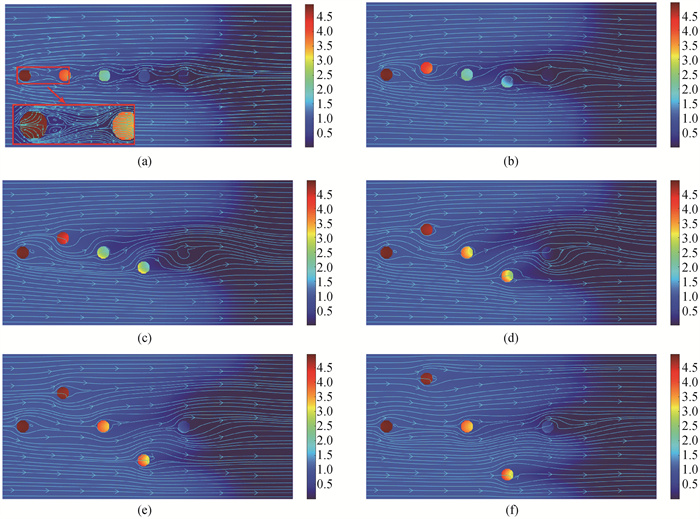
图12 t=10 s时刻CaO颗粒内部CO2浓度及流线分布图 (a) θ=0°;(b) θ=10°;(c) θ=20°;(d) θ=30°;(e) θ=40°;(f) θ=50°
Fig.12 CO2 concentration inside CaO particle and streamline distribution at t=10 s (a) θ=0°; (b) θ=10°; (c) θ=20°; (d) θ=30°; (e) θ=40°; (f) θ=50°
| 1 |
DOI |
| 2 |
魏凤, 江娴, 周洪, 等. 基于CCS的MEA脱碳技术全球专利发展态势[J]. 化工进展, 2015, 34(12): 4415- 4421.
|
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
DOI |
| 5 |
杜旭林, 程林松, 牛烺昱, 等. 考虑水力压裂缝和天然裂缝动态闭合的三维离散缝网数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 453- 464.
DOI |
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
赵红涛, 王树民, 张曼. 不同钙源制备钙基CO2吸收剂研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2019, 39(6): 36-40, 42.
|
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
房凡, 李振山, 蔡宁生. 钙基CO2吸收剂循环反应特性的试验与模拟[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2009, 29(14): 30- 35.
|
| 10 |
李振山, 蔡宁生, 赵旭东, 等. CaO与CO2循环反应动力学特性[J]. 燃烧科学与技术, 2006(6): 481- 485.
|
| 11 |
戢美璇, 蔚喜军, 宋明阳. 一维含化学反应流体力学方程组的ALE间断有限元方法[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(1): 1- 9.
DOI |
| 12 |
雷体蔓, 孟旭辉, 郭照立. 微通道内反应流体粘性指进的数值研究[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(1): 30- 38.
|
| 13 |
杨艳霞, 李静. 膜生物反应器内生化反应过程的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(5): 571- 576.
DOI |
| 14 |
王保文, 郑瑛, 贺铸, 等. CaO高温分离CO2过程的数值模拟[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2006, 27(6): 1051- 1053.
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
张婷, 郭照立, 柴振华, 等. 钙基吸收剂吸收CO2过程的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(S1): 165- 171.
|
| 17 |
孟旭辉, 王亮, 郭照立. 管道中CaO颗粒吸收CO2的格子Boltzmann方法模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2014, 31(2): 173- 184.
|
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
DOI |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
DOI |
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
刘波, 丁玉栋, 廖强, 等. 单颗粒多孔MgO吸附剂CO2吸附流动传输的格子Boltzmann方法模拟[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2020, 37(2): 248- 254.
|
| [1] | 许一帆, 张虎明, 赵明. 偏心圆环空间内自然对流的确定性及混沌[J]. 计算物理, 2025, 42(1): 28-37. |
| [2] | 魏如普, 丁鹏. 反演分布函数的多块网格LBM局部加密方法[J]. 计算物理, 2024, 41(5): 643-650. |
| [3] | 王习文, 叶学民, 李丹, 李春曦. 大液滴撞击不同润湿性小球的三维格子Boltzmann方法模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2024, 41(2): 172-181. |
| [4] | 张浏斌, 单彦广, 戎志成. 基于LBM的均匀电场池沸腾单气泡动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 537-548. |
| [5] | 刘嘉鑫, 郑林, 张贝豪. 多孔介质方腔内双扩散自然对流熵产的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 549-563. |
| [6] | 林品亮, 冯欢欢, 董宇红. 具有多孔介质覆面层的柱体绕流流场分析[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 418-426. |
| [7] | 蔡建超. 多孔介质自发渗吸关键问题与思考[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 505-512. |
| [8] | 郑江韬, 贾宁洪, 胡慧芳, 杨勇, 鞠杨, 王沫然. 分支通道内液-液自发渗吸规律研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 543-554. |
| [9] | 魏祥祥, 冯其红, 张先敏, 黄迎松, 刘丽杰. 基于VOF方法的水驱油藏孔隙尺度剩余油分布状态研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 573-584. |
| [10] | 王敏, 申玉清, 陈震宇, 徐鹏. 随机多孔介质的蒙特卡罗重构与渗流特性模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 623-630. |
| [11] | 娄钦, 汤升, 王浩原. 基于格子Boltzmann大密度比模型的多孔介质内气泡动力学行为数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(3): 289-300. |
| [12] | 万启坤, 罗松, 尚文强, 张莹, 刘昊天, 朱宝杰. 不连续冷源布局多孔介质内热流耦合LBM数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(4): 431-438. |
| [13] | 冯其红, 赵蕴昌, 王森, 张以根, 孙业恒, 史树彬. 基于相场方法的孔隙尺度油水两相流体流动模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(4): 439-447. |
| [14] | 王子墨, 李凌. 超短激光打孔中快速相变的格子玻尔兹曼模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(3): 299-306. |
| [15] | 连小龙, 陈岳, 李培生, 张莹, 李伟, 刘强. 基于MRT-LB伪势模型的液滴撞击液膜数值研究[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(1): 79-87. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
