计算物理 ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 447-455.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8263
收稿日期:2020-08-24
出版日期:2021-07-25
发布日期:2021-12-21
作者简介:闫宇星(1980-), 男, 山西保德人, 博士, 讲师, 研究方向为凝固态物理和新能源材料, E-mail: 58536437@qq.com
基金资助:
Yuxing YAN1( ), Juexuan ZHANG1, Shuai ZHENG2, Fan WANG1, Linqiang XIONG3
), Juexuan ZHANG1, Shuai ZHENG2, Fan WANG1, Linqiang XIONG3
Received:2020-08-24
Online:2021-07-25
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
基于密度泛函理论第一性原理,研究Zn、Nb、O间隙原子对ZnNb2O6体系光电特性的影响。分析显示:间隙原子对体系晶格畸变的影响与间隙原子几何尺寸有关。缺陷结构中,由于间隙原子电负性存在差异,也是产生晶格畸变的因素。光电特性分析显示:含有Zn、Nb间隙原子的体系表现为n型简并半导体。且Nbi表现出较强的介电效应,主要与Nb的离子势与电离能有关。Oi表现为p型简并半导体,对光电效应贡献较小。结果表明Nbi体系有良好的光电特性,在实际应用中具有较大潜力。
中图分类号:
闫宇星, 张珏璇, 郑帅, 汪帆, 熊琳强. 间隙原子对ZnNb2O6光电特性影响的第一性原理研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 447-455.
Yuxing YAN, Juexuan ZHANG, Shuai ZHENG, Fan WANG, Linqiang XIONG. First-principles Study of Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of ZnNb2O6 with Interstitial Atoms[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 38(4): 447-455.
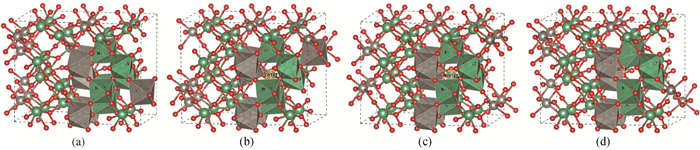
图1 晶体结构(a) ZnNb2O6, (b) Zni, (c) Nbi, (d) Oi (灰色、绿色和红色分别为Zn、Nb、O。)
Fig.1 Crystal structure of (a) ZnNb2O6, (b) Zni, (c) Nbi and (d) Oi (The gray, green and red are Zn, Nb and O atoms, respectively.)
| Epure/eV | Edefect/eV | Eform/eV | |
| ZnNb2O6 | -7 998.113 | ||
| Zni | -7 859.723 | 8.433 | |
| Nbi | -7 851.647 | 5.289 | |
| Oi | -7 775.457 | 7.495 |
表1 ZnNb2O6总能量与间隙原子形成能
Table 1 Total energies and formation energies of ZnNb2O6 with different interstitial atoms
| Epure/eV | Edefect/eV | Eform/eV | |
| ZnNb2O6 | -7 998.113 | ||
| Zni | -7 859.723 | 8.433 | |
| Nbi | -7 851.647 | 5.289 | |
| Oi | -7 775.457 | 7.495 |
| Model | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α | β | γ | ΔV/V/% |
| ZnNb2O6(Ref.[ | 1.420 8 | 0.572 6 | 0.504 0 | 90 | 90 | 90 | |
| ZnNb2O6(This work) | 1.433 4 | 0.583 2 | 0.506 1 | 90.000 1 | 90.000 8 | 90.000 2 | 3.18 |
| Zni | 1.440 4 | 0.584 6 | 0.507 8 | 90.047 1 | 89.604 3 | 90.281 0 | 1.086 |
| Nbi | 1.440 1 | 0.585 0 | 0.507 3 | 89.897 2 | 89.910 6 | 89.721 1 | 1.011 |
| Oi | 1.436 5 | 0.584 0 | 0.507 1 | 89.722 9 | 90.127 9 | 90.036 5 | 0.541 |
表2 各体系的晶格参数
Table 2 Lattice parameters of the model systems
| Model | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α | β | γ | ΔV/V/% |
| ZnNb2O6(Ref.[ | 1.420 8 | 0.572 6 | 0.504 0 | 90 | 90 | 90 | |
| ZnNb2O6(This work) | 1.433 4 | 0.583 2 | 0.506 1 | 90.000 1 | 90.000 8 | 90.000 2 | 3.18 |
| Zni | 1.440 4 | 0.584 6 | 0.507 8 | 90.047 1 | 89.604 3 | 90.281 0 | 1.086 |
| Nbi | 1.440 1 | 0.585 0 | 0.507 3 | 89.897 2 | 89.910 6 | 89.721 1 | 1.011 |
| Oi | 1.436 5 | 0.584 0 | 0.507 1 | 89.722 9 | 90.127 9 | 90.036 5 | 0.541 |
| Model | Bond | Population min(max) | Length min(max)/nm |
| ZnNb2O6 | O-Zn | 0.15(0.29) | 0.207 222(0.222 210 0) |
| O-Nb | 0.21(0.79) | 0.181 660(0.233 858) | |
| O-O | -0.05(0.00) | 0.262 644(0.292 990) | |
| Zni | O-Zn | 0.04(0.43) | 0.193 899(0.264 244) |
| O-Nb | 0.09(0.83) | 0.180 471(0.253 899) | |
| O-O | -0.05(0.00) | 0.260 592(0.299 858) | |
| Zn-Nb | -0.48(-0.30) | 0.284 044(0.299 528) | |
| Zn-Zn | -1.87 | 0.264 037 | |
| Nb-Nb | -0.45 | 0.273 866 | |
| Nbi | O-Zn | -0.01(0.39) | 0.196 825(0.254 825) |
| O-Nb | 0.10(0.82) | 0.180 989(0.245 336) | |
| O-O | -0.05(0.00) | 0.259 177(0.299 995) | |
| Zn-Nb | 0.18 | 0.279 478 | |
| Zn-Zn | |||
| Nb-Nb | -0.81(-0.41) | 0.267 331(0.288 840) | |
| Oi | O-Zn | -0.08(0.36) | 0.195 009(0.288 686) |
| O-Nb | 0.04(0.81) | 0.180 078(0.292 940) | |
| O-O | -0.06(0.18) | 0.145 112(0.298 924) |
表3 各体系键的布居数
Table 3 Bond populations of the model systems
| Model | Bond | Population min(max) | Length min(max)/nm |
| ZnNb2O6 | O-Zn | 0.15(0.29) | 0.207 222(0.222 210 0) |
| O-Nb | 0.21(0.79) | 0.181 660(0.233 858) | |
| O-O | -0.05(0.00) | 0.262 644(0.292 990) | |
| Zni | O-Zn | 0.04(0.43) | 0.193 899(0.264 244) |
| O-Nb | 0.09(0.83) | 0.180 471(0.253 899) | |
| O-O | -0.05(0.00) | 0.260 592(0.299 858) | |
| Zn-Nb | -0.48(-0.30) | 0.284 044(0.299 528) | |
| Zn-Zn | -1.87 | 0.264 037 | |
| Nb-Nb | -0.45 | 0.273 866 | |
| Nbi | O-Zn | -0.01(0.39) | 0.196 825(0.254 825) |
| O-Nb | 0.10(0.82) | 0.180 989(0.245 336) | |
| O-O | -0.05(0.00) | 0.259 177(0.299 995) | |
| Zn-Nb | 0.18 | 0.279 478 | |
| Zn-Zn | |||
| Nb-Nb | -0.81(-0.41) | 0.267 331(0.288 840) | |
| Oi | O-Zn | -0.08(0.36) | 0.195 009(0.288 686) |
| O-Nb | 0.04(0.81) | 0.180 078(0.292 940) | |
| O-O | -0.06(0.18) | 0.145 112(0.298 924) |
| Model | Species | s | p | d | Total | Charge/eV |
| Zn | 0.11 | 0.62 | 9.98 | 10.72 | 1.28 | |
| ZnNb2O6 | Nb | 2.35 | 6.31 | 2.92 | 11.58 | 1.42 |
| O | 1.84~1.86 | 4.80~4.86 | 6.67~6.70 | -(0.70~0.67) | ||
| Zn | 0.07~0.16 | 0.62~0.81 | 9.97~9.98 | 10.68~10.87 | 1.13~1.32 | |
| Zni | Nb | 2.35~2.37 | 6.29~6.34 | 2.91~3.17 | 11.59~11.81 | 1.19~1.41 |
| O | 1.84~1.86 | 4.79~4.93 | 6.65~6.74 | -(0.78~0.65) | ||
| Zn | 0.06~0.10 | 0.61~0.64 | 9.98 | 10.67~10.70 | 1.30~1.33 | |
| Nbi | Nb | 2.34~2.36 | 6.24~6.34 | 2.91~3.65 | 11.58~12.31 | 0.69~1.42 |
| O | 1.84~1.86 | 4.79~4.87 | 6.66~6.72 | -(0.71~0.66) | ||
| Zn | 0.06~0.07 | 0.61~0.63 | 9.98 | 10.66~10.68 | 1.32~1.34 | |
| Oi | Nb | 2.35~2.36 | 6.30~6.34 | 2.88~2.93 | 11.54~11.61 | 1.39~1.46 |
| O | 1.84~1.90 | 4.50~4.87 | 6.39~6.71 | -(0.71~0.39) |
表4 各体系的原子布居数
Table 4 Atomic populations of the model systems
| Model | Species | s | p | d | Total | Charge/eV |
| Zn | 0.11 | 0.62 | 9.98 | 10.72 | 1.28 | |
| ZnNb2O6 | Nb | 2.35 | 6.31 | 2.92 | 11.58 | 1.42 |
| O | 1.84~1.86 | 4.80~4.86 | 6.67~6.70 | -(0.70~0.67) | ||
| Zn | 0.07~0.16 | 0.62~0.81 | 9.97~9.98 | 10.68~10.87 | 1.13~1.32 | |
| Zni | Nb | 2.35~2.37 | 6.29~6.34 | 2.91~3.17 | 11.59~11.81 | 1.19~1.41 |
| O | 1.84~1.86 | 4.79~4.93 | 6.65~6.74 | -(0.78~0.65) | ||
| Zn | 0.06~0.10 | 0.61~0.64 | 9.98 | 10.67~10.70 | 1.30~1.33 | |
| Nbi | Nb | 2.34~2.36 | 6.24~6.34 | 2.91~3.65 | 11.58~12.31 | 0.69~1.42 |
| O | 1.84~1.86 | 4.79~4.87 | 6.66~6.72 | -(0.71~0.66) | ||
| Zn | 0.06~0.07 | 0.61~0.63 | 9.98 | 10.66~10.68 | 1.32~1.34 | |
| Oi | Nb | 2.35~2.36 | 6.30~6.34 | 2.88~2.93 | 11.54~11.61 | 1.39~1.46 |
| O | 1.84~1.90 | 4.50~4.87 | 6.39~6.71 | -(0.71~0.39) |
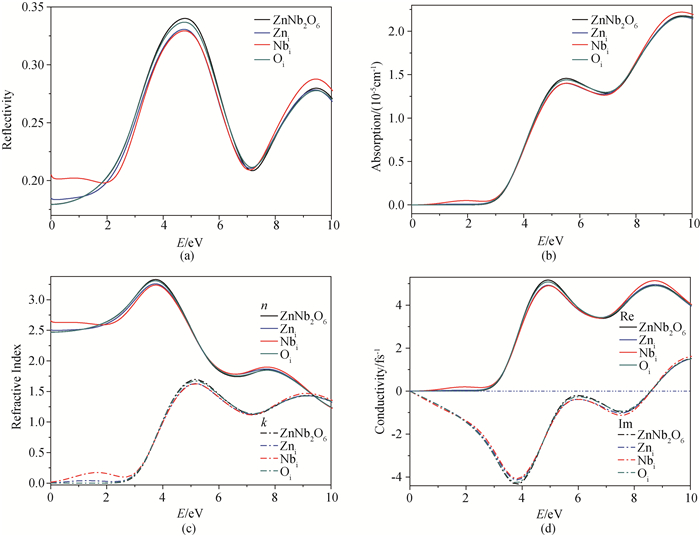
图7 光电特性函数(a) 反射率,(b)吸收率,(c)折射率,(d)传导率
Fig.7 Photoelectric characteristic functions of the model systems (a) reflectivity, (b) absorption, (c) refractive index, (d) conductivity
| 1 |
LIU C, LI F, MA L P, et al. Advanced materials for energy storage[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22 (8): E28- E62.
DOI |
| 2 |
CABALLER A C, FERNABDEZ J F, MOURE C, et al. ZnO-doped BaTiO3: Microstructure and electrical properties[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1997, 17 (4): 513- 523.
DOI |
| 3 |
DONG G X, MA S W, DU J, et al. Dielectric properties and energy storage density in ZnO-doped Ba0.3Sr0.7TiO3 ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2009, 35 (5): 2069- 2075.
DOI |
| 4 |
ZHANG Y C, YUE Z X, GUI Z L, et al. Effects of CaF2 addition on the microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of ZnNb2O6 ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2003, 29 (5): 555- 559.
DOI |
| 5 |
NGAMJARUROJANA A, YIMNIRUN R, ANANTA S. Effect of calcination conditions on phase formation and particle size of zinc niobate powers synthesized by solid-state reaction[J]. Materials Letters, 2006, 60 (23): 2867- 2872.
DOI |
| 6 | XU D P, LIU Y, ZHOU Q, et al. Optical phonon behaviors of columbite ZnNb2O6 single crystal[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, (618): 694- 699. |
| 7 | NEURGAONKAR R R, CORY W K, OLIVER J R. Growth and ferroelectric properties of tungsten bronze Sr2-xCaxNaNb5O15 single crystals[J]. Mater Res Bull, 1988, 223 (10): 1459- 1461. |
| 8 |
NEURGAONKAR R R, NELSON J G, OLIVER J R. Ferroelectric properties of tungsten bronze M62+M24-Nb8O30 solid solutions system[J]. Mater Res Bull, 1992, 27 (6): 677- 684.
DOI |
| 9 | 许煜寰. 铁电与压电材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978: 1- 38. |
| 10 | CHEN C T, CONG S, CHEN H F, et al. First-principles study of electronic structure and optical properties of Bi doped ZnO[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2018, 35 (6): 720- 728. |
| 11 | 张迎春. 铌钽酸盐微波介质陶瓷材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 1- 25. |
| 12 |
WU W M, LIANG S J, DING Z X, et al. A new approach to the preparation of microcrystalline ZnNb2O6 photocatalysts via a water-soluble niobium-citrate-peroxo compound[J]. Solid State Sciences, 2011, 13 (11): 2019- 2023.
DOI |
| 13 |
ZHENG J, CHEN G H, CHEN X, et al. Dielectric properties and energy storage behaviors in ZnNb2O6-doped Sr0.97Nd0.02TiO3 ceramics[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2016, 27 (4): 3759- 3764.
DOI |
| 14 |
WANG T, WEI X Y, HU Q Y, et al. Effects of ZnNb2O6 addition on BaTiO3 ceramics for energy storage[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2013, 178 (16): 1081- 1086.
DOI |
| 15 |
ZHANG Y C, LI L T, YUE Z X, et al. Effects of additives on microstructures and microwave dielectric properties of ZnNb2O6 ceramics[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2003, 99 (1-3): 282- 285.
DOI |
| 16 | 闫宇星, 汪帆, 李付绍, 等. ZnNb2-xTaxO6(x=0~2.0)材料电子结构与光学性质的第一性原理计算[J]. 发光学报, 2020, 41 (1): 38- 47. |
| 17 |
KORMANYOS A, THOMAS A, HUDA M N, et al. Solution combustion synthesis, characterization, and photoelectrochemistry of CuNb2O6 and ZnNb2O6 nanoparticles[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120 (29): 16024- 16034.
DOI |
| 18 |
WABURY M, MUELLER B H. ZnTa2O6, ein neuer vertreter des tri-α-PbO2 typs (mit ergä enzenden Daten über ZnNb2O6)[J]. Zeitschrift Für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie, 1984, 508 (1): 55- 60.
DOI |
| 19 |
刘东豪, 闫宇星, 沈静秋, 等. ZnNb2O6材料光电学特性研究[J]. 曲靖师范学院学报, 2019, 38 (6): 20- 25.
DOI |
| 20 |
HSIAO Y J, FANG T H, JI L W. Synthesis and luminescent properties of ZnNb2O6 nanocrystals for solar cell[J]. Materials Letters, 2010, 64 (23): 2563- 2565.
DOI |
| 21 | JAMES G S. Lange's handbook of chemistry[M]. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies Inc, 2005: 1.152-1.158. |
| 22 | MA R, ZHANG H L. Electronic properties of graphene nanoribbons doped with rhombus born nitride segment[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 36 (1): 99- 105. |
| 23 | 高小奇, 郭志友, 张宇飞, 等. Al-N共掺杂ZnO电子结构和光学性质[J]. 发光学报, 2010, 31 (4): 509- 514. |
| 24 | 张梅玲, 陈玉红, 张材荣, 等. 内在缺陷与Cu掺杂共存对ZnO电磁光学性质影响的第一性原理研究[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68 (8): 087101. |
| 25 | 沈学础. 半导体光谱和光学性质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 1- 32. |
| 26 | 黄昆. 固体物理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1988: 437- 462. |
| 27 | 李名復. 半导体物理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 161- 249. |
| 28 | 楼立人, 尹民, 李清庭. 发光物理基础: 固体光跃迁过程[M]. 合肥: 中国科技大学出版社, 2014: 35- 78. |
| 29 | ZHOU K, FENG Q, TIAN Y, et al. Oxidizing gas NO2 optical gas sensing characteristics of transition metal Cu and Cr doped TiO2 surfaces[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2018, 35 (6): 702- 710. |
| [1] | 严深浪, 项少辉, 龙孟秋. 锯齿型石墨烯纳米带结的自旋输运性质[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(6): 751-756. |
| [2] | 罗强, 马智炜, 蒋冠臻, 邹江峰, 邱毅. Ge掺杂AlN电子和光学性质的第一性原理计算[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 609-616. |
| [3] | 王晓慧, 张平. 高压下FCC相金属氢结构稳定性和非谐效应的理论研究[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 159-164. |
| [4] | 房勇, 金永中, 陈建, 宗洪祥, 张丽英. 石墨烯厚度与其力-距离关系的实验和模拟研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(4): 441-446. |
| [5] | 潘靖, 沈国华. 等价阴-阳离子共掺杂调节ZnO的能带结构及其光催化活性[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(3): 371-378. |
| [6] | 张乐, 孙博, 宋海峰. 钚氧化物中氢行为的第一性原理研究[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 595-602. |
| [7] | 彭军辉. 三元层状陶瓷M-Al-N(M=Ti,Zr,Hf)的结构及力学性质的第一性原理模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 603-611. |
| [8] | 赵一程, 郭俊宏, 胡芳仁. 应变对单层砷烯结构拉曼散射的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(3): 365-370. |
| [9] | 温淑敏, 姚世伟, 赵春旺, 王细军, 李继军. 应变对纤锌矿结构GaN电子结构及光学性质的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(1): 119-126. |
| [10] | 熊宗刚, 杜娟, 张现周. 二维GeSe纳米片五族和七族原子掺杂的受主和施主杂质态[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(6): 733-741. |
| [11] | 秦平, 高振帮, 刘海敌, 陈英才. 过渡金属单硼化物TMB的第一性原理研究[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(4): 491-497. |
| [12] | 刘华忠, 罗春霞. 甲醛分子在羟基化TiO2-B(100)面吸附的第一性原理研究[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(3): 363-378. |
| [13] | 徐建, 杜成旭, 杜颖妍, 贾倩, 刘洋华, 毋志民. Mn掺杂LiZnN新型稀磁半导体磁电性质的第一性原理计算[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 711-719. |
| [14] | 陈春天, 丛珊, 陈鸿菲, 王磊, 李凯. Bi掺杂ZnO光电性能的第一性原理研究[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 720-728. |
| [15] | 田壮壮, 周晓平, 宋国林. 锂薄膜的第一性原理计算:量子尺寸效应和原子氢的吸附[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(6): 729-736. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
