计算物理 ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 106-117.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8807
收稿日期:2023-07-24
出版日期:2025-01-25
发布日期:2025-03-08
通讯作者:
王春妮
作者简介:李艳妮, 女, 硕士研究生, 研究方向为理论物理, E-mail: lyn977462645@163.com
基金资助:
Yanni LI( ), Chunni WANG*(
), Chunni WANG*( )
)
Received:2023-07-24
Online:2025-01-25
Published:2025-03-08
Contact:
Chunni WANG
摘要:
在神经元电路中加入光电管构造一个典型的光敏神经元电路, 该神经元电路在不同频率的周期光电流刺激下呈现生物神经元典型的放电模态, 经过标度变换得到无量纲的光敏神经元模型和能量函数。研究发现: 神经元的放电模态和系统能量相关。用滤波后的混沌光电流信号刺激时, 该神经元呈现混沌放电模态且随着滤波信号强度的增大, 神经元放电模态和能量发生显著变化。考虑到神经突触的多样性及可塑性, 用一个非线性电阻耦合两个光敏神经元电路, 研究周期信号及经滤波后的混沌光电流信号刺激下两个光敏神经元电路在不同初始放电模态下的同步情况及能量在系统内部的流动与转移, 同时研究噪声对同步状态及系统能量的影响。结果表明: 周期光电流刺激下, 耦合系统在任何初始模态下都不能实现完全同步, 耦合强度始终在波动, 两系统能量不能平衡; 一定强度噪声有利于周期光电流刺激下初始态为簇放电模态的两个耦合全同光敏神经元电路的同步但不能使初始态为混沌态的神经元达到同步。适当强度的滤波混沌光电流信号能调节耦合系统间歇性相位锁定甚至于实现近似的相位同步。
李艳妮, 王春妮. 非线性突触耦合光敏神经元的同步分析[J]. 计算物理, 2025, 42(1): 106-117.
Yanni LI, Chunni WANG. Synchronous Stability of Two Photosensitive Neurons Coupled by Nonlinear Synapse[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2025, 42(1): 106-117.
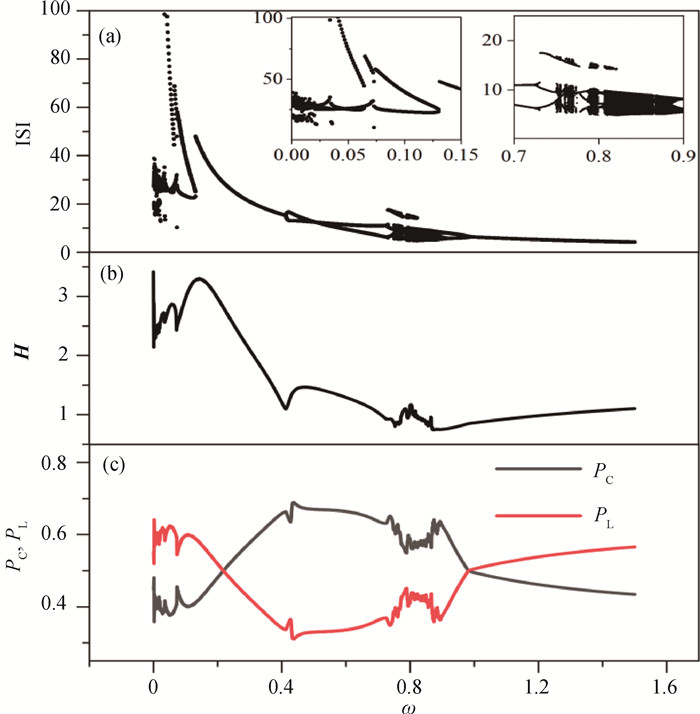
图3 周期光电流信号驱动时单个神经元电路的振动分岔及能量分布(a) 膜电位x的峰峰间隔ISI关于周期信号频率ω分岔图(小图是局部放大图。); (b) 系统总哈密顿能量H随ω的演化图; (c) 对应模态下电场能量占比PC及磁场能量占比PL随刺激频率ω的演化曲线(a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, A=0.6,初始值选取[0.2, 0.1]。)
Fig.3 Bifurcation, Hamilton energy and energy proportion of single neural circuit driven by periodic signals (a) bifurcation diagram of ISI vs. the frequency of the periodic stimulus signal (The small image in the figure is a partial enlargement.); (b) dependence of Hamilton energy on frequency of the Periodic stimulus signal; (c) evolution of the electric energy proportion PC and the magnetic energy proportion PL vs. frequency of the periodic stimulus signal (a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, A=0.6, the initial value is [0.2, 0.1].)
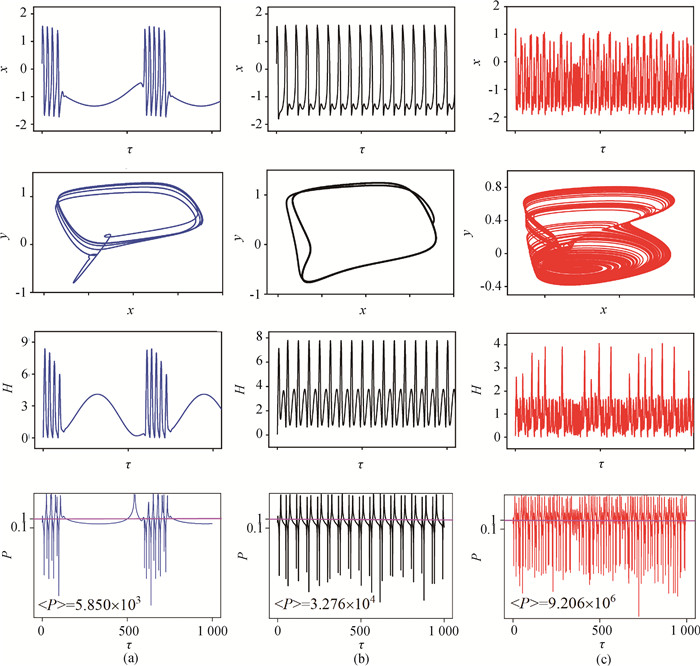
图4 不同频率的周期光电流刺激下, 单个神经元电路的时序图、相位图、能量演化曲线及电场能与磁场能的比值P的演化曲线(a) ω=0.01; (b) ω=0.1; (c) ω=0.81 (A=0.6, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25,初始值为[0.2, 0.1]。)
Fig.4 Sampled time series of membrane potential, attractor, the Hamilton energy and evolution of the ratio P between electric field energy and magnetic field energy of single neuron circuit stimulated by periodic photocurrents of different frequencies ω (a) ω=0.01; (b) ω=0.1; (c) ω=0.81 (a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, A=0.6. The initial value is [0.2, 0.1].)
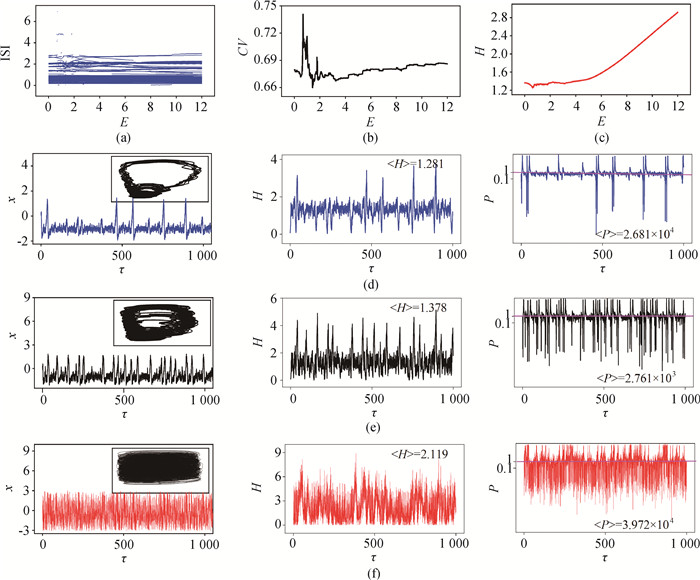
图5 单个神经元电路由滤波后的光电流信号驱动时的放电模态及能量分布(a)ISI关于振幅E的分岔图; (b)系统关联度CV关于振幅E的演化;(c)系统总哈密顿能量H随振幅E的演化图;(d)~(f)行分别为滤波光电流信号幅值E不同时神经元电路的时域演化图(小图为对应的相位图。)、哈密顿能量H及电场能与磁场能的比值P随时间的演化曲线;(d)E=0.69; (e) E=1.43; (f) E=8.4 (a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, α=9.78, β=14.97, γ=0.0, m0=-1.31, m1=-0.75。初始值选择为[0.1, 0.1, 1, 0.2, 0.1]。)
Fig.5 Mode transition, CV distribution and energy evolution of neuron driven by filtered photocurrent signal (a) bifurcation diagram of ISI vs. E. (b) CV vs. E.(c) H vs. E. (d)~(f) are sampled time series of membrane potential (the small image in the figure is the corresponding phase diagram.), Hamiltonian energy H and ratio P of electric field energy to magnetic field energy of neuronal circuit with different amplitude E of filtered photocurrent signal; (d) E=0.69; (e) E=1.43; (f) E=8.4 (a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, α=9.78, β=14.97, γ=0.0, m0=-1.31, m1=-0.75. The initial value is [0.1, 0.1, 1, 0.2, 0.1].)
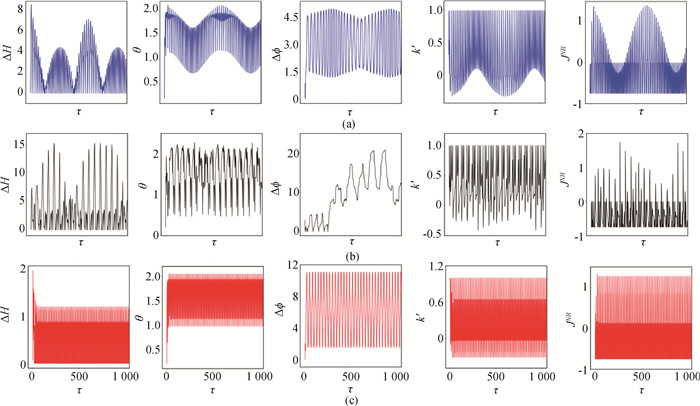
图6 在不同频率的周期光电流刺激下,不同初始态的两耦合神经元系统的能量差、同步误差、相位差、耦合强度和耦合通道能量消耗演化(a)簇放电ω=0.01;(b)尖峰放电ω=0.1;(c)混沌放电ω=0.81 (A=0.6, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25,初始值选择为[0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01]。)
Fig.6 Evolution of energy difference, synchronization error function, phase error, coupling intensity and coupling channel energy consumption of two coupled neurons with different initial states driven by period photocurrent with different frequency (a) bursting pattern, ω=0.01;(b) spiking pattern, ω=0.1;(c) chaos pattern, ω=0.81 (A=0.6, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25. The initial value is [0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01].)
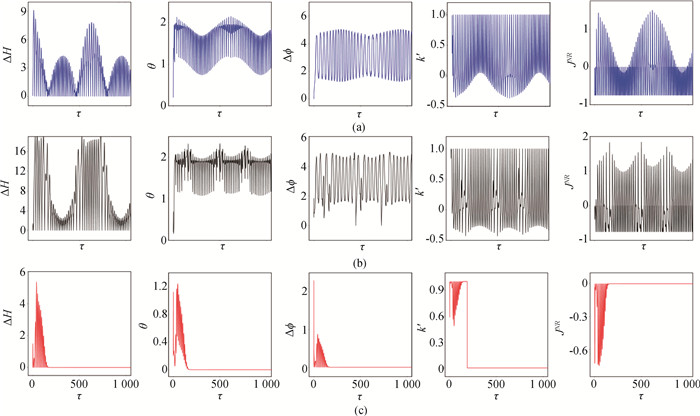
图7 噪声对初始态为簇放电的两个耦合神经元同步状态的影响(a)D=0.05;(b)D=0.2;(c)D=2.0. (ω=0.01, A=0.6, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25。初始值为[0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01]。)
Fig.7 Effect of noise on synchronization state of two coupled bursting neurons (a) D=0.05;(b) D=0.2;(c) D=2.0 (ω=0.01, A=0.6, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25.The initial value is [0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01].)
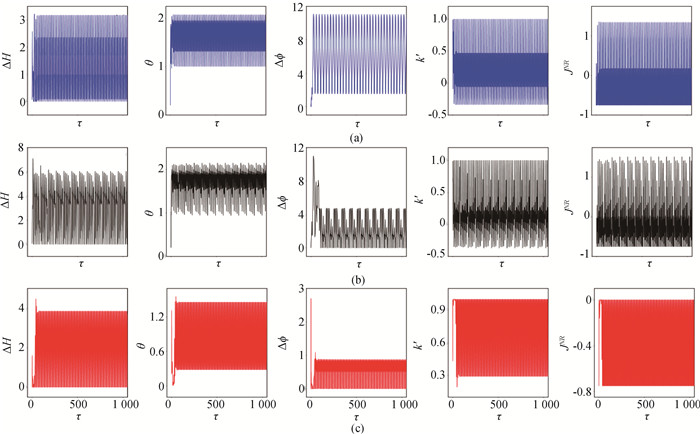
图8 噪声存在时,周期光电流刺激下初始态均为混沌放电的两耦合神经元电路的能量误差、误差函数、相位差、耦合强度和耦合通道热消耗的演化(a)D=0.05;(b)D=0.3;(c)D=1.8 (ω=0.81, A=0.6, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25. 初始值选择为[0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01]。)
Fig.8 Evolution of energy diversity, error function, phase error, coupling intensity and coupling channel energy consumption in two coupled neuronal circuit with chaotic discharge driven by noise and periodic stimulus (a) D=0.05;(b) D=0.3; (c) D=1.8 (ω=0.81, A=0.6, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25. The initial value is [0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01].)
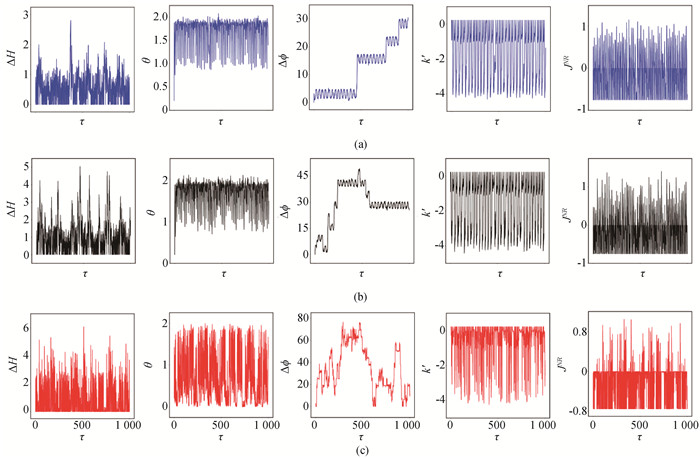
图9 经滤波后的混沌光电流刺激时,耦合神经元电路的同步情况(a)E=0.69; (b)E=1.43; (c)E=8.4 (a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, α=9.78, β=14.97, γ=0.0, m0=-1.31, m1=-0.75. 初始值选择为[0.1, 0.1, 1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01]。)
Fig.9 Evolution of energy diversity, error function, phase error, coupling intensity and coupling channel energy consumption in the two coupled neurons by the filtered chaotic photocurrent (a)E=0.69; (b)E=1.43; (c)E=8.4 (a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, α=9.78, β=14.97, γ=0.0, m0=-1.31, m1=-0.75. The initial value is[0.1, 0.1, 1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01].)
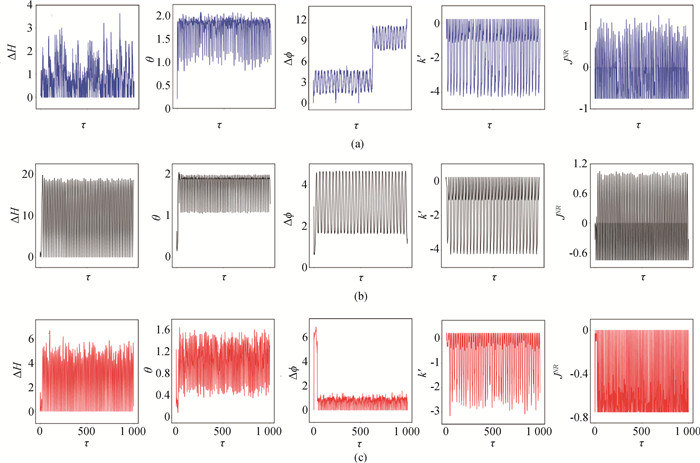
图10 噪声存在时,经滤波后的混沌光电流刺激时,耦合神经元电路的同步情况(a)D=0.04; (b)D=1.0; (c)D=4.0 (E=0.69, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, α=9.78, β=14.97, γ=0.0, m0=-1.31, m1=-0.75. 初始值选择为[0.1, 0.1, 1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01]。)
Fig.10 Evolution of energy diversity, error function, phase error, coupling intensity and energy consumption of two coupled neurons driven by filtered chaotic photocurrent with noise (a)D=0.04; (b)D=1.0; (c)D=4.0 (E=0.69, a=0.7, b=0.8, c=0.1, ζ=0.25, α=9.78, β=14.97, γ=0.0, m0=-1.31, m1=-0.75. The initial value is [0.1, 0.1, 1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.01].)
| 1 |
马军. 功能神经元建模及动力学若干问题[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 40 (5): 307- 323.
|
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
DOI |
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
DOI |
| 7 |
刘丽君, 韦笃取. 忆阻Rulkov神经网络同步研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40 (3): 389- 400.
|
| 8 |
唐利红, 贺宗梅, 姚延立. 忆阻Hopfield神经网络动力学分析及其电路实现[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39 (2): 244- 252.
|
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
DOI |
| 11 |
DOI |
| 12 |
薛晓丹, 王美丽, 邵雨竹, 等. 基于抑制性突触可塑性的神经元放电率自稳态机制[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68 (7): 078701.
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
DOI |
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
DOI |
| 19 |
DOI |
| 20 |
于文婷, 张娟, 唐军. 动态突触、神经耦合与时间延迟对神经元发放的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66 (20): 200201.
DOI |
| 21 |
李国芳, 孙晓娟. 小世界神经元网络随机共振现象: 混合突触和部分时滞的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66 (24): 240501.
DOI |
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
DOI |
| 24 |
谭安杰, 韦笃取, 覃英华. 电磁场耦合忆阻神经网络的放电模式及同步行为研究[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 38 (1): 107- 113.
|
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
DOI |
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
DOI |
| 31 |
DOI |
| 32 |
DOI |
| 33 |
DOI |
| 34 |
周倩, 韦笃取. 场耦合忆阻神经网络的电活动[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37 (6): 750- 756.
|
| [1] | 张少泽, 邹艳丽. 如何避免互联电网中的Braess悖论现象[J]. 计算物理, 2024, 41(5): 680-688. |
| [2] | 肖彤彤, 李新颖, 钱雨晴. 约瑟夫森结作用下神经元的动力学特性分析[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(6): 752-760. |
| [3] | 邵贝贝, 邹艳丽, 洪少燕, 梁婵娟. 基于复杂网络拓扑的电网Braess悖论现象研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(6): 770-778. |
| [4] | 李德奎, 毛北行. 时滞干扰环状网络的修正函数投影同步及仿真[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(5): 643-652. |
| [5] | 陆丽梅, 韦笃取. 电磁场耦合忆阻Izhikevich神经网络电活动研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 490-499. |
| [6] | 曹文鑫, 韦笃取. 基于NG-RC电机系统的混沌预测[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 519-526. |
| [7] | 马秀宝, 崔国民, 周志强, 肖媛, 徐玥, 杨其国. 带有个体淘汰的强制进化随机游走算法优化质量交换网络[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(3): 376-388. |
| [8] | 刘丽君, 韦笃取. 忆阻Rulkov神经网络同步研究[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(3): 389-400. |
| [9] | 李震波, 唐叶芝. 高维混沌系统的多元函数投影同步及其保密通信方案[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(1): 91-105. |
| [10] | 高正, 邹艳丽, 胡均万, 姚高华, 刘唐慧美. 基于复杂网络理论的电网耦合强度分配策略[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(5): 579-588. |
| [11] | 刘凯歌, 韦笃取. 基于WOA-ESN的电机系统混沌振荡预测[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(4): 498-504. |
| [12] | 张少泽, 邹艳丽, 谭秫毅, 李浩乾, 刘欣妍. 基于复杂网络理论的互联电网Braess悖论现象分析[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 233-243. |
| [13] | 邹艳丽, 高正, 梁明月, 李志慧, 何铭. 基于潮流追踪的电网同步性能优化及鲁棒性分析[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 623-630. |
| [14] | 詹杰民, 扁诗奇, 罗莹莹, 胡文清, 龚也君. 雷诺数为15 000方腔环流的基准解和周期性分析[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(4): 413-421. |
| [15] | 石建平, 李培生, 刘国平. 基于改进克隆选择算法的统一混沌系统同步控制与参数辨识[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 240-252. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
