计算物理 ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 345-356.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8710
许铋立1( ), 景昭2, 刘骁3, 代波1, 姬广富4, 张魁宝1, 葛妮娜1,*(
), 景昭2, 刘骁3, 代波1, 姬广富4, 张魁宝1, 葛妮娜1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-17
出版日期:2024-05-25
发布日期:2024-05-25
通讯作者:
葛妮娜
作者简介:许铋立(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生, 研究方向为材料物性模拟, E-mail: 852422334@qq.com
基金资助:
Bili XU1( ), Zhao JING2, Xiao LIU3, Bo DAI1, Guangfu JI4, Kuibao ZHANG1, Nina GE1,*(
), Zhao JING2, Xiao LIU3, Bo DAI1, Guangfu JI4, Kuibao ZHANG1, Nina GE1,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-17
Online:2024-05-25
Published:2024-05-25
Contact:
Nina GE
摘要:
采用分子动力学模拟方法研究纳米SiO2以及甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性酚醛树脂的物理性能。研究表明: 300 K下未改性酚醛树脂玻璃转化温度为362 K, 弹性模量、剪切模量分别为5.45 GPa和2.19 GPa, 热导率和热膨胀系数分别为0.37 W·(m·k)-1和3.8×10-5 K-1, 添加纳米SiO2后玻璃转化温度提高了1.6%, 弹性模量、剪切模量分别提高了34.9%和28.8%, 热导率和热膨胀率分别降低了11%和31.6%。SiO2表面接枝3%、5%、7%和10%硅烷偶联剂以及甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性酚醛树脂玻璃转化温度分别提高了10.5%、15.2%、16.8%、19.3%和1.5%, 弹性模量分别提高了44.4%、53.2%、53.8%、63.5%和13.4%, 而热导率分别降低了12.4%、13.5%、11.2%、7%和10%。此外甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性的酚醛树脂的热膨胀系数较未改性酚醛树脂提高15.7%。研究表明: 掺杂纳米SiO2、SiO2表面接枝硅烷偶联剂以及甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性都能够提高酚醛树脂的玻璃转化温度, 机械性能同时降低热导率, 而对于热膨胀系数, 纳米SiO2掺杂使其减小, 甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性则会使其明显增大。
中图分类号:
许铋立, 景昭, 刘骁, 代波, 姬广富, 张魁宝, 葛妮娜. 硅改性酚醛树脂物理性能的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2024, 41(3): 345-356.
Bili XU, Zhao JING, Xiao LIU, Bo DAI, Guangfu JI, Kuibao ZHANG, Nina GE. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Physical Properties of Silicon Modified Phenolic Resin[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(3): 345-356.
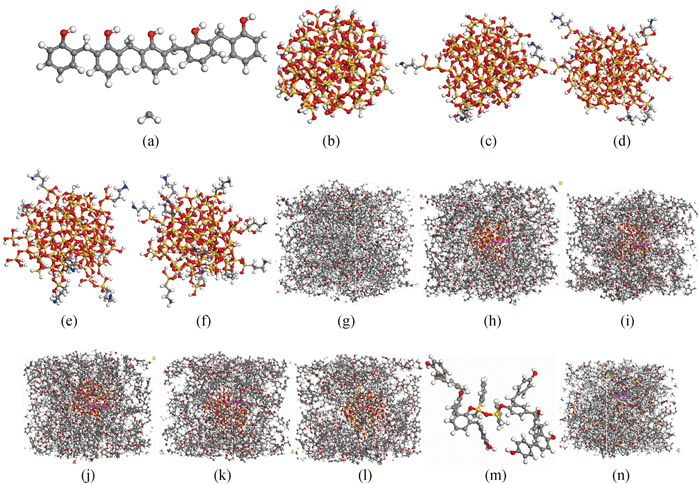
图1 (a) 线性PR和亚甲基单体; (b) SiO2单体; (c) 接枝3%硅烷偶联剂的SiO2纳米颗粒(3%KH550-SiO2); (d) 接枝5%硅烷偶联剂的SiO2纳米颗粒(5%KH550-SiO2); (e) 接枝7%硅烷偶联剂的SiO2纳米颗粒(7%KH550-SiO2); (f) 接枝10%硅烷偶联剂的SiO2纳米颗粒(10%KH550-SiO2); (g) 未改性PR交联模型; (h) SiO2/PR交联模型; (i) 3%KH550-SiO2/PR交联模型; (j) 5%KH550-SiO2/PR交联模型; (k) 7%KH550-SiO2/PR交联模型; (l) 10%KH550-SiO2/PR交联模型; (m) 甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性的线性酚醛树脂单体; (n) 甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性酚醛树脂的交联体系
Fig.1 (a) PR and methylene monomer; (b) SiO2 monomer; (c) 3% KH550-SiO2 monomer; (d) 5% KH550-SiO2 monomer; (e) 7% KH550-SiO2 monomer; (f) 10% KH550-SiO2 monomer; (g) unmodified-PR cross-linking system; (h) nano-SiO2/PR cross-linking system; (i) 3% KH550-SiO2/PR cross-linking system; (j) 5%KH550-SiO2/PR cross-linking system; (k) 7%KH550-SiO2/PR cross-linking system; (l) 10%KH550-SiO2/PR cross-linking system; (m) C9H14O2Si/PR monomer; (n) C9H14O2Si/PR cross-linking system
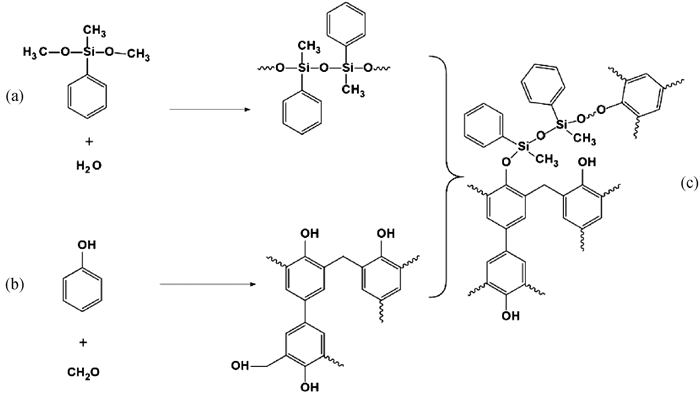
图3 甲基苯基二甲氧基硅烷改性酚醛树脂示意图 (a) 硅烷水解聚合; (b) 酚醛聚合成线性酚醛树脂; (c) 聚硅烷和酚醛树脂合成硅酚醛树脂
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of phenolic resin modified by methylphenyldimethoxysilane (a) silane hydrolysis polymerization; (b) polymerization of phenol and formaldehyde to form novolac resins; (c) synthesis of silicon phenolic resin from polysilane and novolak resin
| 密度/(g·m-3) | 体积/Å3 | 能量/(kcal·mol-1) | |
| 交联前 | 0.88 | 84 284.5 | 6 264.41 |
| 交联后 | 1.06 | 69 434.7 | -2 258.54 |
表1 交联前后体系参数的变化
Table 1 System parameters before and after crosslinking
| 密度/(g·m-3) | 体积/Å3 | 能量/(kcal·mol-1) | |
| 交联前 | 0.88 | 84 284.5 | 6 264.41 |
| 交联后 | 1.06 | 69 434.7 | -2 258.54 |

图6 比体积随温度变化图(a) 未改性PR; (b) 纳米SiO2/PR; (c) 3%KH550-SiO2/PR; (d) 5%KH550-SiO2/PR; (e) 7%KH550-SiO2/PR; (f) 10%KH550-SiO2/PR; (g) C9H14O2Si/PR
Fig.6 Variation of specifice volume with temperature (a) Unmodified-PR (b) SiO2/PR; (c) 3%KH550-SiO2 /PR; (d) 5%KH550-SiO2 /PR; (e) 7%KH550-SiO2/PR; (f) 10%KH550-SiO2/PR; (g) C9H14O2Si/PR
| 模型 | Tg/K | α/(10-6 K-1) | |
| T<Tg | T>Tg | ||
| PR | 362 | 38 | 84 |
| SiO2/PR | 369 | 26 | 72 |
| 3%KH550-SiO2/PR | 400 | 20.8 | 50.6 |
| 5%KH550-SiO2/PR | 415 | 22 | 64 |
| 7%KH550-SiO2/PR | 423 | 8 | 42.9 |
| 10%KH550-SiO2/PR | 429.6 | 30 | 66 |
| C9H14O2Si/PR | 367.5 | 44 | 97.1 |
表2 7种模型的Tg和α
Table 2 Tg and α of 7 models
| 模型 | Tg/K | α/(10-6 K-1) | |
| T<Tg | T>Tg | ||
| PR | 362 | 38 | 84 |
| SiO2/PR | 369 | 26 | 72 |
| 3%KH550-SiO2/PR | 400 | 20.8 | 50.6 |
| 5%KH550-SiO2/PR | 415 | 22 | 64 |
| 7%KH550-SiO2/PR | 423 | 8 | 42.9 |
| 10%KH550-SiO2/PR | 429.6 | 30 | 66 |
| C9H14O2Si/PR | 367.5 | 44 | 97.1 |
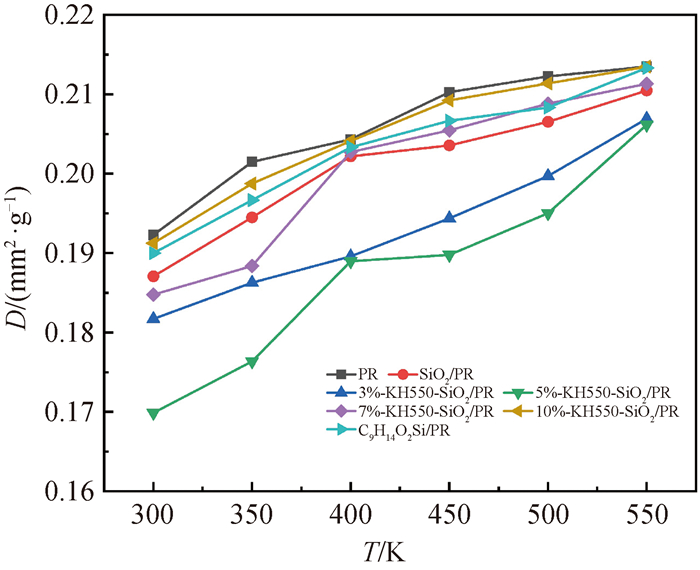
图11 不同模型不同温度下均方位移随时间变化(a) 未改性PR; (b) SiO2/PR; (c) 3%KH550-SiO2/PR; (d) 5%KH550-SiO2/PR; (e) 7%KH550-SiO2/PR; (f) 10%KH550-SiO2/PR; (g) C9H14O2Si/PR
Fig.11 MSD over time with different modules and temperature (a) unmodified-PR; (b) SiO2/PR; (c) 3%KH550-SiO2/PR; (d) 5%KH550-SiO2/PR; (e) 7%KH550-SiO2/PR; (f) 10%KH550-SiO2/PR; (g) C9H14O2Si/PR
| 1 |
TANG Kaihong , ZHANG Ailing , GE Tiejun , et al. Research progress on modification of phenolic resin[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 26, 101879.
DOI |
| 2 | 赵振宁, 王辉, 虎琳. 航空航天先进复合材料研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 炭素, 2021, (2): 24- 29. |
| 3 | 邢亚娟, 孙波, 高坤, 等. 航天飞行器热防护系统及防热材料研究现状[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2018, 48 (4): 9- 15. |
| 4 |
陈智琴, 李文魁, 曾卫军, 等. 耐烧蚀酚醛树脂的研究进展[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2007, 35 (11): 70- 73.
DOI |
| 5 | 许国娟, 陈敬菊, 潘天池, 等. 酚醛树脂耐热改性的研究进展[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2021, (8): 120- 128. |
| 6 |
江立鼎, 张健, 刘智伟. 酚醛树脂耐热改性研究进展[J]. 山东化工, 2021, 50 (5): 100- 101.
DOI |
| 7 | 向靖宇, 刘春霞, 马凤国. 高性能有机硅改性酚醛树脂的研究进展[J]. 有机硅材料, 2019, 33 (1): 71- 74. |
| 8 |
孙保帅, 彭进, 邹文俊. 纳米SiO2改性酚醛树脂结合剂耐热性能的研究[J]. 化学工程师, 2009, 23 (9): 4- 6.
DOI |
| 9 |
ASARO L , MANFREDI L B , PELLICE S , et al. Innovative ablative fire resistant composites based on phenolic resins modified with mesoporous silica particles[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2017, 144, 7- 16.
DOI |
| 10 |
DING Jie , QIN Zhiying , LUO Haitao , et al. Nano-silica modified phenolic resin film: Manufacturing and properties[J]. Nanotechnology Reviews, 2020, 9 (1): 209- 218.
DOI |
| 11 | 薛茹君. 无机纳米材料的表面修饰改性与物性研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2008. |
| 12 |
游胜勇, 戴润英, 董晓娜, 等. 硅烷偶联剂改性酚醛树脂的合成[J]. 合成树脂及塑料, 2017, 34 (6): 17- 19.
DOI |
| 13 |
DUAN Liuyang , ZHAO Xing , WANG Yiguang . Oxidation and ablation behaviors of carbon fiber/phenolic resin composites modified with borosilicate glass and polycarbosilane interface[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 827, 154277.
DOI |
| 14 |
LI Shan , HAN Yue , CHEN Fenghua , et al. The effect of structure on thermal stability and anti-oxidation mechanism of silicone modified phenolic resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2016, 124, 68- 76.
DOI |
| 15 |
ZHANG Guangwu , SHI Minxian , HUANG Chi , et al. Synthesis and properties of polyphenylsilsesquioxane modified phenolic resin by in-situ polymerization from phenyltriethoxysilane precursor[J]. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part B, 2016, 55 (8): 810- 821.
DOI |
| 16 |
SHUDO Y , IZUMI A , HAGITA K , et al. Structure-mechanical property relationships in crosslinked phenolic resin investigated by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Polymer, 2017, 116, 506- 514.
DOI |
| 17 |
SHUDO Y , IZUMI A , HAGITA K , et al. Large-scale molecular dynamics simulation of crosslinked phenolic resins using pseudo-reaction model[J]. Polymer, 2016, 103, 261- 276.
DOI |
| 18 |
MONK J D , HASKINS J B , BAUSCHLICHER C W Jr , et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of phenolic resin: Construction of atomistic models[J]. Polymer, 2015, 62, 39- 49.
DOI |
| 19 |
王中. SiO2纳米粒子改性对酚醛树脂材料性能的影响[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2013, 30 (12): 1465- 1470.
DOI |
| 20 | 林杰. 基于Materials Studio的聚合物基纳米复合材料力学性能模拟[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2013. |
| 21 | 张惠. 改性纳米粒子增强聚合物基复合材料力学性能的分子动力学模拟研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2014. |
| 22 | 杜灵根, 焦丕玉, 王晓梅. 环氧树脂结构建模及玻璃化转变温度模拟计算[J]. 绝缘材料, 2012, 45 (2): 44- 47. |
| 23 |
曹炳阳. 一种模拟热导率的非平衡分子动力学方法[J]. 计算物理, 2007, 24 (4): 463- 466.
DOI |
| 24 |
MVLLER-PLATHE F . A simple nonequilibrium molecular dynamics method for calculating the thermal conductivity[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1997, 106 (14): 6082- 6085.
DOI |
| 25 |
JUND P , JULLIEN R . Molecular-dynamics calculation of the thermal conductivity of vitreous silica[J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59 (21): 13707- 13711.
DOI |
| 26 |
刘其鑫, 姜培学, 向恒. 纳米多孔氩薄膜热导率的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2008, 25 (4): 457- 462.
DOI |
| 27 |
LUSSETTI E , TERAO T , MVLLER-PLATHE F . Nonequilibrium molecular dynamics calculation of the thermal conductivity of amorphous polyamide-6, 6[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2007, 111 (39): 11516- 11523.
DOI |
| 28 |
MATSUBARA H , KIKUGAWA G , BESSHO T , et al. Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation as a method of calculating thermodynamic coefficients[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2016, 421, 1- 8.
DOI |
| 29 |
NIETO-DRAGHI C , AVALOS J B . Non-equilibrium momentum exchange algorithm for molecular dynamics simulation of heat flow in multicomponent systems[J]. Molecular Physics, 2003, 101 (14): 2303- 2307.
DOI |
| 30 |
ZHANG Xiaoxing , WEN Hao , WU Yunjian , et al. Computational thermomechanical properties of silica-epoxy nanocomposites by molecular dynamic simulation[J]. Polymers, 2017, 9 (9): 430.
DOI |
| 31 |
WANG Liang , LIU Mengxin , YANG Feihao , et al. Comparative study on the structure, mechanical, thermal, and tribological properties of PF composites reinforced by different kinds of mesoporous silicas[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2021, 31 (7): 2939- 2948.
DOI |
| 32 | BIAN Cheng , WANG Shujuan , LIU Yuhong , et al. Role of nonbond interactions in the glass transition of novolac-type phenolic resin: A molecular dynamics study[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55 (35): 9440- 9451. |
| 33 |
MONK J D , BUCHOLZ E W , BOGHOZIAN T , et al. Computational and experimental study of phenolic resins: Thermal-mechanical properties and the role of hydrogen bonding[J]. Macromolecules, 2015, 48 (20): 7670- 7680.
DOI |
| 34 |
JITHIN A J A , PANIGRAHI S K , SASIKUMAR P , et al. Ablative properties, thermal stability, and compressive behaviour of hybrid silica phenolic ablative composites[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2022, 203, 110063.
DOI |
| 35 |
YEH M K , TAI N H , LIN Y J . Mechanical properties of phenolic-based nanocomposites reinforced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes and carbon fibers[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2008, 39 (4): 677- 684.
DOI |
| 36 | TAHERI-BEHROOZ F , MEMAR MAHER B , SHOKRIEH M M . Mechanical properties modification of a thin film phenolic resin filled with nano silica particles[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 96 (Part B): 411- 415. |
| 37 | 孙伟松, 于思荣, 陈生辉, 等. 高交联度DGEBA/3, 3'-DDS环氧树脂涂层热力学性能的分子动力学模拟[J]. 当代化工, 2022, 51 (10): 2445-2449, 2454. |
| 38 |
ZHENG Wei , TANG Chao , XIE Jufang , et al. Micro-scale effects of nano-SiO2 modification with silane coupling agents on the cellulose/nano-SiO2 interface[J]. Nanotechnology, 2019, 30 (44): 445701.
DOI |
| 39 | 王雪梅, 董斌, 朱子亮, 等. 聚合物分子与官能化纳米管相互作用及扩散特性的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37 (5): 589- 594. |
| [1] | 韦昭召, 刘凯, 李会军. NiAl合金纳米线弯曲形变行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 425-435. |
| [2] | 侯兆阳, 牛媛, 肖启鑫, 王真, 邓庆田. Al纳米线不同晶向力学行为和变形机制的模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(3): 341-351. |
| [3] | 阿湖宝, 杨志兵, 胡冉, 陈益峰. 纳米尺度下毛细流动的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 603-611. |
| [4] | 王国华, 崔雅茹, 杨泽, 李小明, 汤宏亮, 杨树峰. FexO-SiO2-CaO-MgO-“NiO”系镍渣势函数及分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(2): 215-223. |
| [5] | 彭军辉. 三元层状陶瓷M-Al-N(M=Ti,Zr,Hf)的结构及力学性质的第一性原理模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 603-611. |
| [6] | 和二斌, 罗志荣, 朱留华. 肌红蛋白力致去折叠的全原子分析[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 205-211. |
| [7] | 周璐, 马红和. 超临界水中硫酸钠结晶动力学的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 212-220. |
| [8] | 史晓蕊, 刘振宇, 吴慧英. 纳米孔壁面作用对蛋白质过孔影响的粗粒化分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(1): 63-68. |
| [9] | 梁华, 李茂生. 孔洞和空位对单晶铝力学性能影响的分子动力学研究[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(2): 211-218. |
| [10] | 张海燕, 殷新春. 简单金属固液界面固化过程生长机制的分子动力学研究[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(1): 80-88. |
| [11] | 唐秋明, 甄天熠, 李丹云, 高强. 石墨烯/羟基磷灰石复合材料力学性能的数值研究[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(1): 71-76. |
| [12] | 王意, 邹艳丽, 黄李, 李可. 综合考虑局部和全局特性的电网关键节点识别[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(1): 119-126. |
| [13] | 祁美玲, 杨琼, 王苍龙, 田园, 杨磊. 结构材料辐照损伤的分子动力学程序GPU并行化及优化[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 461-467. |
| [14] | 邹济杭, 叶振强, 曹炳阳. 势能模型对石墨烯导热性质分子动力学模拟的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(2): 221-229. |
| [15] | 魏庆华, 汪焰恩, 杨明明, 柴卫红, 张映锋. 含水量对PAM/PVA互穿网络水凝胶性能的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2015, 32(5): 572-578. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
