Chinese Journal of Computational Physics ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 680-688.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8762
• Research Reports • Previous Articles
Shaoze ZHANG1,2,3( ), Yanli ZOU1,2,*(
), Yanli ZOU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-23
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-09-14
Contact:
Yanli ZOU
CLC Number:
Shaoze ZHANG, Yanli ZOU. How to Avoid Braess Paradox in Interconnected Power Grid[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(5): 680-688.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cjcp.org.cn/EN/10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8762
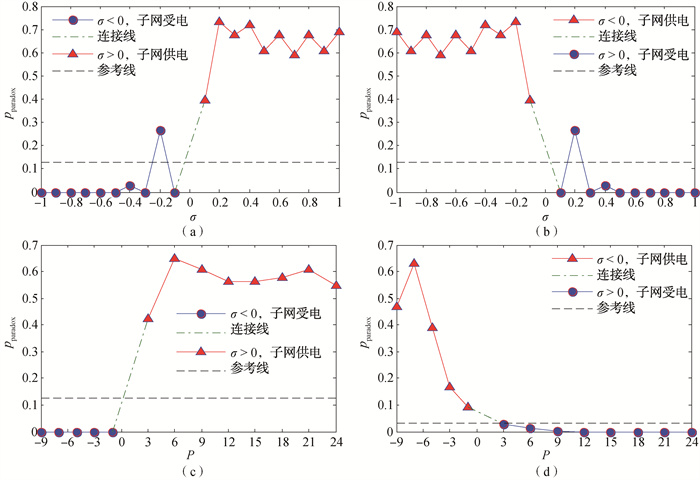
Fig.1 Variation of probability of Braess paradox occurring on new lines of subnets with transmission power (a) IE14-14 subnet A; (b) IE14-14 subnet B; (c) IE14-30 subnet A; (d) IE14-30 subnet B
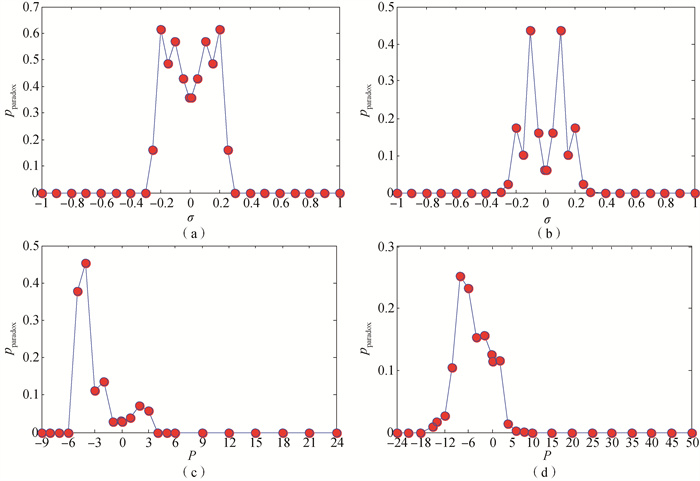
Fig.3 Variation of probability of Braess paradox occurring on new lines of subnets with transmission power (a) IE14-14; (b) IE30-30; (c) IE14-30; (d) IE30-57
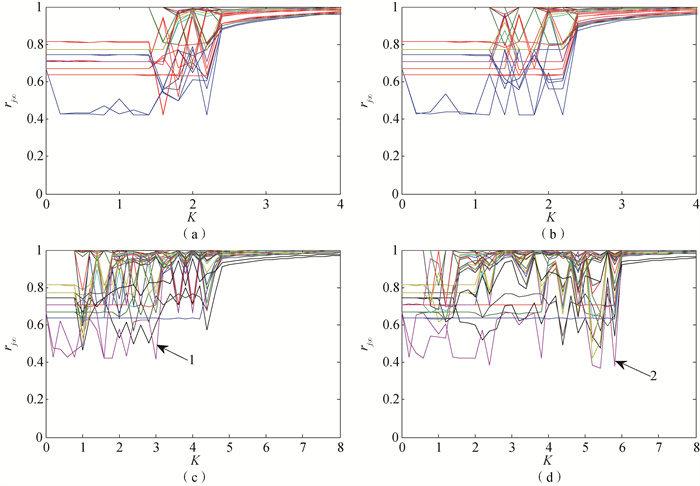
Fig.4 Variation of steady-state local order parameter of IE14-14 with coupling strength (Red thick lines represent generator nodes, blue thick lines represent hub nodes adjacent to generator nodes, black thick lines represent two endpoints of transmission line between networks, and the other colored broken lines represent remaining nodes in the network except the above nodes.) (a) σ=0.01; (b) σ=0.05; (c)σ=0.4; (d) σ=0.5
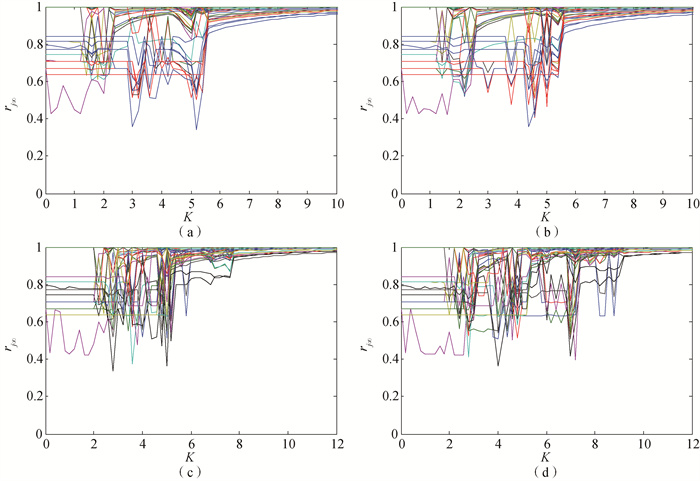
Fig.5 Variation of steady-state local order parameter of IE14-30 with coupling strength (Red thick lines represent generator nodes in the IEEE30 subnet, blue thick lines represent hub nodes adjacent to generator nodes in IEEE30 subnet, black thick lines represent two endpoints of the transmission line between networks, and the other colored broken lines represent remaining nodes in the network except the above nodes.) (a) P=1 pu; (b) P=2 pu; (c)P=5 pu; (d) P=6 pu
| 1 |
BRAESS D . Vber ein paradoxon aus der verkehrsplanung[J]. Mathematical Methods of Operational Research, 1968, 12 (1): 258- 268.
DOI |
| 2 |
BRAESS D , NAGURNEY A , WAKOLBINGER T . On a paradox of traffic planning[J]. Transportation Science, 2005, 39 (4): 446- 456.
DOI |
| 3 | XUE J, GEHLOT H, UKKUSURI S V. Braess's paradox in scale-free networks[C]. The 8th International Symposium on Dynamic Traffic Assignment. Seattle, WA. June 29 to July 1, 2020. |
| 4 |
MA Chunyao , CAI Qing , ALAM S , et al. Airway network management using Braess's Paradox[J]. Transportation Research. Part C Emerging Technologies, 2019, 105, 565- 579.
DOI |
| 5 |
鲁丛林, 蔡宁. Braess's Paradox的博弈论分析[J]. 长沙交通学院学报, 2003, 19 (3): 69- 72.
DOI |
| 6 |
COLOMBO R M , HOLDEN H . On the braess paradox with nonlinear dynamics and control theory[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2016, 168 (1): 216- 230.
DOI |
| 7 | 辛绍平. 论西电东送的心要性和可行性[J]. 中国电力, 2001, 34 (2): 1- 3. |
| 8 | 张国宝. "西电东送" 工程: 中国电力史上的重要篇章[J]. 中国经济周刊, 2019, (12): 48- 52. |
| 9 | 李飏, 周永章. 珠江流域"西电东送" 能源空间配置的综合效益分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2008, 18 (3): 147- 151. |
| 10 |
朱法华, 王圣, 刘思湄. 中国电力规划环评的发展与建议[J]. 电力环境保护, 2007, 23 (5): 9- 13.
DOI |
| 11 |
WANG Dayong , JIA Guozhu , ZONG Hengshan , et al. Abnormal dynamics induced by congestion effect in cascading failures[J]. Modern Physics Letters B, 2019, 33 (2): 1950001.
DOI |
| 12 |
WITTHAUT D , TIMME M . Braess's paradox in oscillator networks, desynchronization and power outage[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2012, 14, 083036.
DOI |
| 13 | 李浩乾, 邹艳丽, 张少泽, 等. 基于复杂网络的电网结构健壮性及Braess悖论现象研究[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38 (4): 470- 478. |
| 14 | WANG Xiangrong, KOC Y, KOOIJ R E, et al. A network approach for power grid robustness against cascading failures[C]//2015 7th International Workshop on Reliable Networks Design and Modeling (RNDM). Munich: IEEE, 2015: 15589535. |
| 15 | BAILLIEUL J, ZHANG Bowen, WANG Shuai. The Kirchhoff-Braess paradox and its implications for smart microgrids[C]//2015 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). Osaka: IEEE, 2015: 6556-6563. |
| 16 | 张少泽, 邹艳丽, 谭秫毅, 等. 基于复杂网络理论的互联电网Braess悖论现象分析[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39 (2): 233- 243. |
| 17 |
WU Zhihao , MENICHETTI G , RAHMEDE C , et al. Emergent complex network geometry[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5, 10073.
DOI |
| 18 | ZHOU Jin , YU Xinghuo , LU Junan . Node importance in controlled complex networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2019, 66 (3): 437- 441. |
| 19 | STROGATZ S H . Exploring complex networks[J]. Nature, 2001, 410 (6825): 268- 276. |
| 20 | BOCCALETTI S , LATORA V , MORENO Y , et al. Complex networks: Structure and dynamics[J]. Physics Reports, 2006, 424 (4/5): 175- 308. |
| 21 | 汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣. 复杂网络理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006. |
| 22 | 蔡泽祥, 王星华, 任晓娜. 复杂网络理论及其在电力系统中的应用研究综述[J]. 电网技术, 2012, 36 (11): 114- 121. |
| 23 | FILATRELLA G , NIELSEN A H , PEDERSEN N F . Analysis of a power grid using a Kuramoto-like model[J]. The European Physical Journal B, 2008, 61, 485- 491. |
| 24 | NISHIKAWA T , MOTTER A E . Comparative analysis of existing models for power-grid synchronization[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2015, 17, 015012. |
| 25 | 王意. 复杂电力网络的动力学行为及关键节点识别研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2017. |
| 26 | 邹艳丽, 王瑞瑞, 吴凌杰, 等. 基于局部序参数的电网同步性能优化[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36 (4): 498- 504. |
| [1] | Qinghua QI, Dadong WEN, Bei CHEN, Ming GAO, Zhou YI, Yonghe DENG, Ke DENG, Ping PENG. Heredity and Evolution of Cluster in Rapid Solidification of Liquid Ni50Zr50 Alloy under Different Cooling Rates [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(4): 494-502. |
| [2] | Bili XU, Zhao JING, Xiao LIU, Bo DAI, Guangfu JI, Kuibao ZHANG, Nina GE. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Physical Properties of Silicon Modified Phenolic Resin [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(3): 345-356. |
| [3] | Xiaoyang XU, Yuting ZHAO. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Simulation of Non-isothermal eXtended Pom-Pom Poiseuille Flow [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(2): 161-171. |
| [4] | Boyao WEN, Genying GAO, Xi LU, Songtao GUAN, Zhengyuan LUO, Bofeng BAI. Ionic Regulation Mechanisms of Surfactant Desorption from the Spherical Micelles [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(2): 193-202. |
| [5] | Xudong GAO, Shuyi SUN, Wenjing WEI, Gongping LI. A Simulation Study on Irradiation Damage of Rutile TiO2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(2): 214-221. |
| [6] | Zhangyuan ZHU, Qiuling WANG. Complex Network Restoration Dynamics Method Considering Continuity between Cascading Failure and Restoration [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(2): 258-267. |
| [7] | Shuang ZHAO, Xiangjun CHEN, Yunzhen ZHANG. Dynamics Analysis and Circuit Implementation of the Memristive Lorenz Chaotic System [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 41(2): 268-276. |
| [8] | Beibei SHAO, Yanli ZOU, Shaoyan HONG, Chanjuan LIANG. Study on Braess Paradox of Power Grid Based on Complex Network Topology [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(6): 770-778. |
| [9] | Yu LI, Huiqing LIU, Yabin FENG, Xiaohu DONG, Qing WANG, Bo ZHANG. Adsorption Behavior of Heavy Oil on Montmorillonite Surface by Typical Surfactant: Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 583-596. |
| [10] | Yongyan GUO, Zhichun ZENG, Lei HE, Qianwei HE, Xueqin YAN, Zhong ZHAO. Numerical Simulation of DLR-F11 High-lift Configuration [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 401-415. |
| [11] | Zhaozhao WEI, Kai LIU, Huijun LI. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Deformation Behavior of NiAl Nanowire Under Bending [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(4): 425-435. |
| [12] | Tianye SUN, Baoshan ZHU, Hongbiao WANG. Experimental and Numerical Simulation of Boundary Layer Transition in Plane Cascade [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(3): 307-313. |
| [13] | Shenshen CHEN, Xianyi ZHU, Qinghua LI. An Interpolating Element Free Galerkin Method Based on Self-adaptive Precise Algorithm in Time Domain and Its Application in Elastodynamics [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(3): 353-358. |
| [14] | Liqing FANG, Hao ZHANG, Sushuang SHI, Mingchuan WANG, Dongliang CHEN, Zhanqun SHI. Numerical Simulation of Lubrication Characteristics of Journal Bearings Under Oil-air Mixed Lubrication [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(1): 47-56. |
| [15] | Dengliang YU, Guofang NAN, Shan JIANG, Chuanchong SONG. Coupling Fault Dynamics of Rotor System Supported by Rolling Bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 39(6): 733-743. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © Chinese Journal of Computational Physics
E-mail: jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
Supported by Beijing Magtech Co., Ltd.
