计算物理 ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 583-596.DOI: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.8647
李禹1,2( ), 刘慧卿1,2,*(
), 刘慧卿1,2,*( ), 冯亚斌2, 东晓虎1,2, 王庆2, 张波3
), 冯亚斌2, 东晓虎1,2, 王庆2, 张波3
收稿日期:2022-10-10
出版日期:2023-09-25
发布日期:2023-11-02
通讯作者:
刘慧卿
作者简介:李禹(1997-),男,博士研究生,研究方向为油藏数值模拟及分子模拟, E-mail: ly15872410897@163.com
基金资助:
Yu LI1,2( ), Huiqing LIU1,2,*(
), Huiqing LIU1,2,*( ), Yabin FENG2, Xiaohu DONG1,2, Qing WANG2, Bo ZHANG3
), Yabin FENG2, Xiaohu DONG1,2, Qing WANG2, Bo ZHANG3
Received:2022-10-10
Online:2023-09-25
Published:2023-11-02
Contact:
Huiqing LIU
摘要:
为探究蒸汽与表面活性剂复合驱对稠油与黏土矿物表面吸附稳定性的影响, 建立表活剂溶液、稠油和蒙脱石的三元吸附体系, 采用分子动力学方法阐释稠油与表活剂在蒙脱石表面的微观竞争吸附机理。计算结果表明: 非离子型表活剂难以与蒙脱石表面接触, 但在高温吸附质环境中具有较强的扩散能力; 阳离子型表活剂在较低温度下占据蒙脱石表面吸附位点并使稠油分子脱离蒙脱石; 而阴离子表活剂在高温条件下容易使稠油分子远离蒙脱石。高温促使沥青质聚集核离散, 从而促进稠油的流动, 但会导致部分表活剂更加亲附蒙脱石而造成非必要的损失。本研究为合理调整温度与表活剂的匹配性, 为敏感性稠油油藏的开发提供了良好的应用前景及推广意义。
李禹, 刘慧卿, 冯亚斌, 东晓虎, 王庆, 张波. 典型表活剂与稠油在蒙脱石表面吸附行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(5): 583-596.
Yu LI, Huiqing LIU, Yabin FENG, Xiaohu DONG, Qing WANG, Bo ZHANG. Adsorption Behavior of Heavy Oil on Montmorillonite Surface by Typical Surfactant: Molecular Dynamics Simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 40(5): 583-596.
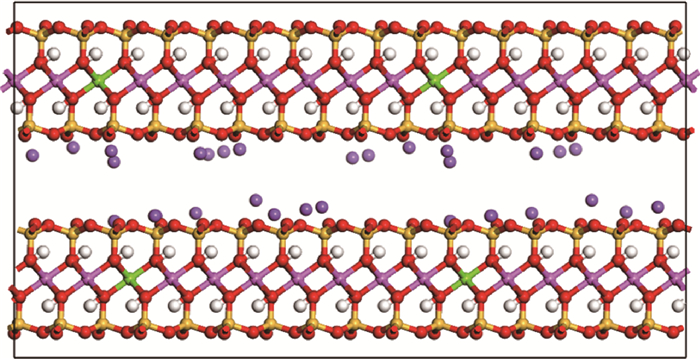
图1 钠基蒙脱石分子球棍模型(黄,红,粉,绿,紫和白色分别为硅,氧,铝,镁,钠和氢原子。)
Fig.1 Ball-and-stick model of sodium-montmorillonite molecules (Yellow, red, pink, green, purple, and white are silicon, oxygen, aluminum, magnesium, sodium, and hydrogen, respectively.)
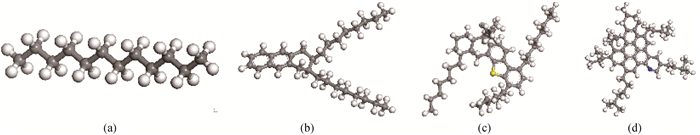
图2 4组分球棍模型(灰色,白色,蓝色和黄色分别代表碳原子,氢原子,氮原子和硫原子。) (a) 饱和烃(C12H26); (b) 芳香烃(C30H46); (c) 胶质(C50H80S); (d) 沥青质(C56H71N)
Fig.2 Ball-and-stick models of the four components in heavy oil (Gray, white, blue and yellow represent carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur atoms respectively.) (a) saturate (C12H26); (b) aromatic (C30H46); (c) resin (C50H80S); (d) asphaltene (C56H71N)
| 表活剂种类 | 数量 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 1.826 | 2.284 | 2.512 |
| 10 | 2.115 | 2.442 | 2.667 | |
| 20 | 2.229 | 2.552 | 2.732 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 1.812 | 2.244 | 2.417 |
| 10 | 2.076 | 2.375 | 2.636 | |
| 20 | 2.334 | 2.791 | 2.914 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 1.823 | 2.063 | 2.227 |
| 10 | 1.778 | 2.015 | 2.294 | |
| 20 | 1.928 | 2.284 | 2.352 | |
表1 不同条件下沥青质分子的质心与蒙脱石表面的平均距离das-mo(nm)
Table 1 Average distance das-mo (nm) between the centroid of asphaltene molecules and montmorillonite at different temperatures and surfactant concentrations
| 表活剂种类 | 数量 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 1.826 | 2.284 | 2.512 |
| 10 | 2.115 | 2.442 | 2.667 | |
| 20 | 2.229 | 2.552 | 2.732 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 1.812 | 2.244 | 2.417 |
| 10 | 2.076 | 2.375 | 2.636 | |
| 20 | 2.334 | 2.791 | 2.914 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 1.823 | 2.063 | 2.227 |
| 10 | 1.778 | 2.015 | 2.294 | |
| 20 | 1.928 | 2.284 | 2.352 | |
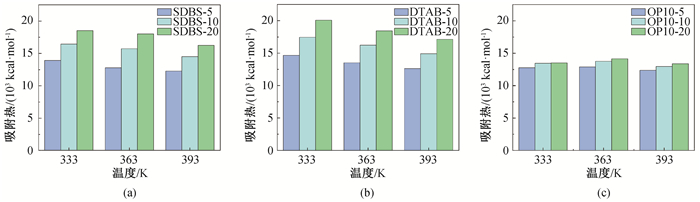
图5 三元吸附体系在吸附过程中释放的吸附热 (a)SDBS体系吸附热;(b)DTAB体系吸附热;(c)OP-10体系吸附热
Fig.5 Adsorption heat of ternary adsorption system on the surface of montmorillonite (a)adsorption heat of SDBS system; (b)adsorption heat of DTAB system; (b)adsorption heat of OP-10 system
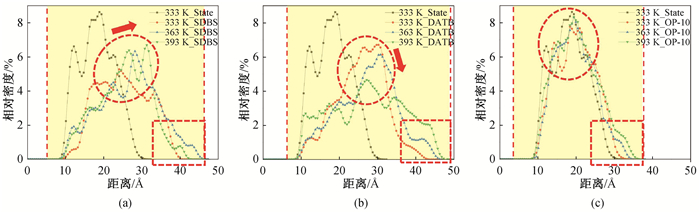
图6 升温过程中沥青质组分在蒙脱石表面的相对密度分布(表活剂分子数为10) (a)SDBS;(b)DTAB;(C)0P-10
Fig.6 Relative concentration of asphaltenes on montmorillonite surface during heating (number of surfactant molecules 10) (a)SDBS; (b)DTAB; (c)OP-10
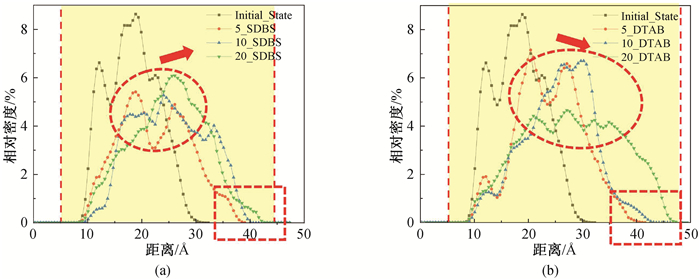
图7 表活剂浓度升高过程中沥青质组分在蒙脱石表面的相对密度分布(温度为333 K) (a)SDBS;(b)DTAB
Fig.7 Relative concentration of asphaltenes on montmorillonite surface during increase concentration (temperature 333 K) (a)SDBS; (b)DTAB
| 表活剂类型 | 333 K | 363 K | 393 K |
| SDBS | 0.092 9 | 0.104 0 | 0.116 1 |
| DTAB | 0.086 5 | 0.084 9 | 0.085 5 |
| OP-10 | 0.273 2 | 0.311 4 | 0.342 5 |
表2 表活剂自扩散系数,D(10-8 m2 ·s-1)
Table 2 Self-diffusivity of different types of surfactant, D(10-8 m2·s-1)
| 表活剂类型 | 333 K | 363 K | 393 K |
| SDBS | 0.092 9 | 0.104 0 | 0.116 1 |
| DTAB | 0.086 5 | 0.084 9 | 0.085 5 |
| OP-10 | 0.273 2 | 0.311 4 | 0.342 5 |
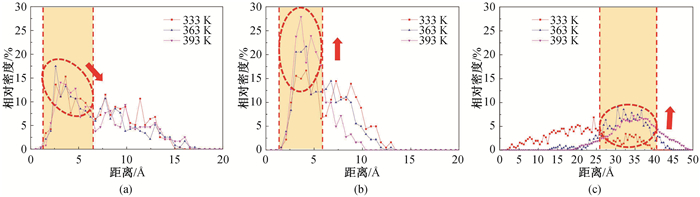
图9 不同类型表活剂分子在蒙脱石表面垂向上的相对浓度分布(表活剂分子数为10) (a)SDBS;(b)DTAB;(C)0P-10
Fig.9 Relative concentrations of different types of surfactant molecules on montmorillonite surface (number of surfactant molecules 10) (a)SDBS; (b)DTAB; (c)OP-10
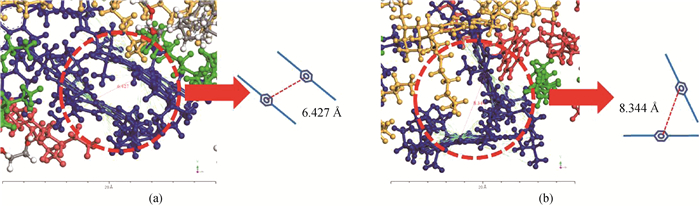
图10 平衡状态下的沥青质分子堆积构型(DTAB表活剂分子数为5) (a)错位面对面堆积作用(F型);(b)边对面堆积作用(T型)
Fig.10 The accumulative configuration of asphaltene molecules at equilibrium (number of DTAB surfactant molecules 5) (a) staggered face-to-face stacking (F-shaped); (b) side to side stacking (T-shape)
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 0.896 | 1.045 | 1.232 |
| 10 | 0.935 | 1.127 | 1.288 | |
| 20 | 0.976 | 1.195 | 1.372 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 0.903 | 1.011 | 1.247 |
| 10 | 1.017 | 1.178 | 1.294 | |
| 20 | 1.252 | 1.367 | 1.433 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 |
| 10 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
| 20 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
表3 不同条件下沥青质分子的质心平均距离din(nm)
Table 3 Average distance din (nm) between the center of mass of asphaltene molecules at different temperatures and surfactant concentrations
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 0.896 | 1.045 | 1.232 |
| 10 | 0.935 | 1.127 | 1.288 | |
| 20 | 0.976 | 1.195 | 1.372 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 0.903 | 1.011 | 1.247 |
| 10 | 1.017 | 1.178 | 1.294 | |
| 20 | 1.252 | 1.367 | 1.433 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 |
| 10 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
| 20 | 0.861 | 1.084 | 1.135 | |
| 表活剂类型 | 温度/K | 沥青质吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | 表活剂吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | |||
| 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | |||
| SDBS | 333 | -265 | -420 | -6 000 | 82 | |
| 363 | -255 | -380 | -6 035 | 85 | ||
| 393 | -223 | -329 | -6 001 | 86 | ||
| DTAB | 333 | -259 | -442 | -5 661 | 16 | |
| 363 | -242 | -377 | -5 760 | 33 | ||
| 393 | -217 | -280 | -5 804 | 47 | ||
| OP-10 | 333 | -366 | -553 | 0 | 0 | |
| 363 | -356 | -333 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 393 | -344 | -273 | 0 | 0 | ||
表4 沥青质、表活剂在蒙脱石表面的范德华能和静电作用势能
Table 4 Van der Waal energy and electrostatic potential energy of asphaltenes and surfactants on montmorillonite surface
| 表活剂类型 | 温度/K | 沥青质吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | 表活剂吸附质-蒙脱石吸附剂 | |||
| 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 静电势能/(kcal·mol-1) | 范德华势能/(kcal·mol-1) | |||
| SDBS | 333 | -265 | -420 | -6 000 | 82 | |
| 363 | -255 | -380 | -6 035 | 85 | ||
| 393 | -223 | -329 | -6 001 | 86 | ||
| DTAB | 333 | -259 | -442 | -5 661 | 16 | |
| 363 | -242 | -377 | -5 760 | 33 | ||
| 393 | -217 | -280 | -5 804 | 47 | ||
| OP-10 | 333 | -366 | -553 | 0 | 0 | |
| 363 | -356 | -333 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 393 | -344 | -273 | 0 | 0 | ||
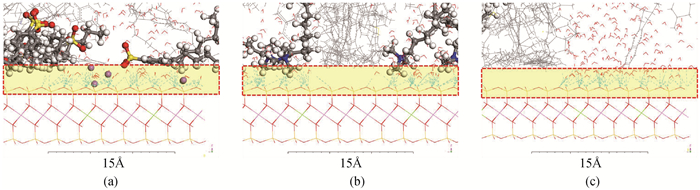
图11 蒙脱石表面的氢键分布(温度为333 K,分子数为5) (a)SDBS;(b)DTAB;(C)0P-10
Fig.11 Hydrogen bond distribution on the montmorillonite surface (The temperature is 333 K, number of molecules is 5) (a)SDBS; (b)DTAB; (c)OP-10
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 198 | 207 | 214 |
| 10 | 220 | 227 | 233 | |
| 20 | 267 | 276 | 281 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 226 | 220 | 218 |
| 10 | 254 | 247 | 242 | |
| 20 | 288 | 271 | 263 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 187 | 195 | 208 |
| 10 | 185 | 196 | 210 | |
| 20 | 184 | 196 | 211 | |
表5 水分子与蒙脱石之间存在的氢键数量
Table 5 The number of hydrogen bonds between water molecules and montmorillonite
| 表活剂类型 | 分子个数 | 温度 | ||
| 333 K | 363 K | 393 K | ||
| SDBS | 5 | 198 | 207 | 214 |
| 10 | 220 | 227 | 233 | |
| 20 | 267 | 276 | 281 | |
| DTAB | 5 | 226 | 220 | 218 |
| 10 | 254 | 247 | 242 | |
| 20 | 288 | 271 | 263 | |
| OP-10 | 5 | 187 | 195 | 208 |
| 10 | 185 | 196 | 210 | |
| 20 | 184 | 196 | 211 | |
| 1 |
曹仁义, 黄涛, 程林松, 等. 水驱油藏中原油极性物质对吸附和润湿性影响的分子模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38 (5): 595- 602.
DOI |
| 2 |
DOI |
| 3 |
张雪芳, 刘宗宾, 刘超, 等. 辽东湾坳陷X油田黏土矿物对注水开发储层物性的影响[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2017, 36 (5): 62- 67.
DOI |
| 4 |
刘刚, 侯吉瑞, 李秋言, 等. 二类油层中三元复合驱体系的损耗及有效作用距离[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39 (6): 171- 177.
DOI |
| 5 |
刘慧卿, 东晓虎. 稠油热复合开发提高采收率技术现状与趋势[J]. 石油科学通报, 2022, 7 (2): 174- 184.
|
| 6 |
杜春泽, 刘卫东, 孙灵辉, 等. 黏土矿物对化学驱提高采收率的影响[J]. 应用化工, 2018, 47 (11): 2314- 2316.
DOI |
| 7 |
DOI |
| 8 |
DOI |
| 9 |
DOI |
| 10 |
柴汝宽, 刘月田, 王俊强, 等. 分子动力学模拟方解石和白云石润湿性[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36 (4): 474- 482.
DOI |
| 11 |
于维钊, 乔贵民, 张军, 等. 沥青质在石英表面吸附行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2012, 28 (1): 76- 82.
DOI |
| 12 |
宋圣晗. 稠油中沥青质与表面活性剂相互作用的分子模拟[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019: 21-36.
|
| 13 |
DOI |
| 14 |
郭东红, 李森, 袁建国. 表面活性剂驱的驱油机理与应用[J]. 精细石油化工, 2002, (7): 36- 41.
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
DOI |
| 17 |
DOI |
| 18 |
杨胜来, 魏俊之. 油层物理学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2013: 159- 166.
|
| 19 |
黄小娟, 徐加放, 丁廷稷, 等. 有机胺抑制蒙脱石水化机理的分子模拟[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2017, 39 (4): 442- 448.
DOI |
| 20 |
DOI |
| 21 |
吕兆兰. 超临界二氧化碳在页岩黏土矿物中吸附行为的分子模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2020: 22-24.
|
| 22 |
DOI |
| 23 |
熊凯阳. 烷烃与CO2在不同岩石孔内吸附及驱替特性的分子动力学模拟[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2020: 17-20.
|
| 24 |
刘霞, 陈敬中, 韩炜. 纳米级蒙脱石晶胞参数计算与研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2003, (5): 13- 17.
|
| 25 |
DOI |
| 26 |
王子军. 石油沥青质的化学和物理Ⅱ沥青质的化学组成和结构[J]. 石油沥青, 1996, (1): 26- 36.
|
| 27 |
DOI |
| 28 |
DOI |
| 29 |
DOI |
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
纪德罗. 沥青质在亲水/亲油表面吸附的分子动力学模拟[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020: 18-21.
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
王鹏, 黄世军, 赵凤兰, 等. 沥青质微观聚集特征的分子动力学研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28 (4): 77- 85.
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
苑世领, 张恒, 张冬菊. 分子模拟—理论与实验[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2017: 86- 89.
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
柴汝宽, 刘月田, 杨莉, 等. 两种不同极性有机小分子在方解石(104)面吸附的密度泛函研究[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37 (2): 221- 230.
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
蔡新恒, 龙军, 任强, 等. 沥青质分子聚集体的解离对策[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2020, 36 (5): 889- 898.
|
| 45 |
|
| [1] | 韦昭召, 刘凯, 李会军. NiAl合金纳米线弯曲形变行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2023, 40(4): 425-435. |
| [2] | 侯兆阳, 牛媛, 肖启鑫, 王真, 邓庆田. Al纳米线不同晶向力学行为和变形机制的模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(3): 341-351. |
| [3] | 王晓慧, 张平. 高压下FCC相金属氢结构稳定性和非谐效应的理论研究[J]. 计算物理, 2022, 39(2): 159-164. |
| [4] | 阿湖宝, 杨志兵, 胡冉, 陈益峰. 纳米尺度下毛细流动的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(5): 603-611. |
| [5] | 王国华, 崔雅茹, 杨泽, 李小明, 汤宏亮, 杨树峰. FexO-SiO2-CaO-MgO-“NiO”系镍渣势函数及分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2021, 38(2): 215-223. |
| [6] | 王雪梅, 董斌, 朱子亮, 杨俊升. 聚合物分子与官能化纳米管相互作用及扩散特性的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(5): 589-594. |
| [7] | 和二斌, 罗志荣, 朱留华. 肌红蛋白力致去折叠的全原子分析[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 205-211. |
| [8] | 周璐, 马红和. 超临界水中硫酸钠结晶动力学的分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(2): 212-220. |
| [9] | 史晓蕊, 刘振宇, 吴慧英. 纳米孔壁面作用对蛋白质过孔影响的粗粒化分子动力学模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2020, 37(1): 63-68. |
| [10] | 柴汝宽, 刘月田, 王俊强, 辛晶, 皮建, 李长勇. 分子动力学模拟方解石和白云石润湿性[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(4): 474-482. |
| [11] | 王帅创, 张弓木, 孙博, 宋海峰, 田明锋, 方俊, 刘海风. 量子分子动力学模拟液体钚的输运性质[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(3): 253-258. |
| [12] | 梁华, 李茂生. 孔洞和空位对单晶铝力学性能影响的分子动力学研究[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(2): 211-218. |
| [13] | 张海燕, 殷新春. 简单金属固液界面固化过程生长机制的分子动力学研究[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(1): 80-88. |
| [14] | 马江将, 李克训, 周必成, 谷建宇, 贾琨. 缺陷位置对单层石墨烯拉伸形变的影响[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(4): 475-480. |
| [15] | 祁美玲, 杨琼, 王苍龙, 田园, 杨磊. 结构材料辐照损伤的分子动力学程序GPU并行化及优化[J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(4): 461-467. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 《计算物理》编辑部
地址:北京市海淀区丰豪东路2号 邮编:100094 E-mail:jswl@iapcm.ac.cn
本系统由北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司设计开发
